SECTION 16
ORTHODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Orthodontics is the study of the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of irregularities of the teeth and jaws. Orthodontic instruments are used in conjunction with fixed and removable appliances.
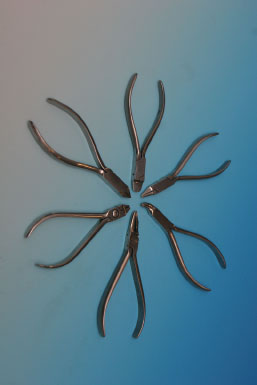
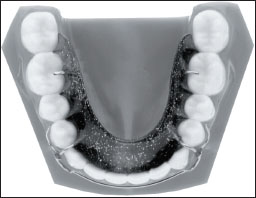
ORTHODONTIC APPLIANCES
FIGURE 16.1
Name
Removable orthodontic appliance (Hawley retainer)
Features
- Is removable and depends on patient compliance for success
- Constructed from acrylic and a combination of stainless steel retentive clasps and springs
- The acrylic of a removable appliance can be adjusted by grinding with a straight handpiece and acrylic bur, and the clasps and spring can be adjusted with a variety of orthodontic pliers
Varieties
There are many types of removable appliances depending on the needs of the patient (e.g. expansion appliances and Hawley retainers)
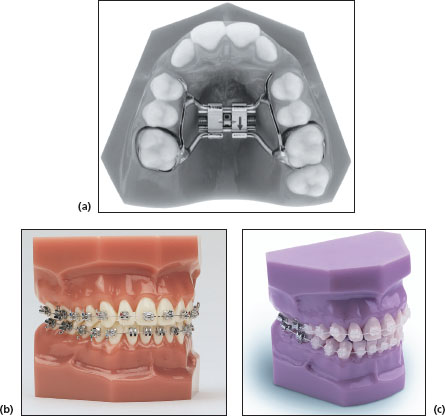
FIGURE 16.2a, b, c
Name
Fixed orthodontic appliances: (a) Rapid palatal expander (b) Metal fixed appliance (c) Ceramic fixed appliance
Features
- Are cemented to the teeth and cannot be removed by the patient
- Consist of a combination of orthodontic bands, orthodontic brackets or orthodontic wires
- Require special orthodontic pliers for adjustments
Varieties
There are many types of fixed appliances depending on the needs of the patient (e.g. braces and palatal expanders)


FIGURE 16.3
Name
Headgear and face bow
Function and features
- Has an inner bow (fits into the buccal tubes of the fixed appliance) soldered to an outer bow (can be attached to a strap)
- The headgear is worn outside the mouth, and the face bow is attached to the buccal tubes intra-orally
- The orthodontic headgear is used to prevent establishment of deep overbites by restricting the growth of the maxillary arch. Can also be used to prevent mesial drifting of maxillary molars when teeth have been extracted anterior to the molars
- The strap has a safety mechanism which prevents the bow from springing back at the patient if it is pulled forwards
Varieties
Different sizes available colour coded
ORTHODONTIC MATERIALS
FIGURE 16.4
Name
Elastic separators
Function and placement
- Used to create inter-proximal space to allow orthodontic bands to be placed
- Separators can be placed with floss or separator placing pliers (see Figure 6.11)


FIGURE 16.5
Name
Orthodontic band
Function, features and placement
- Used to secure auxiliary devices to aid in tooth positioning
- Stainless steel bands are cemented on posterior teeth
- Pre-formed – variety of sizes available
- Occlusal edge is slightly rounded, whereas gingival edge is straight
- Placement is preceded by placement of separators to create interproximal space
Varieties
Available in different shapes and sizes
FIGURE 16.6a, b
Name
(a) Metal orthodontic bracket (b) Ceramic orthodontic bracket
Function and features
- Used to secure an orthodontic archwire in place
- Most often bonded to the buccal surface of the tooth
- Orthodontic brackets may have coloured indicators to help orientate placement
- Orthodontic brackets often have a textured back that aids in bonding to the tooth
Varieties
- Many different brands and sizes available
- Can be made from different materials (e.g. stainless steel and ceramics)


FIGURE 16.7
Name
- Orthodontic archwire
Function and mechanism of action
- Archwires are tied into orthodontic brackets that have been previously bonded to teeth, and these act as a track to facilitate movement of teeth
- The archwire is pre-formed. When tied into the bracket its shape may be altered. This results in force being applied to the teeth as the archwire tries to regain its original shape
Varieties
- Available in different shapes and diameters
- Made from many different materials, e.g. stainless steel and nickel titanium
FIGURE 16.8
Name
Elastomeric modules
Function and directions for use
- Used to ligate or hold the orthodontic archwire in place
- Used with mosquito artery forceps or Mathieu ligature pliers to place around orthodontic brackets
- One use and changed each time the archwire is changed
Varieties
- Can be made from a variety of materials
- Available in many colours
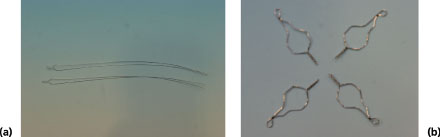

FIGURE 16.9a, b
Name
Ligatures
Function and directions for use
- Used to ligate or hold the orthodontic archwire in place
- Used with mosquito artery forceps or Mathieu ligature pliers to place around orthodontic brackets
- Changed each time the archwire is changed
- The excess ligature wire is cut with various orthodontic pliers and should be disposed of in the sharps’ bin
- One use
Varieties
- Can be made from a variety of materials
- Different types: (a) long ligature, (b) ‘quick ligs’ and Kobayashi tie hooks that facilitate tying elastics around
FIGURE 16.10
Name
Patient relief wax (bee’s wax)
Function
Given to the patient after fixed appliance placement to help relieve discomfort from tissue trauma
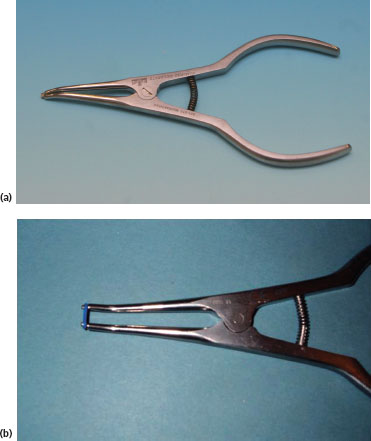
ORTHODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
FIGURE 16.11a, b
Name
Separator placing pliers
Function and features
- Used for placing elastic separators interproximally
- Single-ended instrument – handle is adapted for a palm grasp
Varieties
Different sizes and shapes are available
False friends
Rubber dam clamp forceps and Coons ligature pliers
FIGURE 16.12
/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


