20
Complete denture bases—acrylic resin
Figure 20.1 Maxillary complete denture. (Lucitone 199, courtesy of Dentsply International.)
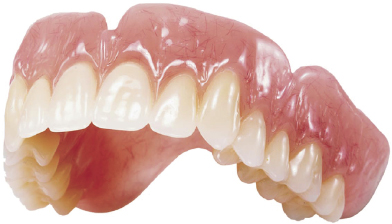
Figure 20.2 Reaction initiation—decomposition of benzoyl peroxide molecule into two free radicals.
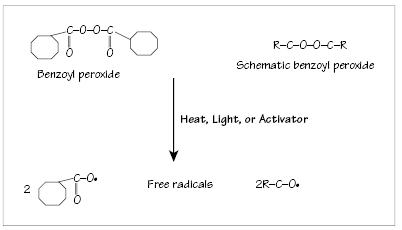
Figure 20.3 Reaction propagation—interaction between free radicals and monomer.
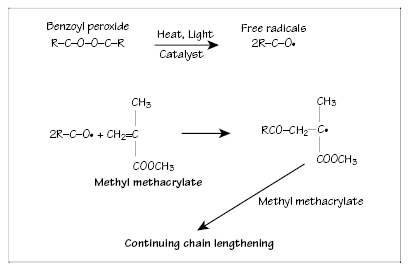
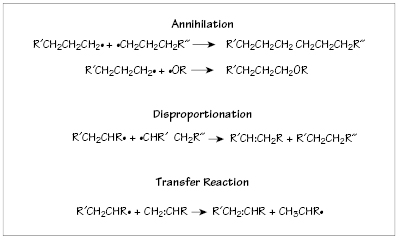
Figure 20.4 Reaction termination by annihilation, disproportionation, or transfer reaction.
Box 20.1 Required properties of denture base materials (in alphabetical order)
Absence of taste and odor
Biocompatibility
Bondable to resins, metal, and porcelain
Chemical stability
Color stability
Ease of fabrication and repair
Insolubility in oral fluids
Long shelf life
Low sorption of oral fluids
Moderate cost
Natural appearance
Processing accuracy and dimensional stability
Satisfactory thermal properties
Strength and durability
Wear and abrasion resistance
Table 20.1 Stages during monomer–polymer reaction
| Stage | Mix characteristic |
|---|---|
| 1 | Sandy |
| 2 | Stringy |
| 3 | Doughy |
| 4 | Rubbery |
| 5 | Stiff |
Table 20.2 Glass transition temperatures (Tg) of methacrylate resins
| Methacrylate resin | Glass transition temperature, Tg (°C) |
|---|---|
| Methyl | 125 |
| Ethyl | 65 |
| n-Propyl | 38 |
| Isopropyl | 95 |
| n-Butyl | 33 |
| Isobutyl | 70 |
| sec-Butyl | 62 |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


