46 Neck swelling
Figure 46.1 Cervical lymphadenopathy: causes.
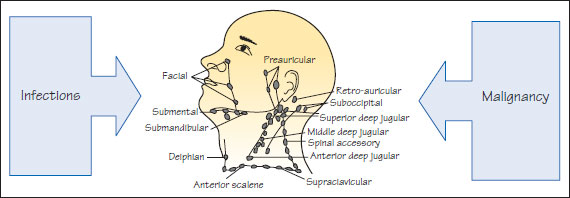
Figure 46.2 Lymphadenitis.
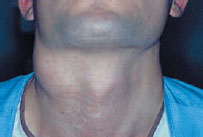
Figure 46.3a Lymph node metastasis.
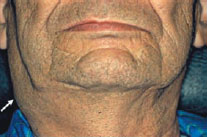
Figure 46.3b Metastasis from squamous carcinoma 40 x.
Figure 46.4a Diagnosis of neck lumps. US–FNA, ultrasound and fine needle aspiration biopsy.
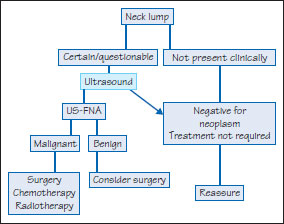
Figure 46.4b Ultrasound of a large jugulodigastric lymph node. Courtesy of J. Brown, C. Scully and Private Dentistry.
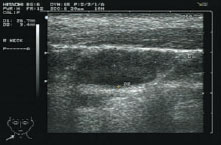
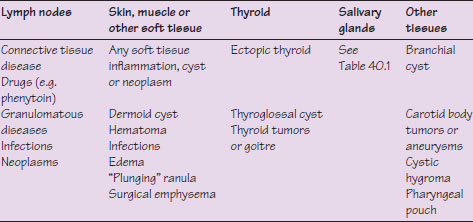
Table 46.1 Main causes of swelling in the neck.
Discrete swellings in the neck
These commonly arise in cervical lymph nodes but may occasionally arise elsewhere (Table 46.1).
There are approximately 300 cervical lymph nodes (about one-third of the body’s lymphoid tissue). Lymphadenopathy, the term meaning “disease of lymph nodes” is often used synonymously with “swollen/ enlarged lymph nodes”; it generally signifies pathology in the local area of drainage (Table 46.2), usually an infection, when the term “lymphadenitis” is appropriate, but sometimes it is caused by malignancy (Figure 46.1).
Cervical lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenitis is the most common cause of cervical lymphadenopathy, and of a swelling in the neck (Figure 46.2).
Infection
Cervical lymphadenitis in isolation usually arises because of an immune response to an infectious agent. The nodes are then often firm, discrete and tender, but are mobile. The responsible focus can usually be found in the drainage area (Table 46.2). Any bacterial in/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


