Providing Supportive Treatment Services
QUESTIONS
1. From the following list, select the three materials that are considered rigid dental impression materials:
2. Model plaster, dental stone, and high-strength dental stone all have the same crystal size and porosity. These three materials are all made of the same chemical, calcium sulfate hemihydrate (CaSO4—½H2O).
C The first statement is true, and the second statement is false.
D The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
3. Select the three properties that are associated with agar from the following list.
4. The wettability of solids by liquids, for example, the wetting of tooth enamel by pit and fissure sealants, is important in dentistry. A material that is hydrophilic shows a contact angle of 90 degrees or greater.
C The first statement is true, and the second statement is false.
D The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
5. Which of the following restorative dental materials has the LOWEST compressive strength?
6. Which of the following dental cements inhibits the polymerization of a composite restorative material and should NOT be placed under the restoration?
7. Which of the following MOST likely caused the incisal wear to the teeth of the patient shown?
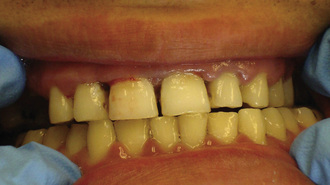
8. Select the two materials that will act as retarders for the setting of model plaster, dental stone, or high-strength stone from the following list.
9. Which of the following waxes is classified as a pattern wax?
10. Which of the following materials with small particle sizes is intended to remove softer materials that adhere to enamel or restorative material substrates?
11. Which of the following compositions is used as a home whitening product?
12. Which of the following are uses of ZOE? (Select all that apply.)
13. Cements are created by combining different powders and liquids. For each numbered resulting cement listed, select the MOST closely linked powder–liquid components from the list provided:
| Resulting Cement | Powder/Liquid |
| ____ 1. ZOE | A. Powdered glass and polyacrylic acid |
| ____ 2. Zinc phosphate | B. Zinc oxide and polyacrylic acid |
| ____ 3. Zinc polycarboxylate | C. Zinc-oxide and phosphoric acid |
| ____ 4. Glass ionomer | D. Zinc-oxide and eugenol |
| ____ 5. Resin cement | E. Resin and glass materials |
14. Which of the following is the term for the uptake of water by a hydrocolloid?
15. The layer of debris that remains on the tooth after a tooth is prepared or cut for a restoration is known as a/an
16. Order the steps involved in the polymerization of composite materials. Match each letter with its proper sequence number.
1. _____ A. A free radical is formed.
2. _____ B. Remaining free radicals combine.
3. _____ C. A free radical reacts with a monomer, forming a new bond.
17. Which of the following characteristics apply to composite resin materials? (Select all that apply.)
B Sets through condensation polymerization
C Expands when polymerization takes place
D Macrofilled composites are used most often
E Polymerization through heat, light, or chemical activation
18. Before a denture is made, a denture try-in is performed. The denture try-in simulates the proper bite, vertical dimension, and esthetics of the final denture.
C The first statement is true, and the second statement is false.
D The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
19. Failure of bonding of dental materials is known as cohesive failure. An example of cohesive failure would be an orthodontic bracket that breaks off, removing part of the tooth to which it was bonded.
C The first statement is true, and the second statement is false.
D The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
20. Which of the following restorative materials releases and absorbs fluoride and is used to prevent recurrent decay?
21. Which composite would be the BEST choice for an occlusal restoration?
22. Which of the following are the benefits of adding high amounts of copper to an amalgam alloy? (Select all that apply.)
23. All of the following practices apply when mixing alginate impression materials EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
B Using a clean bowl and spatula
C Powder-to-liquid ratio of 1:2
24. When filling the impression tray with alginate, begin loading the tray from the anterior portion of the tray. When inserting the impression tray in the patient’s mouth, bring anterior teeth into position in the tray and then posterior teeth.
C The first statement is true, and the second statement is false.
D The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
25. A Class V restoration is found in/on the
B incisal angle of an anterior tooth.
C proximal surfaces of anterior teeth.
26. It is important to pour up alginate impressions within 30 minutes of taking the impression, because hysteresis occurs with alginate impressions.
A Both the statement and the reason are correct and related.
B Both the statement and the reason are correct but NOT related.
C The statement is correct, but the reason is NOT.
27. An athletic mouth guard protects teeth as it absorbs energy and then returns to its original shape and can be used again. This property is known as
28. The property that causes gradual dimensional change of a dental material under load or stress is
29. Which term BEST describes the intensity of a color?
30. Light-cure sealant materials cannot be activated by natural light. The manufacturer’s instructions must be followed to avoid overcuring the sealant material.
C The first statement is true, and the second statement is false.
D The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
31. Percolation is a concern with composite restorations because the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is higher in enamel than it is in composites.
A Both the statement and the reason are correct and related
B Both the statement and the reason are correct but NOT related.
C The statement is correct, but the reason is NOT.
32. The particle shape of the alloy determines the amount of mercury needed to wet the surface of the amalgam alloy particles. The purpose of mercury is to increase the strength of an amalgam.
C The first statement is true, and the second statement is false.
D The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
33. A portion of the tooth surface has a glossy opaque appearance, exhibits smoothness on tactile exploration, and produces a dull sound when tapped. Which of the following is the MOST likely finding?
34. All of the following are benefits of sharpening dental hygiene instruments EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
35. A study model is a positive reproduction of the structure it represents. The impression is a negative reproduction of the structure on which it is taken.
C The first statement is true, and the second statement is false.
D The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
36. The primary indication for polishing enamel is to
37. Which two of the following factors will produce the MOST abrasion to the tooth surface?
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


