MUCOSA
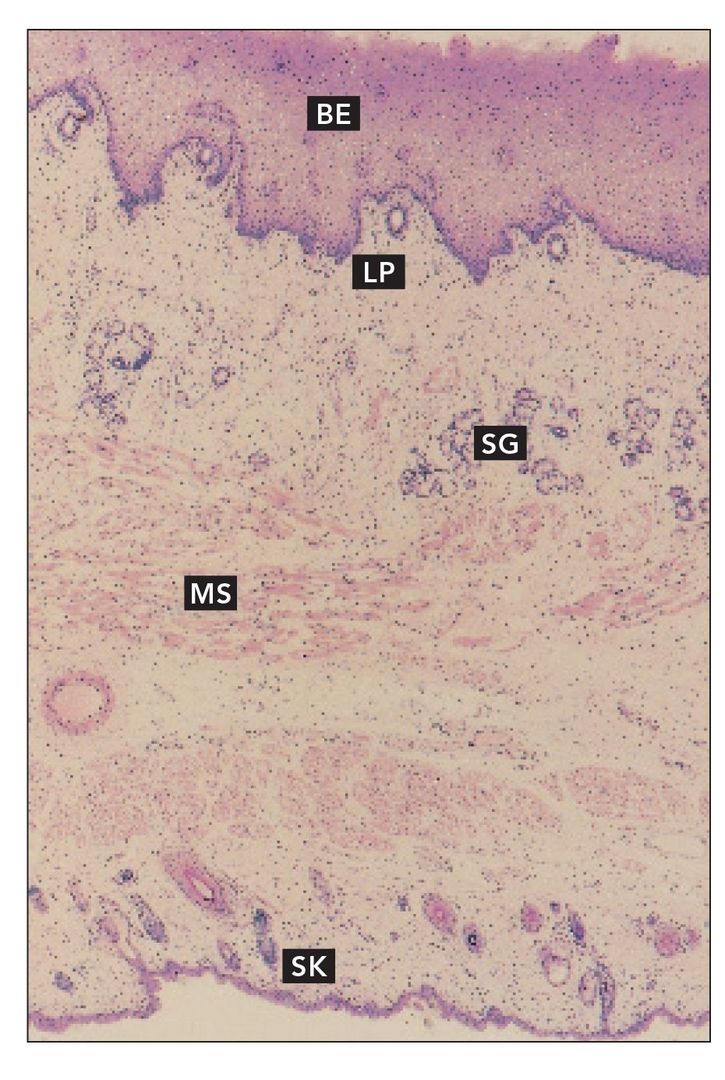
Cheek section
Full-thickness section through the cheek. Buccal epithelium (BE) and lamina propria (LP) overlie the submucosa, which contains minor salivary glands (SG). The buccinator muscle (MS) is sandwiched between the mucosa and submucosa and the skin (SK) (H and Lee stain; ×40).
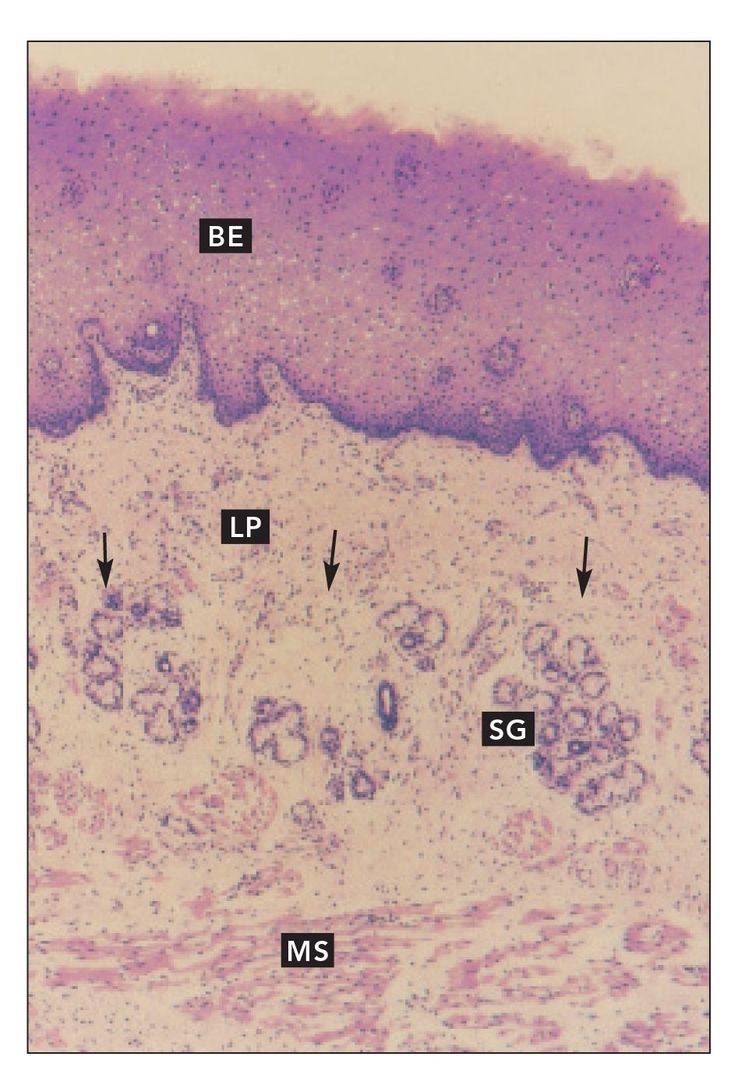
FIG 9-2
Cheek section
Higher magnification of the mucosal side of the section of the cheek shown in Fig 9-1. The lamina propria (LP) is continuous with the submucosa (arrows). Numerous minor salivary glands (SG) reside in the submucosa, which is loosely attached to the buccinator muscle (MS) (×64).
FIG 9-3
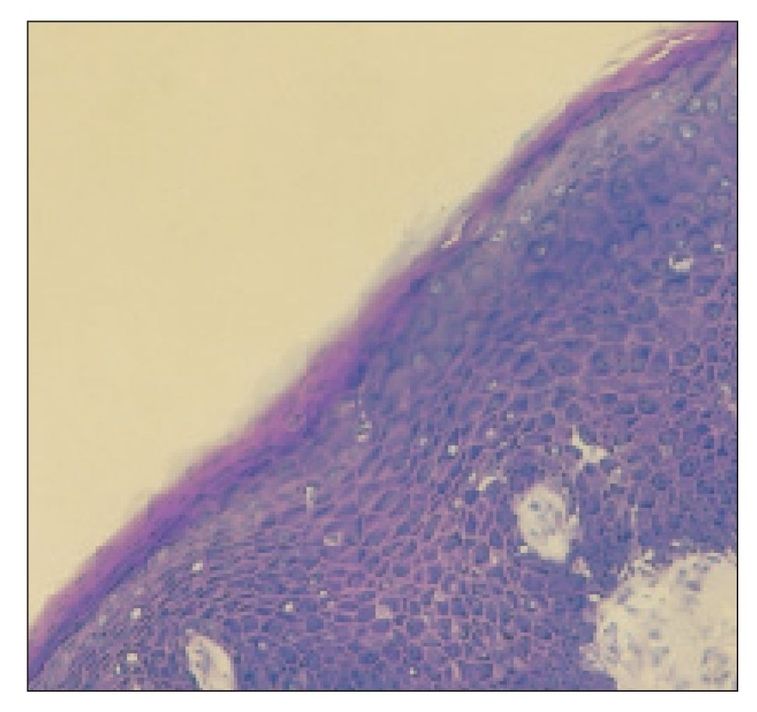
Buccal mucosa
Buccal epithelium (BE) and lamina propria (LP) comprise the buccal mucosa (H and Lee stain; ×160).
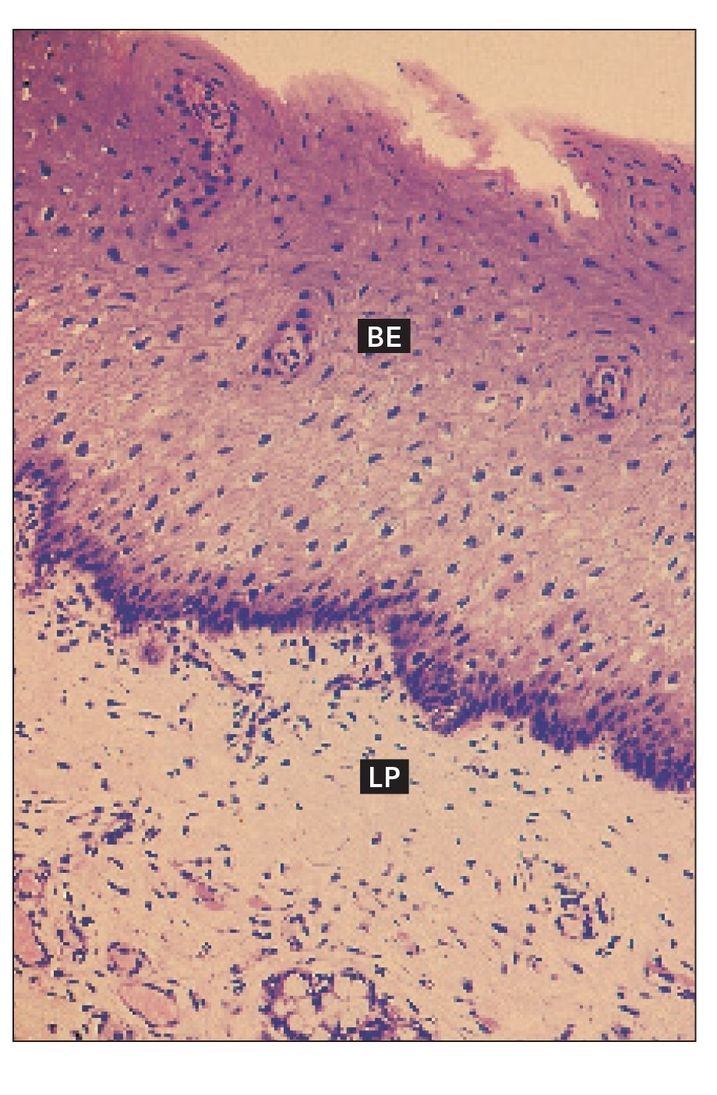
FIG 9-4
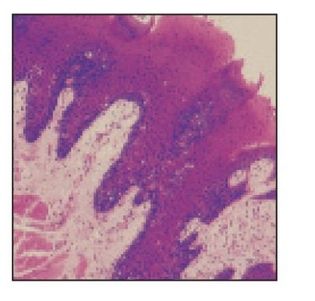
Epidermis and dermis
Epidermis (EPD) and dermis (DE) of the skin of the cheek. Arrows indicate hair follicles (H and Lee stain; ×64).
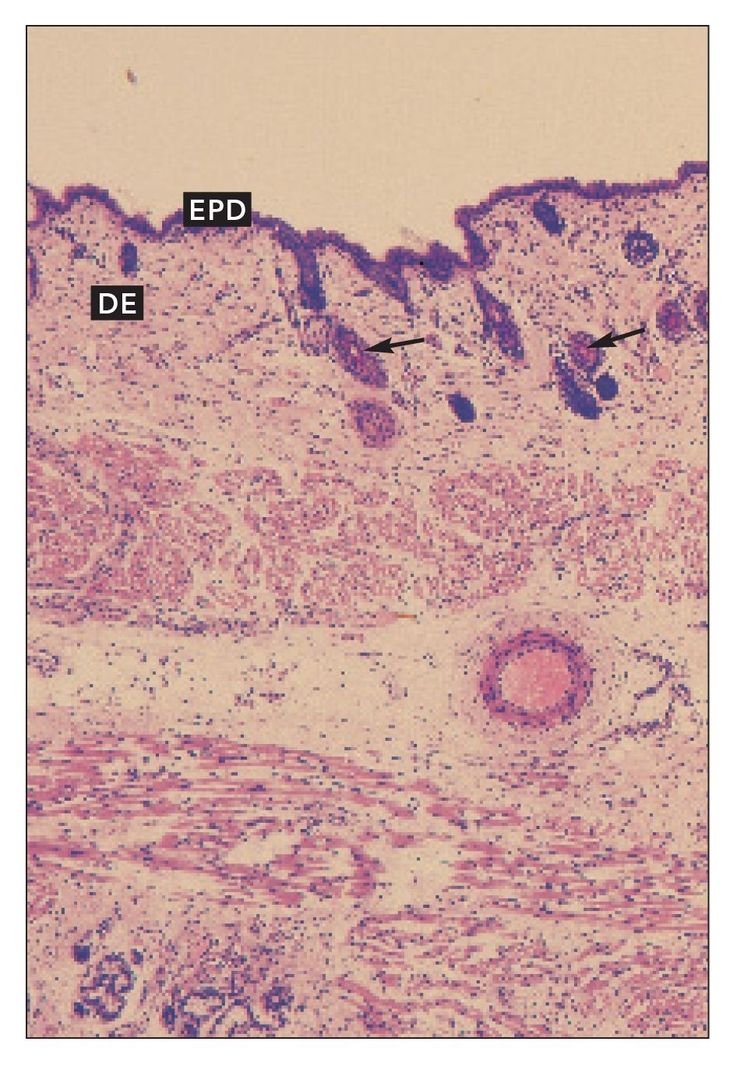
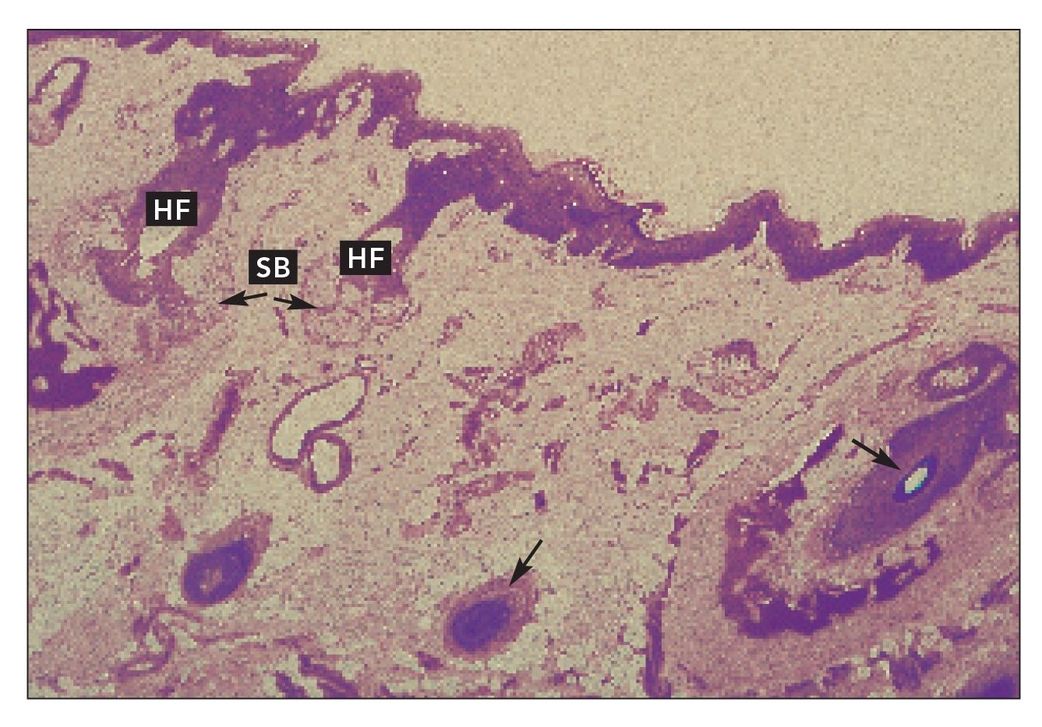
FIG 9-5
Sebaceous glands
Sebaceous glands (SB) associated with hair follicles (HF) in cheek skin. Arrows indicate hair follicles cut at different angles and depths (H and Lee stain; ×160).
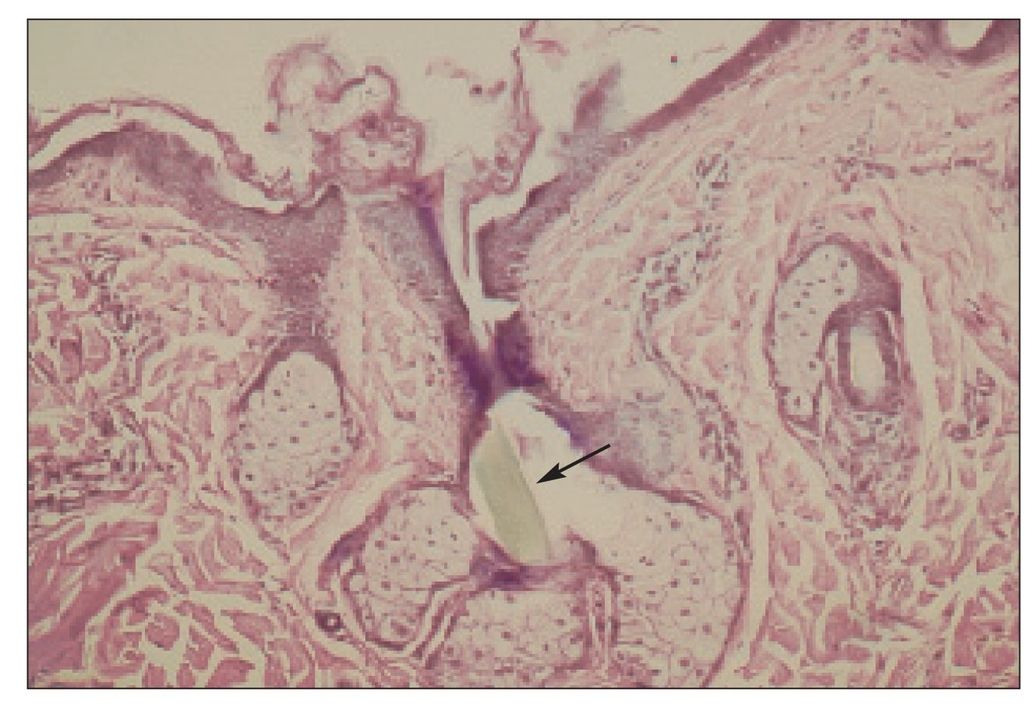
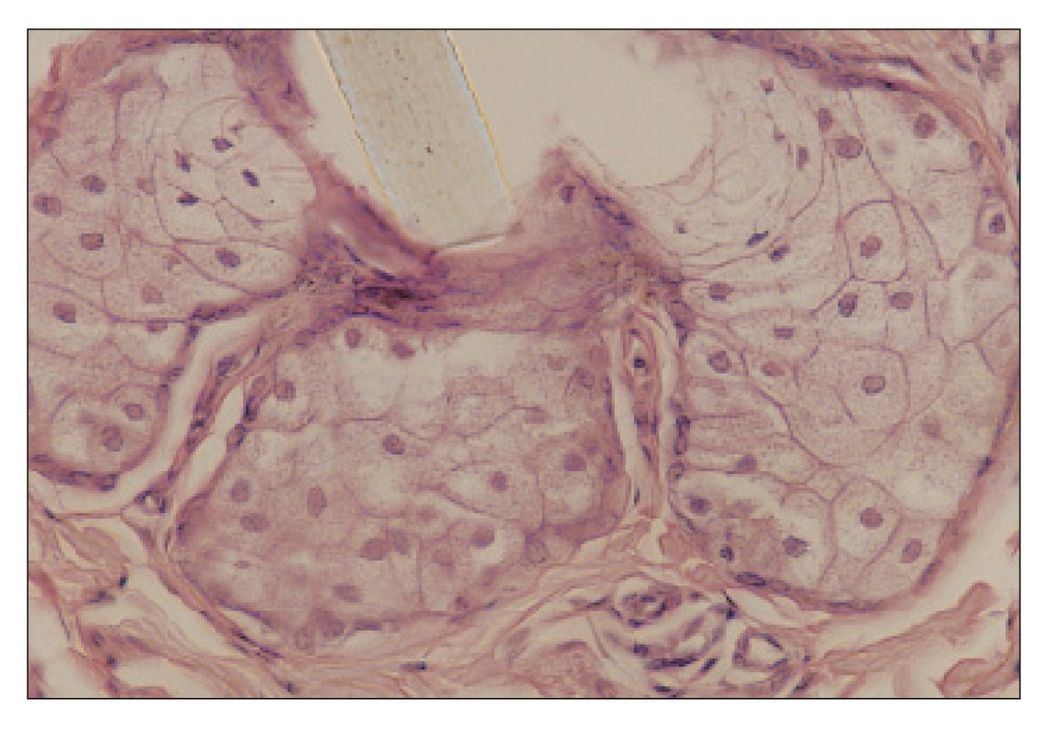
FIG 9-7
Hair shaft
Higher magnification of Fig 9-6. Note absence of ducts within the sebaceous glands (×400).
FIG 9-8
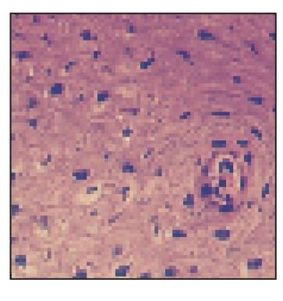
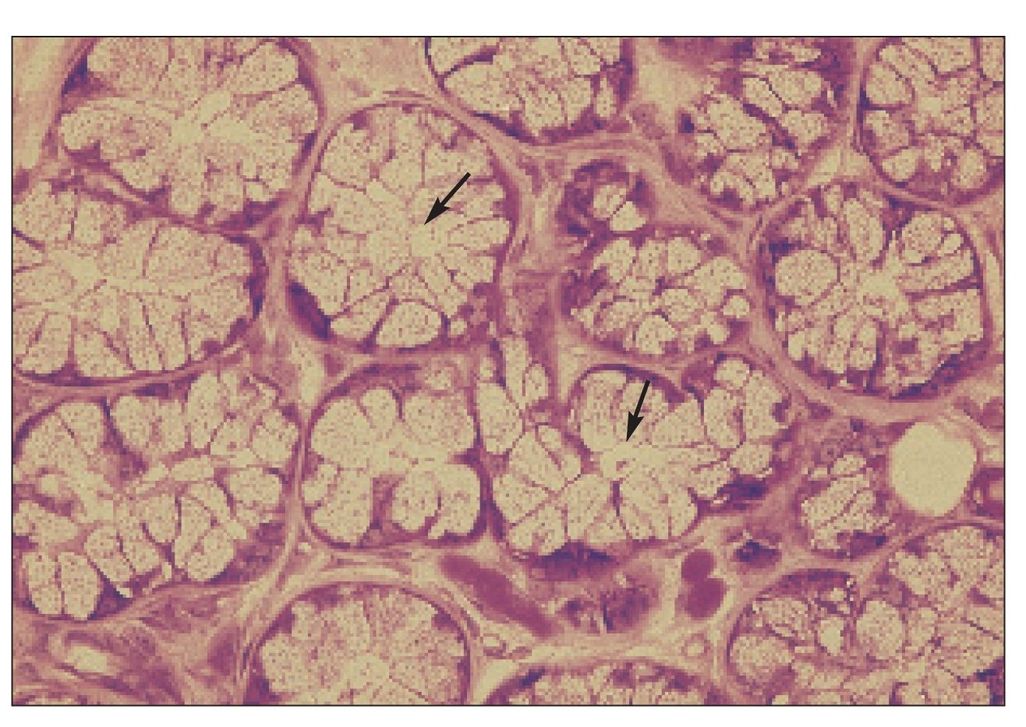
Sebaceous gland
Sebaceous glands in the buccal mucosa are called Fordyce’s spots. They appear as yellow spots visible through the epithelium. The arrow is in the single duct (H and E stain; ×400).
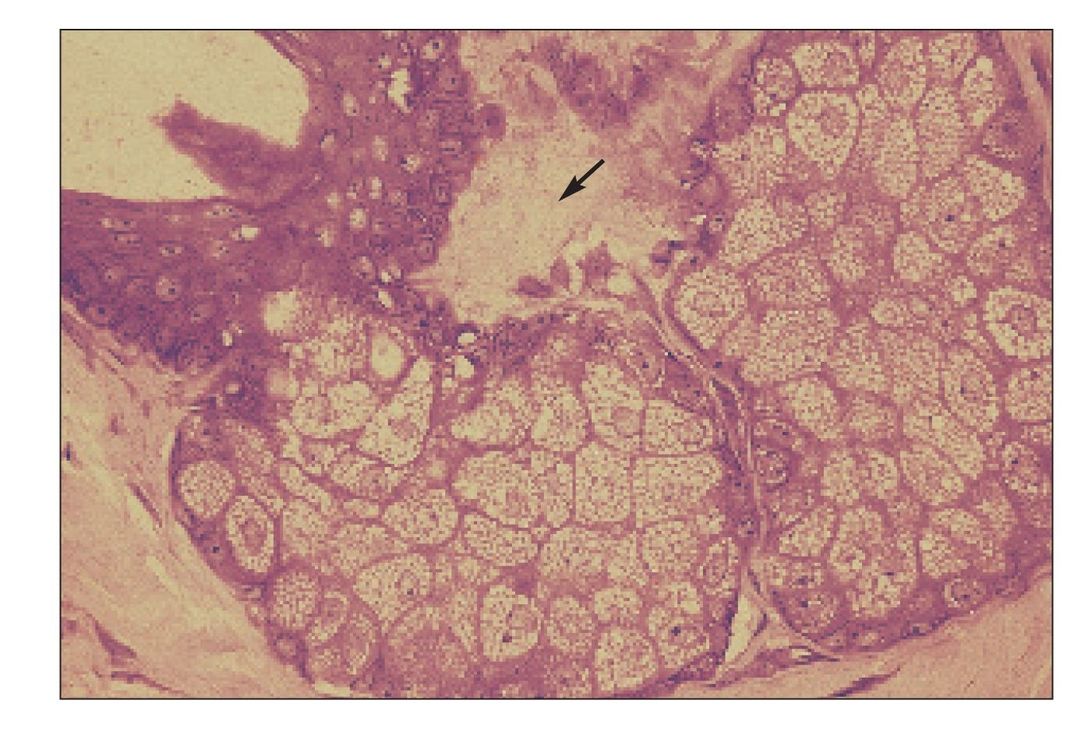
FIG 9-9
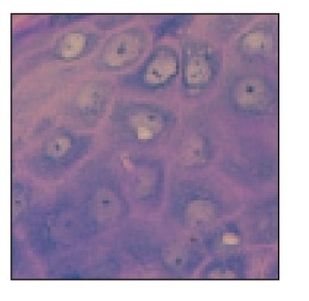
Salivary gland
Minor salivary gland in the buccal submucosa. Arrows indicate beginning of the duct system and intercalated ducts (H and E stain; ×400).
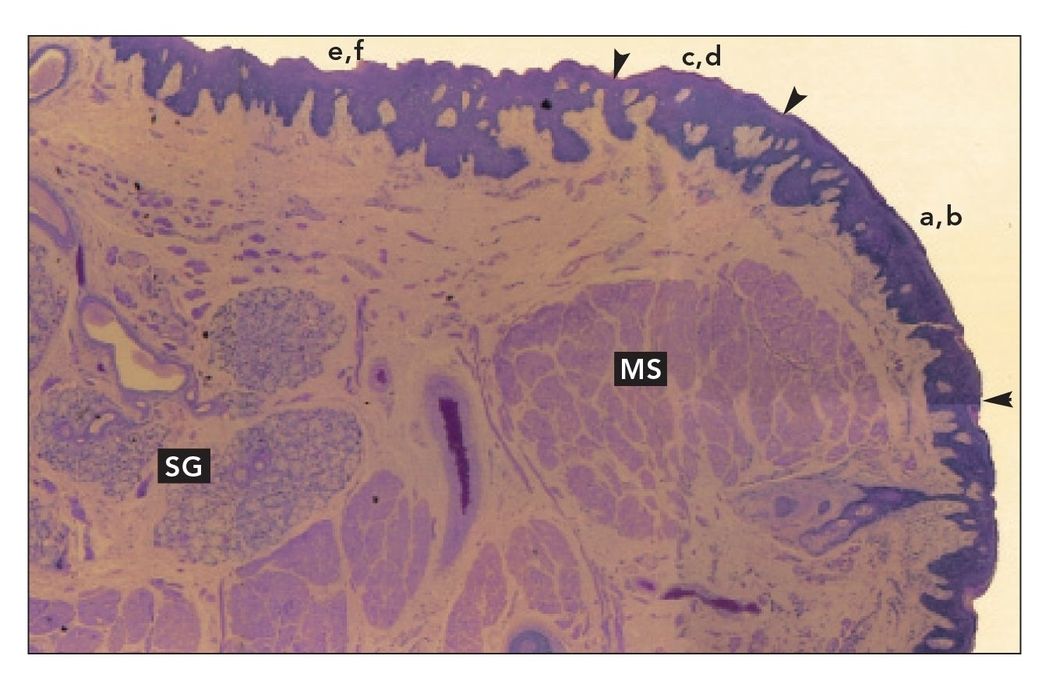
Lip section (monkey)
Sagittal section of rhesus monkey lip. The vermilion border is the area labeled a,b (arrowheads); the intermediate zone is the area labeled c,d (arrowheads); and the labial mucosa is the area labeled e,f. Many minor salivary glands (SG) are located in the submucosa of the labial mucosa. The orbicularis oris and other muscles of the lips (MS) form the substance of the lip (H and Lee stain; ×40).
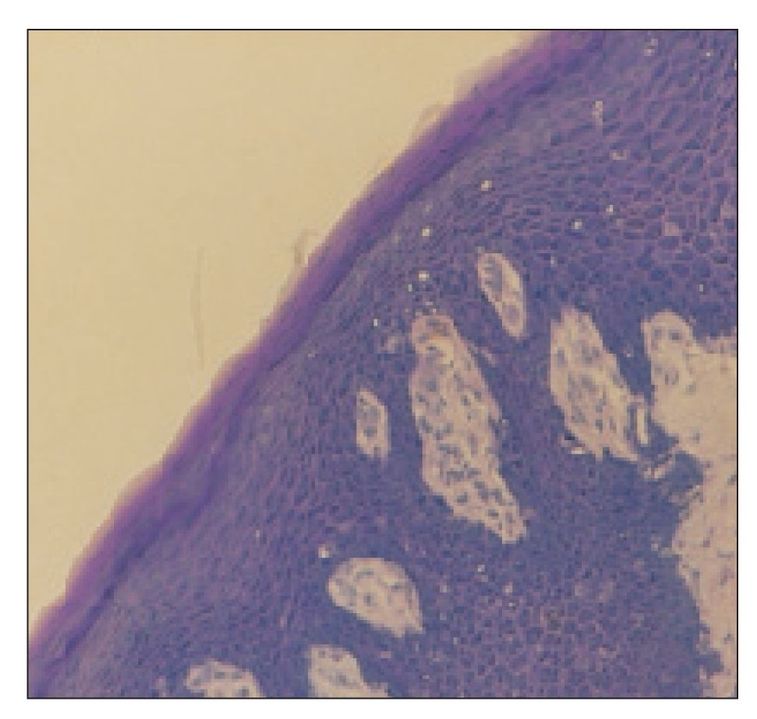
FIGS 9-11a TO 9-11f
Lip epithelium
Higher magnifications of the epithelium in areas of the rhesus lip indicated in Fig 9-10 (a–f).
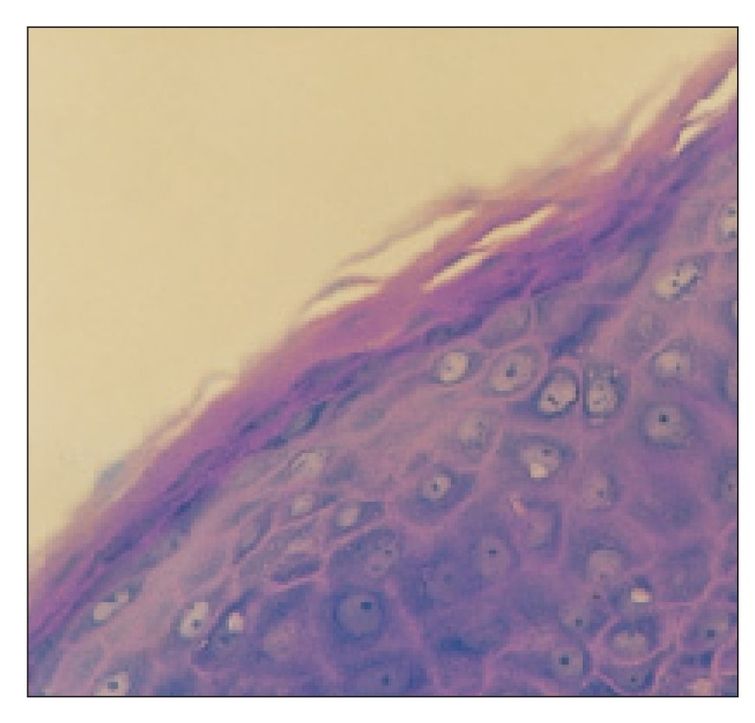
Lip epithelium
The epithelium of the vermilion border is fully keratinized (×160).
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses