42 Salivary conditions: Sjögren syndrome
Figure 42.1 Causes of Sjögren syndrome (SS).
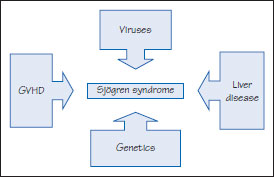
Figure 42.2 Secondary Sjögren syndrome (SS-2).
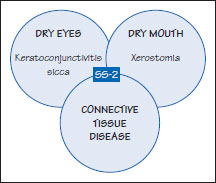
Figure 42.3 Primary Sjögren syndrome (sicca syndrome).
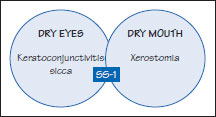
Figure 42.4 Dry mouth.
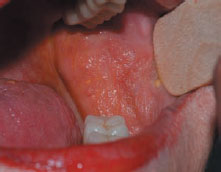
Figure 42.5 Dry mouth.
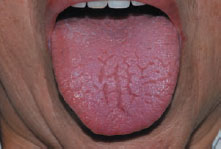
Figure 42.6 Salivary swelling in SS.
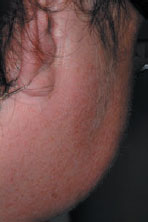
Figure 42.7 Hand deformities in rheumatoid arthritis in SS.
Figure 42.8 Algorithm for diagnosis of SS.
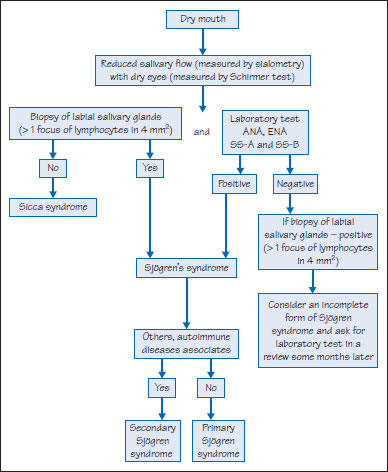
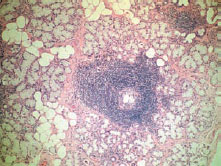
Figure 42.9 Sjögren syndrome focal lymphocytic adenitis.
Definition: The association of dry mouth (xerostomia) and dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis sicca).
Prevalence (approximate): Uncommon.
Age mainly affected: Older people.
Gender mainly affected: F > M.
Etiopathogenesis: A benign autoimmune inflammatory exocrinopathy (epithelitis) directed against alpha fodrin, a cytoskeletal protein involved in actin binding, with lymphocyte-mediated destruction of salivary, lacrimal and other exocrine glands. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interferon (IFN) and B cell activating factor (BAFF) are implicated. A viral etiology, possibly human retrovirus 5 (HRV-5), and a genetic predisposition may be implicated. A SS type of disease may follow HIV, EBV, HCV, or Helicobacter pylori infection, or graft-versus-host disease (Figure 42.1).
Most common is secondary SS (SS-2) which comprises dry eyes and dry mouth and an autoimmune disease – usually primary biliary cirrhosis or a connective tissue disease such as rheumatoid arthritis (Figure 42.2).
The same features in the absence of systemic autoimmune disease are termed primary SS (SS-1 or sicca syndrome) (Figure 42.3).
Diagnostic features
History
Oral: May include:
- xerostomia and sequelae (Chapter />
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


