48
Osseointegration
Apart from G.V. Black, P-I. Brånemark has made the most significant contribution to dentistry in the last century. His invention of dental implants has revolutionised the replacement of single teeth, partial edentulous segments and totally edentulous dental arches with both fixed and removable prostheses. Furthermore, implants are also used for providing anchorage for orthodontic, orthopaedic and orthognathic movements as part of oral rehabilitation.
Definitions
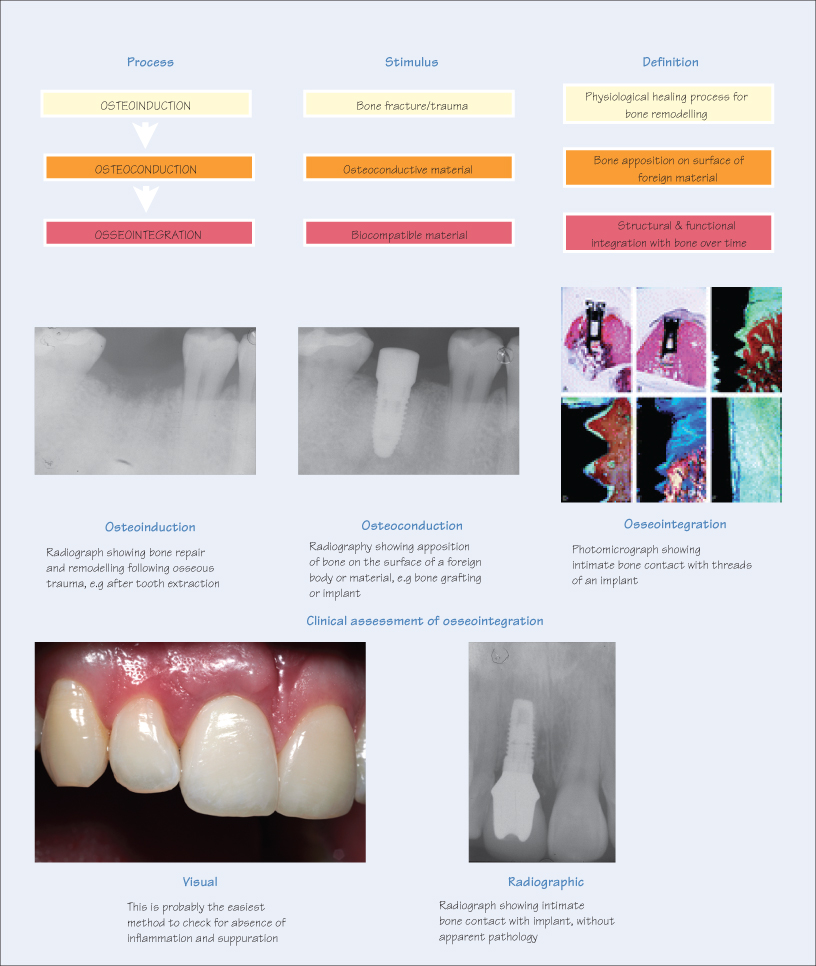
Three distinct processes describe bone healing and remodelling: osteoinduction, osteoconduction and osseointegration. These three mechanisms are interrelated but not interchangeable. However, terminology associated with bone growth, remodelling and repair is frequently misused and inaccurate. The definitions for the above are as follows:
- Osteoinduction – physiological process of bone healing and repair by osteogenesis following traumatic fractures;
- Osteoconduction – bone growth on the surface of osteoconductive foreign bodies, e.g. implants or synthetic bone grafting materials;
- Osseointegration – direct contact of living bone with an implant surface (without formation of fibrous tissue), which is maintained during functional loading over a long period.
Processes
The osteoinduction healing process is initiated following trauma to bone. Undifferentiated, mesenchymal cells are converted to preosteoblasts, which are eventually transformed to bone-forming osteoblasts and osteocytes by stimulation from inductive transformation growth factors such as bone BMP (bone morphogenic proteins). This is the normal mechanism that occurs during repair of a bone fracture and implant integration.
Osteoconduction is bone apposition on the surface of implants from pre-existin/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


