SCALP AND MUSCLES OF FACIAL EXPRESSION
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
Overview of Muscles of Facial Expression
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
GENERAL INFORMATION
SCALP
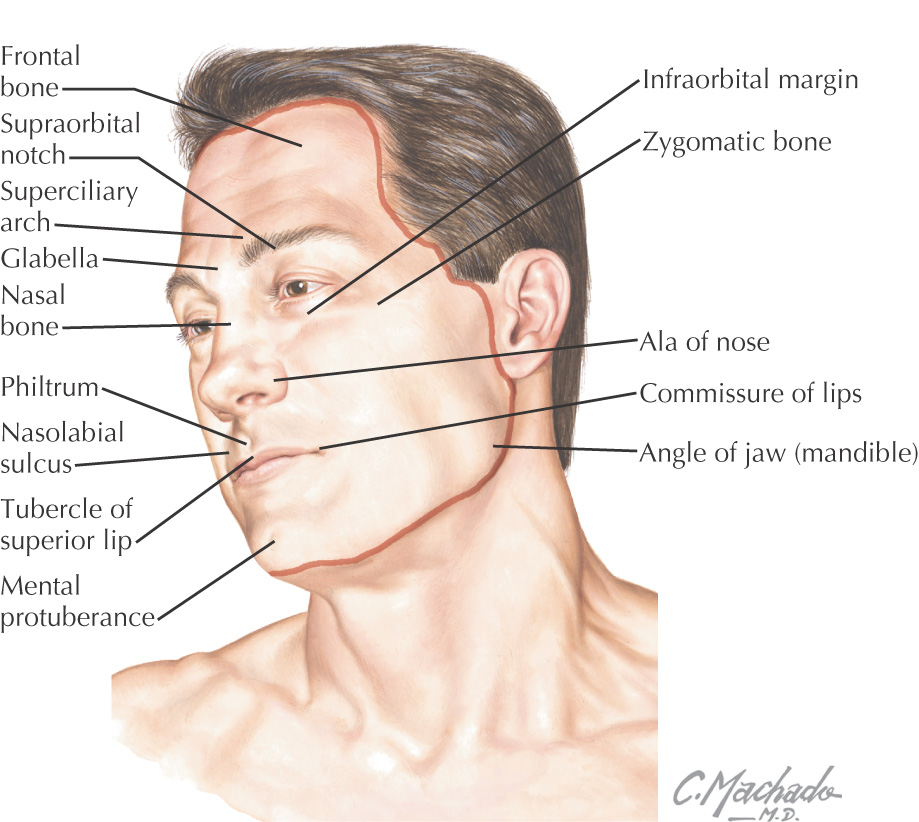
The area bordered by the forehead, superior part of the cranium, and occipital area immediately superior to the superior nuchal line
The lateral portion of the scalp blends with the temporal area because it extends inferiorly to the zygomatic arch
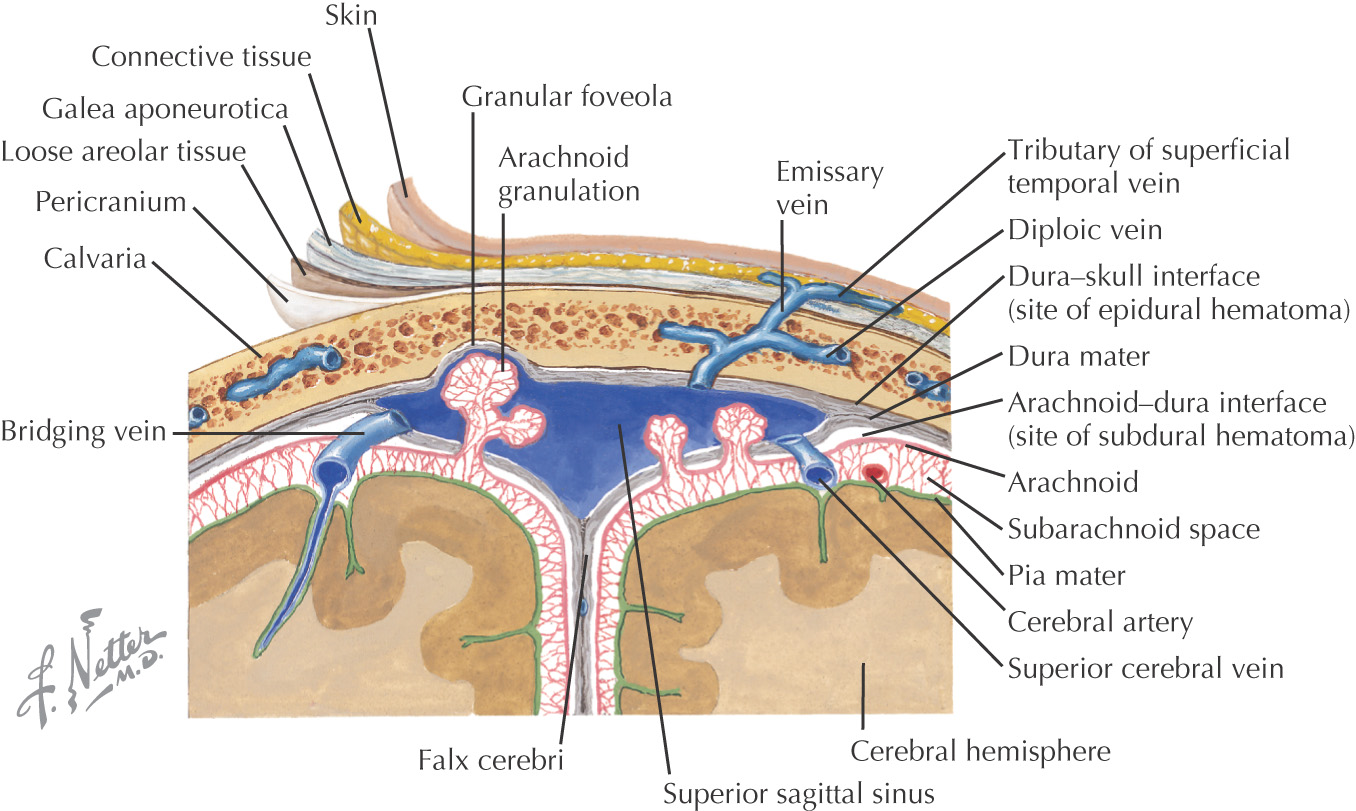
Anatomy of the scalp is important because of frequent trauma in this region
FACE
The area bordered within the hairline, anterior border of the auricles, and the chin
Major contents: eyes, nose, mouth, muscles of facial expression, muscles of mastication, parotid gland, trigeminal nerve, and facial nerve
BONES
Bones of the facial skeleton:
• Maxilla
• Mandible
Besides the nasal bone, the most commonly fractured bone of the facial skeleton is the zygomatic bone
MUSCLES OF FACIAL EXPRESSION
Innervated by the facial nerve
Derivatives of the 2nd pharyngeal arch
Originate from either bone or fascia and insert on the skin
The Superficial Muscular Aponeurotic System (SMAS) is a term used to describe the relationship of the muscles of facial expression located within the superficial fascia
The SMAS is maneuvered in a rhytidectomy (facelift)
There is no deep fascia along the face
Overview of the Scalp
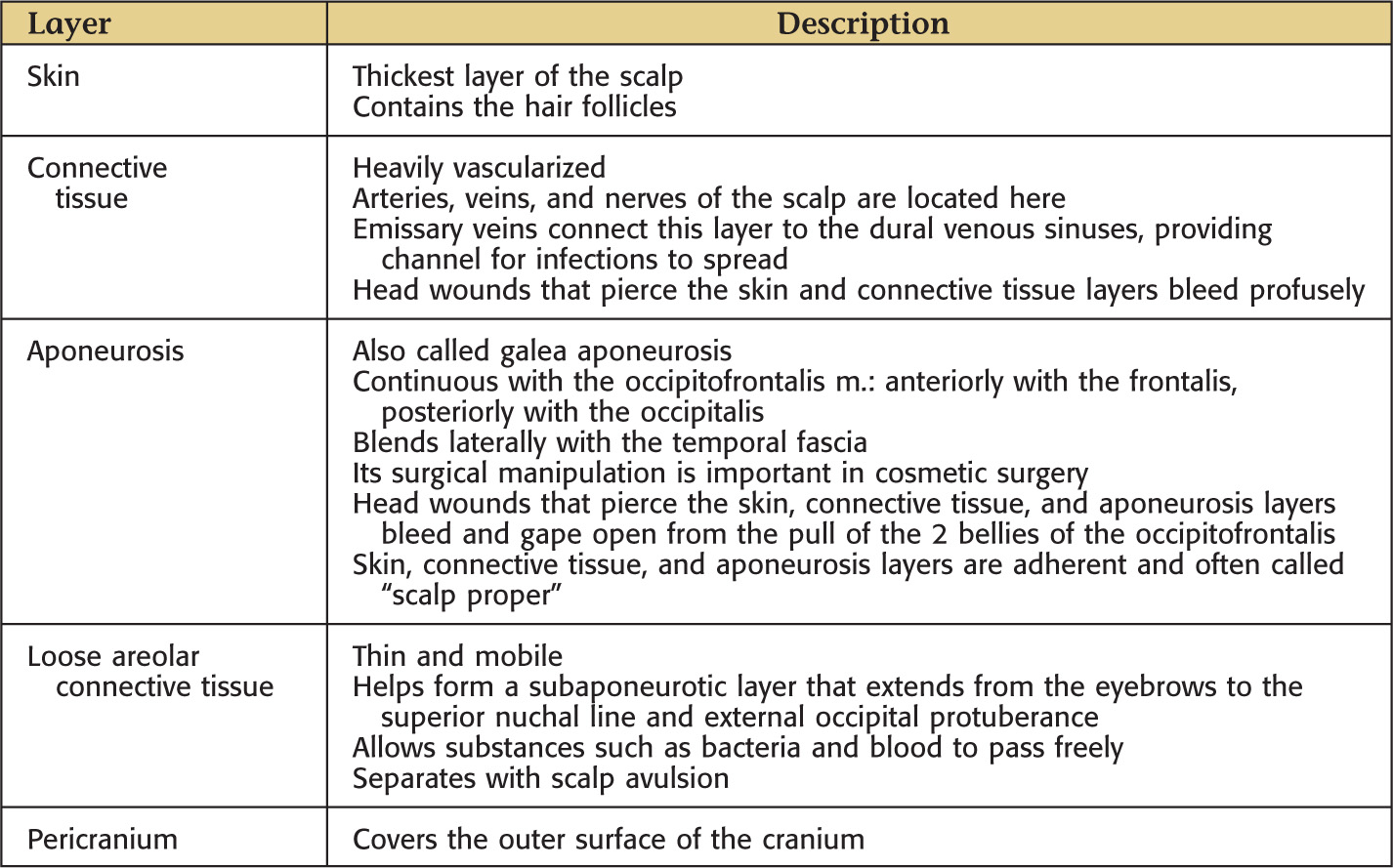
GENERAL INFORMATION
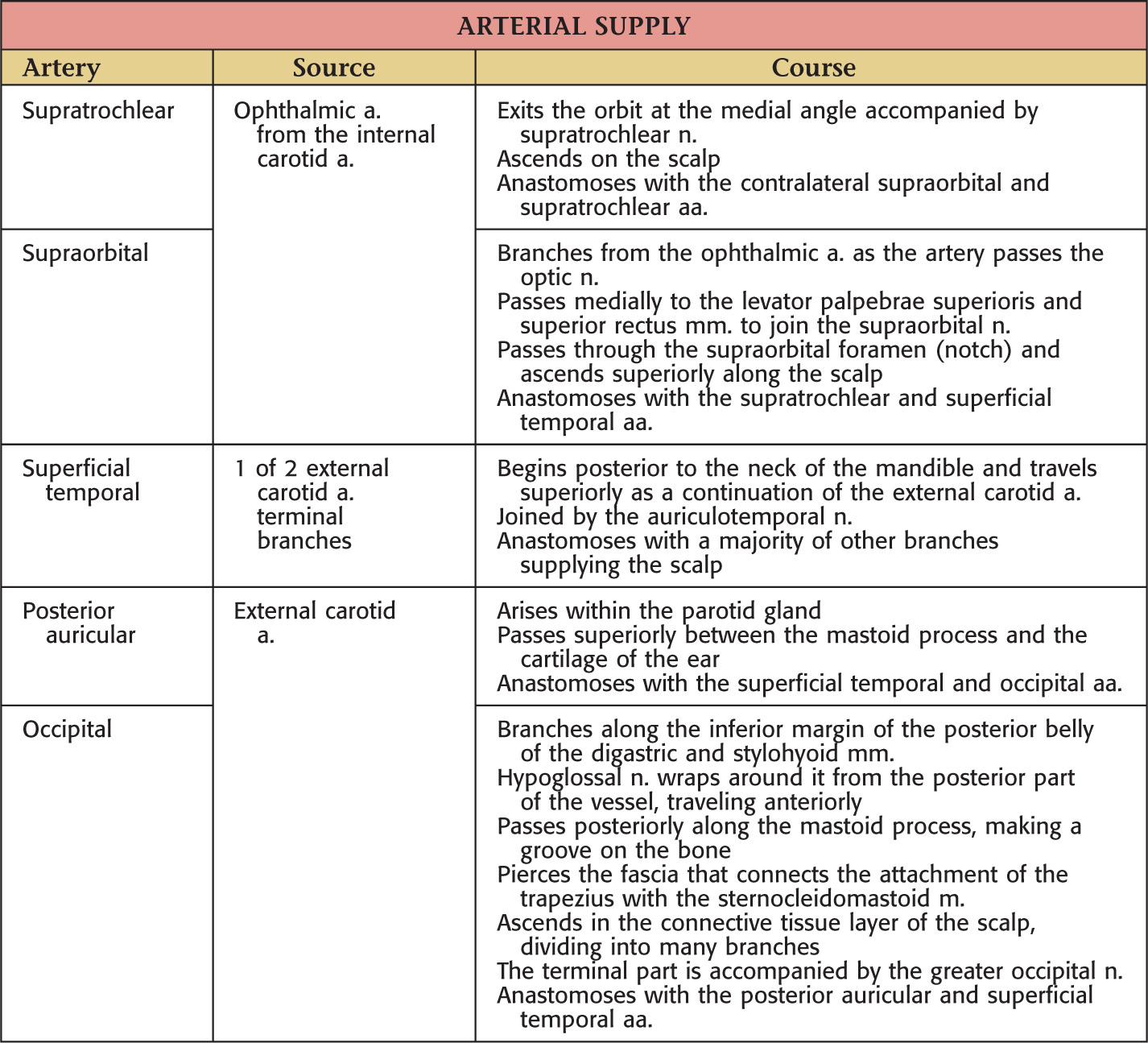
Vascular Supply of the Scalp
GENERAL INFORMATION
Highly vascularized; the vessels anastomose freely on the scalp
Arteries are derived from the external and the internal carotid arteries
The neurovascular supply arises from the anterior, lateral, and posterior scalp regions
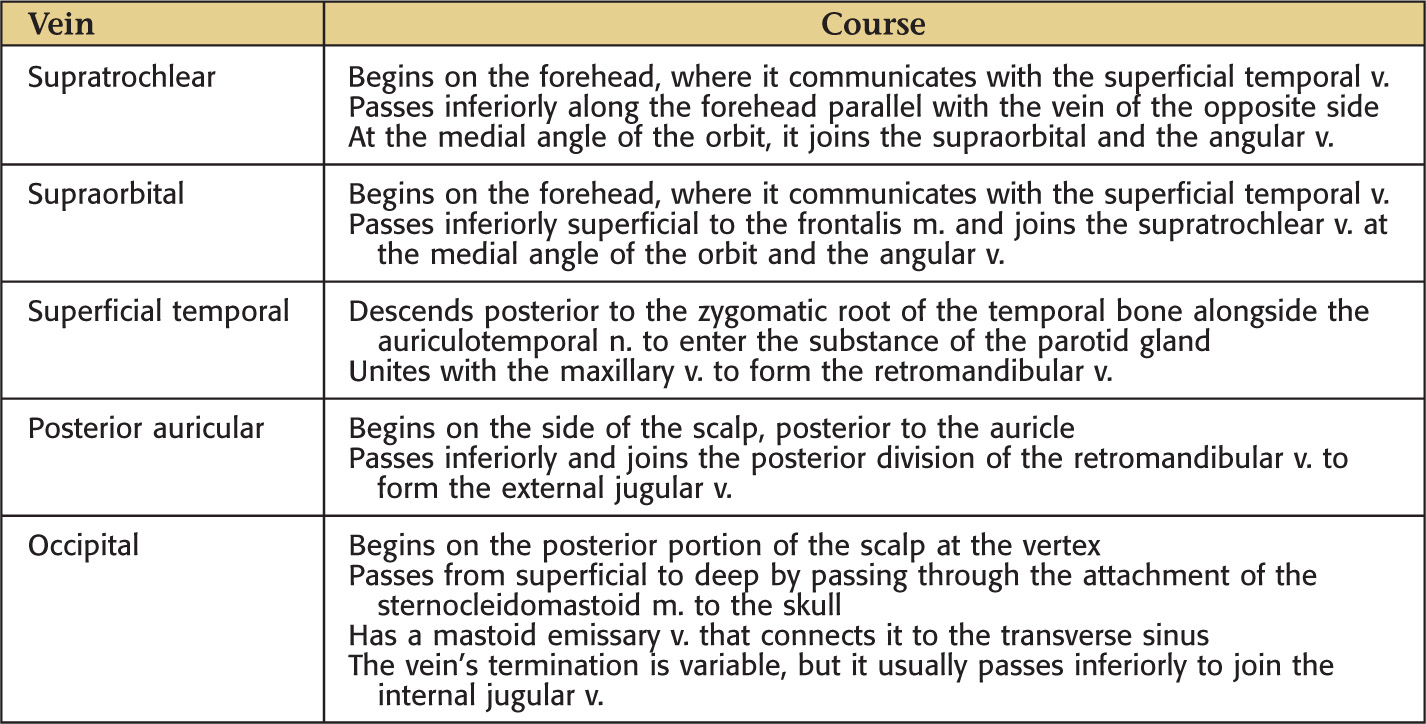
VENOUS DRAINAGE
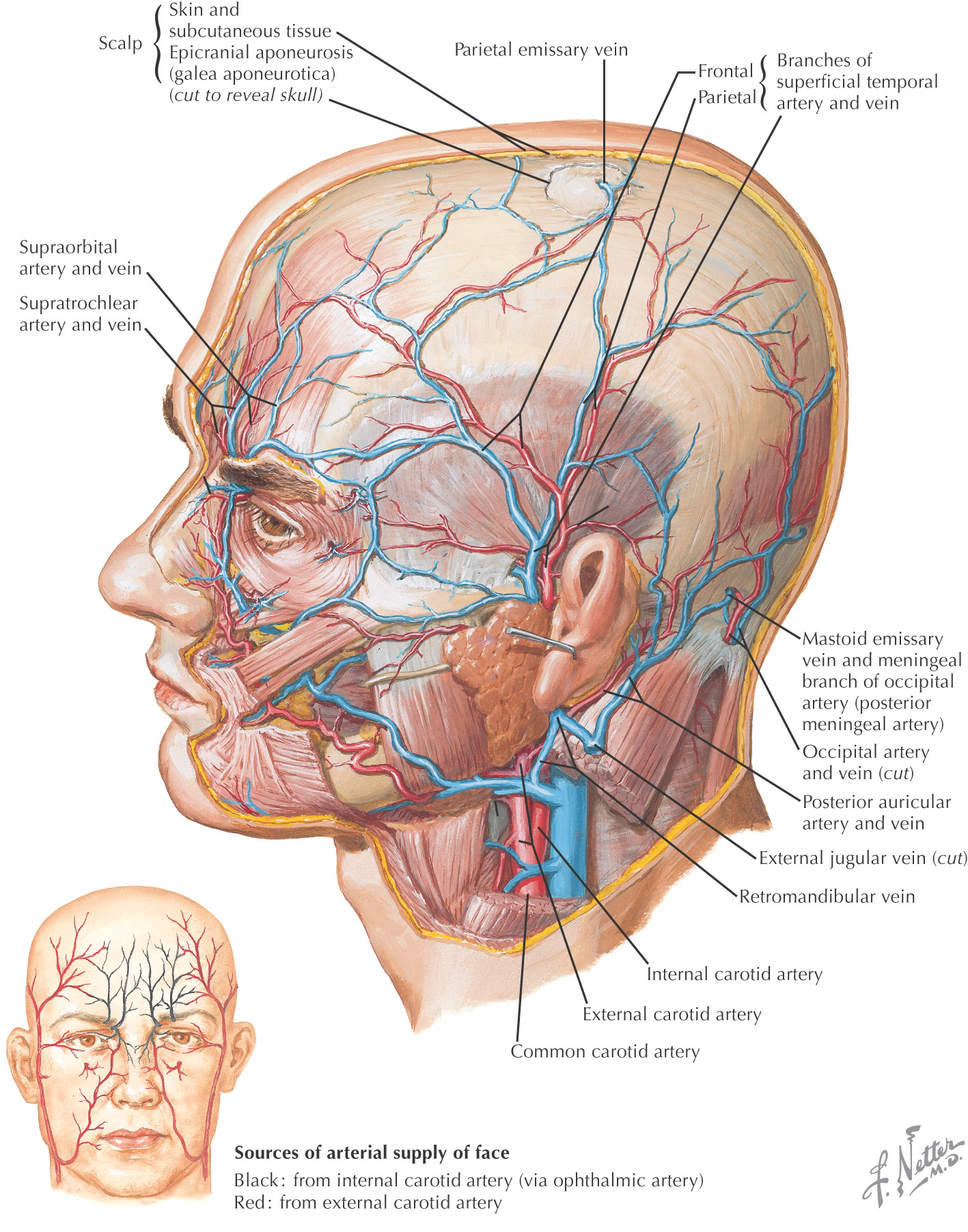
Nerve Supply of the Scalp
SENSORY DISTRIBUTION
Sensory supply is derived from all 3 divisions of the trigeminal nerve, branches of the cervical plexus, and upper cervical dorsal rami
These nerves travel in the scalp’s connective tissue layer
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses