45 Salivary conditions: Mucoceles, sialosis
Figure 45.1 Mucocele.
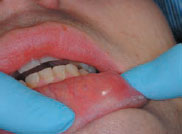
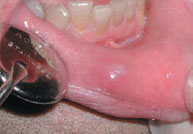
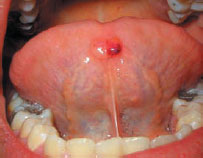
Figure 45.4 Mucocele (ranula).
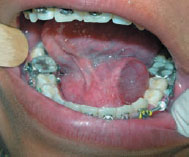
Figure 45.5 Retention cyst of minor salivary gland.
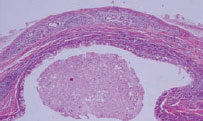
Figure 45.6 Sialosis: causes.
Figure 45.7 Sialosis.
Figure 45.8 MRI in sialosis.
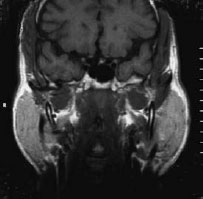
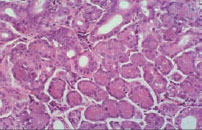
Figure 45.9 Histopathology in sialosis showing acinar hypertrophy.
Mucoceles (mucous cyst; mucus extravasation phenomenon; myxoid cyst)
Definition: A mucus-filled cyst.
Prevalence (approximate): Common.
Age mainly affected: Young adults/children.
Gender mainly affected: M > F.
Etiopathogenesis; Most mucus-filled cysts are mucoceles (90–95%) – extravasation mucoceles due to ductal damage; most are seen in the lower labial mucosa or on the lower lip, presumably resulting from trauma from lip-biting, resulting from the escape of mucus from a damaged minor salivary gland duct into the lamina propria.
Occasionally, mucus-filled cysts are mucus retention cysts – mucus is retained within a salivary gland or duct; most are seen in the upper lip or sublingually (ranula).
Rarely, mucus extravasates intra- or subepithelially – superficial mucoceles, seen mainly in lichen planus; palatal lesions are most common.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


