Avulsion
OBJECTIVES
1 Identify the tissues involved.
2 Know recommended emergency acute priority treatment.
3 Describe healing complications.
4 Select treatment options, based on root development and severity of injury.
DESCRIPTION AND CLINICAL APPEARANCE
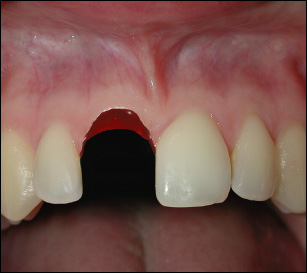
In this trauma situation, the tooth is displaced totally out of its socket. Clinically, the socket is found empty or filled with a coagulum.
RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
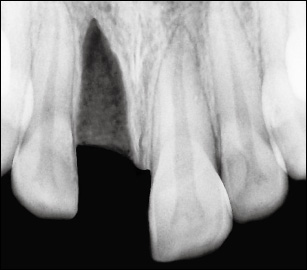
The socket is empty; fracture lines in the socket may be present.
BIOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS AND TREATMENT PRINCIPLES
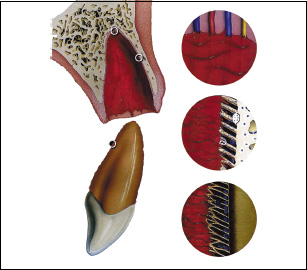
Immediately after injury, the PDL and pulp of the avulsed tooth begin to suffer ischemic injury, which is soon aggravated by drying, exposure to bacteria or chemical irritants. These events can kill PDL and pulpal cells even after a short extra-alveolar period.111 Treatment outcome is strongly dependent on the length of the dry extra-alveolar time period and the storage media used.111 If the extra-alveolar period is less than 1 hour, complete or partial PDL healing is possible. However, total PDL death can be expected after more than 1 hour of drying (delayed replantation); and progressive root resorption will be the result.111 While some might argue that due to the certainty of resorption in replanting teeth with more than 1 hour extra-alveolar exposure, such teeth should not be replanted, it is important to consider that with techniques such as decoronation, delayed replantation of teeth in children can be beneficial in order to save and maintain the alveolar growth in the region (see page 68). In patients with fully formed teeth, delayed replantation can allow for many years of good service.111
FIRST AID FOR AVULSED TEETH
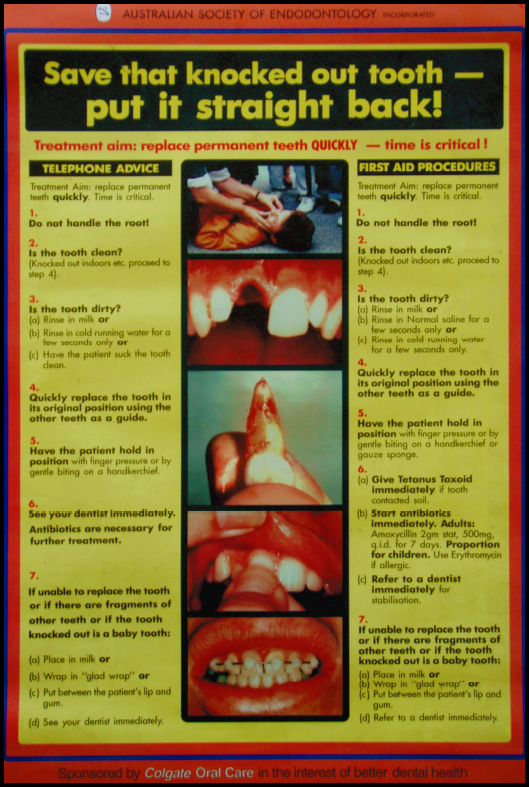
Dentists should always be prepared to give appropriate advice to the public about first aid for avulsed teeth.112 An avulsed permanent tooth is one of the few real emergency situations in dentistry. Public awareness needs to be increased, and health care professionals, parents and teachers should receive information on how to proceed following these severe, unexpected injuries. Instructions can be given by telephone to parents when an emergency occurs. If a tooth has been avulsed, make sure it is a permanent tooth (primary teeth should not be replanted).112
When a tooth has been knocked out:
- Keep the patient calm.
- Find the tooth and pick it up by the crown (the white part). Avoid touching the root.
- If the tooth is dirty, wash it briefly (10 seconds) under cold running water and then reposition it. Try to encourage the patient/parent to replant the tooth. Bite on a handkerchief to hold it in position.
- If it is not possible to reposition the tooth, place the tooth in a suitable storage medium, e.g. a glass of milk or a special storage media for avulsed teeth, if available. The tooth can also be transported in the mouth, keeping it between the molars and the inside of the cheek. Avoid storage in water.
- Seek emergency dental treatment immediately.
TREATMENT SCENARIOS
The following situations may preclude replantation of an avulsed tooth: age of the patient (primary tooth); extensive carious destruction of the tooth; extensive loss of marginal periodontal support; medically compromised patients (e.g. infectious endocarditis, immunosuppressive treatment).
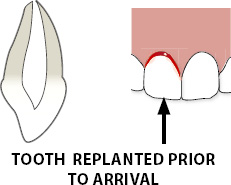
CLOSED APEX: TOOTH REPLANTED PRIOR TO THE PATIENT’S ARRIVAL AT THE CLINIC
- Leave the tooth in place.
- Clean the area with water spray, saline, or chlorhexidine.
- Suture gingival lacerations, if present.
- Verify normal position of the replanted tooth both clinically and radiographically.
- Apply a flexible splint for up to 2 weeks.
- Administer systemic antibiotics.
Please remember to read the sections on antibiotics, patient information and follow-up
CLOSED APEX: EXTRAORAL DRY TIME LESS THAN 60 MIN. THE TOOTH HAS BEEN KEPT IN PHYSIOLOGIC STORAGE MEDIA
Physiologic media include Hank’s balanced salt solution, milk, physiologic saline or saliva.
- Clean the tooth with saline.
- Irrigate the socket with saline.
- Examine the alveolar socket. If there is a fracture of the socket wall, reposition it with a suitable instrument.
- Replant the tooth with gentle pressure. Do not use force!
- Sutur/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


