42
Computer-Aided Design and Manufacture Technology
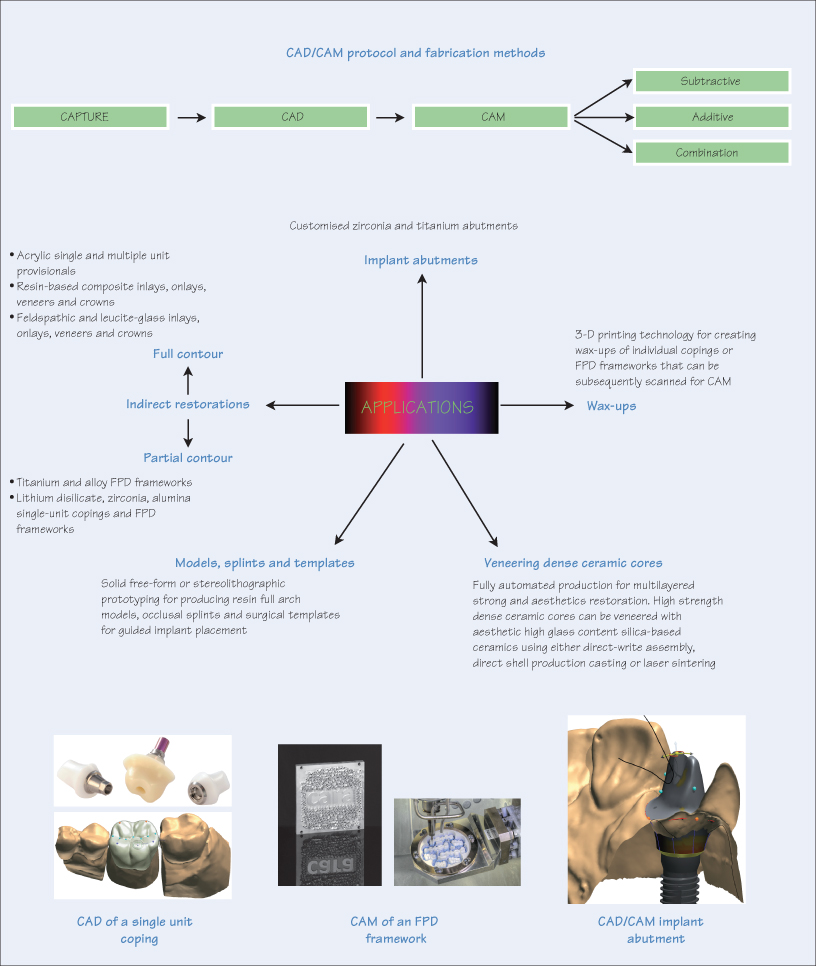
CAD/CAM (computer-aided design and computer aided manufacture) technology is heralding a new age of digital dentistry. CAD/CAM involves three distinct processes: capture, design and fabrication.
Capture
Capture or digitisation is converting a 3-D structure into a dataset for creating a virtual representation of an object, e.g. by a triangulation process. This is achieved using 3-D scanners, which are either optical or mechanical. An optical scanner uses white light projections or laser beams, while a mechanical scanner uses a ruby ball which traverses the object and converts the information into a graphical computer image.
Capture can either be intra-oral, i.e. an optical impression of the prepared tooth/teeth and full-arch digital impressions, or anatomical dental duplicate, e.g. scanning an impression of the tooth preparations, poured plaster dies, or proposed wax-up of the prostheses.
Design
CAD is designing a restoration, which is subsequently stored as a computer file. At present there is no industry standard file format, and each system is manufacturer-specific and non-interchangeable. Several design processes are possible, including:
- Extrapolation technique – the morphology of the restoration is obtained from a software database;
- Correlation technique – involves taking two optical impressions, one of the prepared tooth and one of the envisaged occlusal morphology, which can either be a preoperative impression or a scan of a proposed wax-up;
- Replication – copying the occlusal anatomy of a similar type of contralateral tooth;
- Functional technique – two optical impressions, on/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


