56 Jaw conditions: Bone disorders
Figure 56.1a Solitary bone cyst.
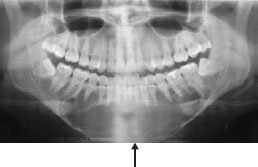
Figure 56.1b Solitary bone cyst aspirate.
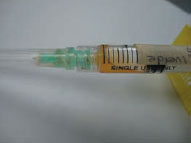
Figure 56.2 Bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis.
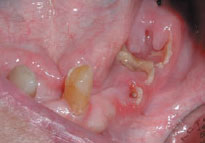
Figure 56.3a Giant cell granuloma.
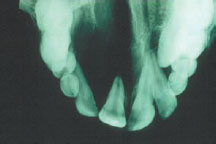
Figure 56.3b Giant cell granuloma.
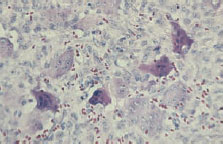
Figure 56.4 Langerhans cells histiocytosis lesions in ramus and condyle.
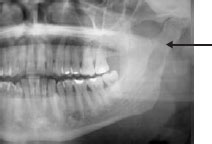
Figure 56.5a Multiple myeloma (from Bagan JV, Scully C. Medicinay Patologia Oral, 2006).
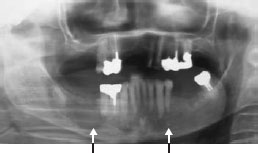
Figure 56.5b Multiple myeloma fracture of jaw through a lesion.
Table 56.1 Bone neoplasms.
| Benign | Malignant |
| Chondroma | Chondrosarcoma |
| Osteoblastoma | Osteosarcoma |
| Osteochondroma | |
| Osteoma |
Some jaw bone conditions are “pseudo-diseases”, such as unerupted teeth, bone marrow defects, Stafne bone defect (static bone cyst), osteosclerosis, pseudocyst of maxillary sinus, or sub-pontic osseous hyperplasia. Traumatic (solitary) bone cyst arises from trauma causing intramedullary hemorrhage that subsequently leaves a radiolucency with characteristic scalloped superior margin (it rarely damages teeth) (Figures 56.1a and b). Bone diseases that may affect the jaws are described below.
Non-neoplastic diseases
- Osteonecrosis. Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) and bisphosphonate-related osteochemonecrosis of the jaws (BRONJ) are uncommon complications of radi/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


