7 Ulcerative and Inflammatory Conditions
Ulcerative Conditions
Recurrent Aphthous Ulcers and Traumatic Ulcers
Clinical Findings
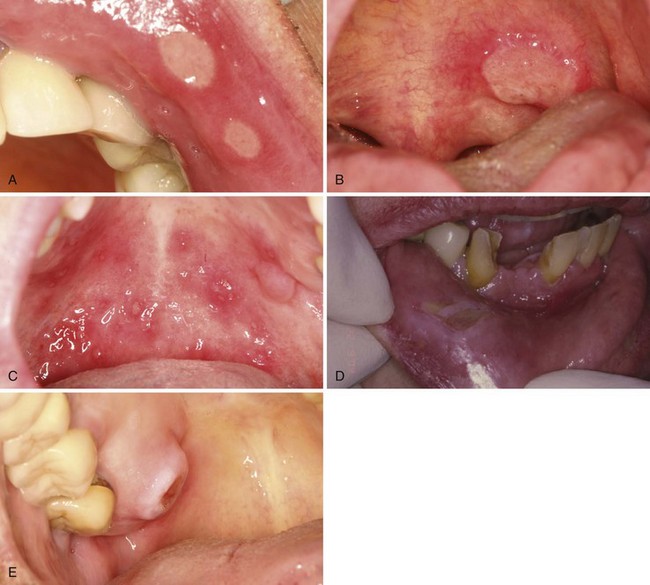
• Recurrent aphthous ulcers begin in the second and third decades of life and diminish in severity with age; ulcers are episodic or continuous and only on the nonkeratinized mucosa, although tongue dorsum may be involved in hematinic deficiency; a yellow fibrin membrane with surrounding erythema is present (Fig. 7-1, A-C).
• Minor ulcers are the most common, are smaller than 1 cm in size, and last 1 to 2 weeks; major ulcers are the least common, are larger than 1 cm in size, last for weeks or months, and often are associated with scarring—this form is often seen in HIV/AIDS. Herpetiform ulcers are uncommon and number more than 10 minor ulcers at each episode; severe aphthous ulcers present as continuous ulcerations.
• Traumatic ulcers can occur whenever there is history of trauma, particularly if the area is protuberant (see Fig. 7-1, D and E).
Etiopathogenesis and Histopathologic Features
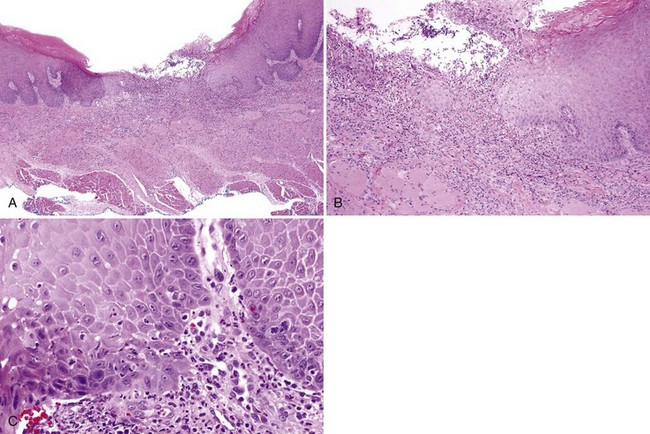
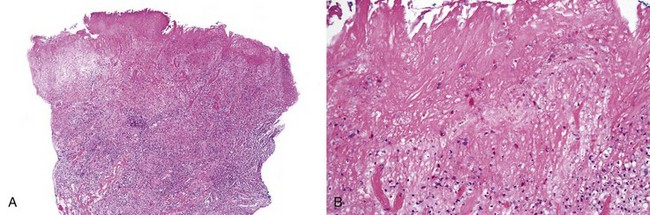
• Fibrin membrane with enmeshed neutrophils and underlying granulation tissue with acute and chronic inflammatory cells confined to the lamina propria; adjacent epithelium exhibits spongiotic pustules and reactive atypia (such as multinucleated epithelial cells and basal cell hyperplasia) (Fig. 7-2); traumatic ulcers often show adjacent hyperparakeratosis and surface bacterial colonies.
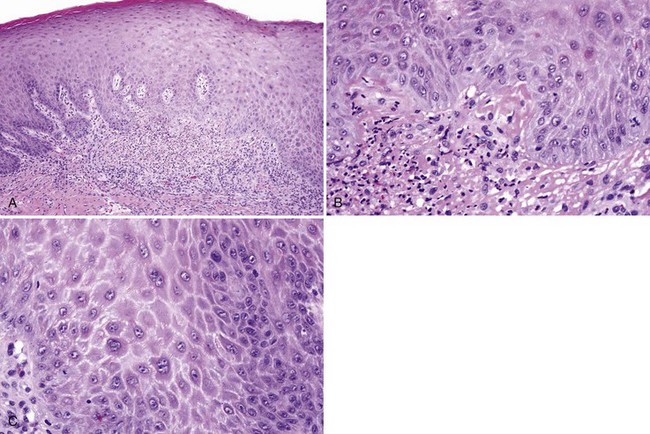
• Early or healing lesions show subepithelial fibrin deposition, spongiotic pustules, reactive epithelial atypia with multinucleated epithelial cells, and often intraepithelial hemorrhage (Fig. 7-3).
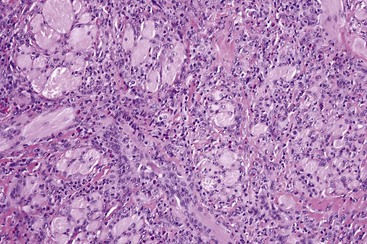
• Spread of inflammation to underlying muscle may lead to presence of eosinophils and histiocyte-like mononuclear cells (Fig. 7-4) (see Traumatic Ulcerative Granulomas later in this chapter.)
Differential Diagnosis
• Evaluate for herpes simplex virus in the adjacent epithelium, and cytomegalovirus and fungi in the lamina propria in immunocompromised patients.
• Neutropenic ulcers have scarce neutrophils (Fig. 7-5).
• Medication-induced oral ulcers are not strictly aphthae and are particularly dramatic in patients on mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors.
• Coagulation of the epithelium suggests concomitant contact with a caustic agent.
Management and Prognosis
• Topical or systemic steroid therapy or other immunosuppressive agents (see Appendix A) and topical analgesia are indicated.
• For systemic conditions presenting with aphthous-like ulcers, careful history-taking and work-up are important.
• Adenotonsillectomy may be effective in some patients with PFAPA syndrome.
Albanidou-Farmaki E, Deligiannidis A, Markopoulos AK, et al. HLA haplotypes in recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a mode of inheritance? Int J Immunogenet. 2008;35:427-432.
Burton MJ, Pollard AJ, Ramsden JD. Tonsillectomy for periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis and cervical adenitis syndrome (PFAPA). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010:CD008669.
Feder HM, Salazar JC. A clinical review of 105 patients with PFAPA (a periodic fever syndrome). Acta Paediatr. 2010;99:178-184.
Gattorno M, Caorsi R, Meini A, et al. Differentiating PFAPA syndrome from monogenic periodic fevers. Pediatrics. 2009;124:e721-728.
Jurge S, Kuffer R, Scully C, Porter SR. Mucosal disease series. Number VI. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Oral Disease. 2006;12:1-21.
Mendes D, Correia M, Barbedo M, et al. Behçet’s disease—a contemporary review. J Autoimmun. 2009;32:178-188.
Schena FP, Pascoe MD, Alberu J, et al. Conversion from calcineurin inhibitors to sirolimus maintenance therapy in renal allograft recipients: 24-month efficacy and safety results from the CONVERT trial. Transplantation. 2009;87:233-242.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses