10
Risk and periodontal diseases
Figure 10.1 Pack years of cigarette smoking and clinical attachment loss.
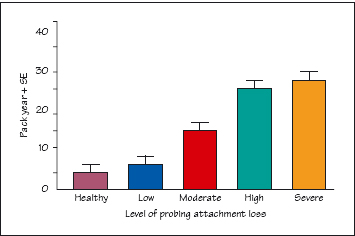
Figure 10.2 Periodontal disease and glycaemic control: cause or effect?
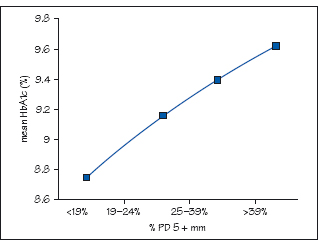
Figure 10.3 Interaction of periodontal microflora, the inflammatory response and risk factors.
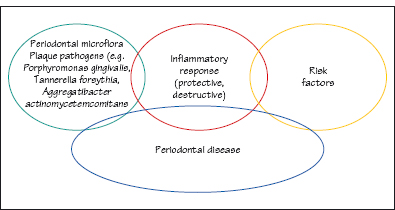
Table 10.1 Levels of evidence for risk determinants in chronic diseases and characteristics of these studies which make the factors more convincing, and not likely to be spurious associations.
| Type of study | Study characteristics |
| Cross-sectional or case–control studies | Confounding factors are eliminated or adjusted for in the analysis |
| Longitudinal epidemiological studies (establish temporality and evidence for effects in causal pathway) | Dose–response effects |
| Mechanism studies | Study results are consistent among various independent studies |
| Intervention studies | Effects are clinically meaningful Relationship is biologically plausible |
Table 10.2 Systemic risk determinants for periodontal disease.
| Systemic risk factors | Systemic risk indicators |
| Smoking | Low dietary calcium |
| Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 | Postmenopausal osteoporosis and osteopenia |
| Race | Visceral obesity |
| Genetics Male gender Polymorphonuclear leukocyte (neutrophil) function Socioeconomic status (low educational level) Acquired systemic infections (e.g. human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)) Severe malnutrition (cancrum oris) |
Stress and inadequate coping |
Table 10.3 Modification of risk factors for periodontal disease.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel
VIDEdental - Online dental courses
 Get VIDEdental app for watching clinical videos
Get VIDEdental app for watching clinical videos

|