and Angela J. Yoon1
(1)
Columbia University College of Dental Medicine and Department of Pathology and Cell Biology, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA
11.1 Physical Abuse
Injuries to the head and neck occur in over fifty percent of child abuse cases.
A careful and thorough extraoral and intraoral examination must be performed. Intraoral findings of physical abuse include mucosal ulcers, lacerations, ecchymosis, and burns of the tongue, lips, buccal mucosa, palate (soft and hard), gingiva, alveolar mucosa, or frenum. Such injuries can be sustained by eating utensils or bottles during forced feedings or from the forced ingestion of scalding hot foods and liquids or caustic substances. Lacerations of the gingiva, lip, and frenum can also be caused by extraoral trauma from the hands of the abuser. Facial bruises, injuries to the ears, fractured or avulsed teeth, and jaw or xygomatic fractures are also findings in cases of physical abuse. Injuries observed in exposed skin of the extremities including scars, bruises, cigarette burns, and bite marks are also highly indicative of physical abuse.
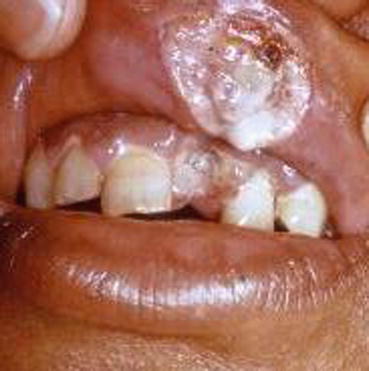

Fig. 11.1
Physical abuse. Avulsed central incisor and ulcerated upper lip as a result of inflicted trauma
Accidental injuries to the mouth are a common occurrence in children. Therefore, it is critical to distinguish accidental injuries from abuse. Multiple injuries, injuries in different stages of healing, or doubtful history of how the injury occurred should arouse a suspicion of abuse. If there is suspicion of abuse, the appropriate agency must be contacted so that the case can be properly investigated.
11.1.1 Neglect
Oral findings in children suffering from neglect include: rampant tooth decay, gingivitis, and generalized poor oral health. These children might also appear unkempt and show signs of nutritional deficiency.
Dental neglect is a form of child abuse. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry defines dental neglect as a “willful failure of parent or guardian to seek and follow through with treatment necessary to ensure a level of oral health essential for adequate function and freedom from pain and infection”. Some parents/guardians fail to seek dental care for their children because they are not educated on the importance of childhood dental health. Therefore, the clinician must attempt to educate the parents/guardian.
11.1.2 Sexual Abuse
Oral findings seen in children suffering sexual abuse includes oral and perioral gonorrhea, oral condyloma, injury, or petechiae of the palate.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


