Extrusive Luxation
OBJECTIVES
1 Differentiate type of luxation injury.
2 Identify injured tissues involved.
3 Define objectives of acute treatment.
4 Estimate frequency and type of complications.
DESCRIPTION AND CLINICAL APPEARANCE
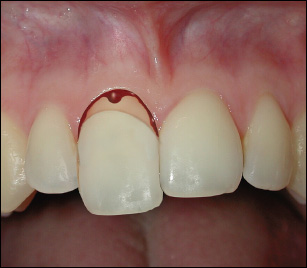
The tooth is partially displaced out of its socket.
The tooth appears elongated and is usually displaced palatally. The tooth is very loose, with bleeding from the gingival sulcus.
RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
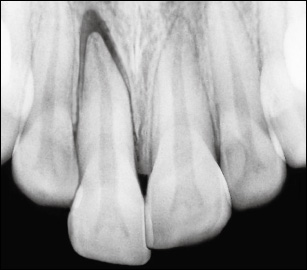
The tooth appears dislocated, with the apical part of the socket empty.
BIOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS AND TREATMENT PRINCIPLES
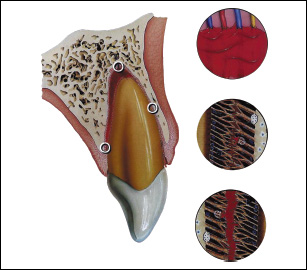
The impact results in partial disruption of the PDL attachment as well as rupture of the apical neurovascular bundle, causing increased mobility of the tooth and pulpal infarction (coagulation necrosis). The disruption of the neurovascular supply is frequently reflected in ne/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


