18
Early Childhood Caries
Early Childhood Caries (ECC)
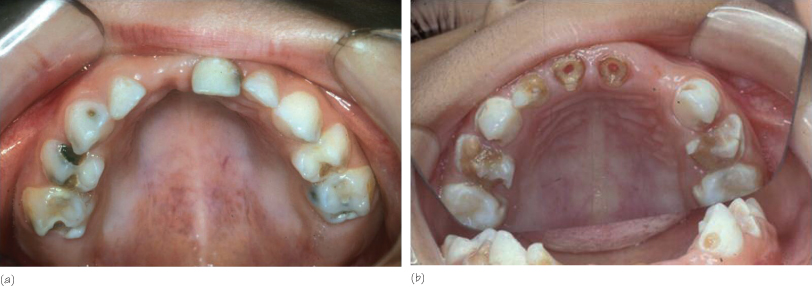
The decline in caries is bimodal and for young children 75–80% of dental caries occurs in as little as 20–25% of the population. Allowing young children to sleep with a bottle is one of the main causes of ECC or rampant caries. ECC (Fig. 18.1) occurs worldwide with reported prevalence values ranging from 5% (USA) to 55% (South Korea).
Figure 18.1 Early childhood caries (ECC) of maxillary primary incisors and molars.
Nomenclature
- Rampant caries.
- Nursing caries syndrome.
- Nursing bottle caries.
- Bottle mouth caries.
- Early childhood caries.
- Severe ECC (S-ECC).
Definitions
ECC: occurrence of any sign of dental caries on any tooth surface during the first 3 years of life.
S-ECC: children with atypical, progressive or rampant patterns of dental caries (described separately for each age group):
- <3 years: any sign of dental caries in smooth surfaces;
- 3–5 years: one or more cavitated, missing (due to caries) or filled smooth surfaces in maxillary teeth or a dmfs score of 4, 5 or 6 surfaces for ages 3, 4 and 5 years respectively.
Aetiology
- Exposure for long periods of time to cariogenic substrates (usually sugary drinks) in nursing bottles and/or feeder cups given as pacifiers.
- Nursing bottle given at bedtime.
- Low salivary rates at night.
- Reduced buffering capacity.
- Parent/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


