4
Diagnostics: Initial Consultation
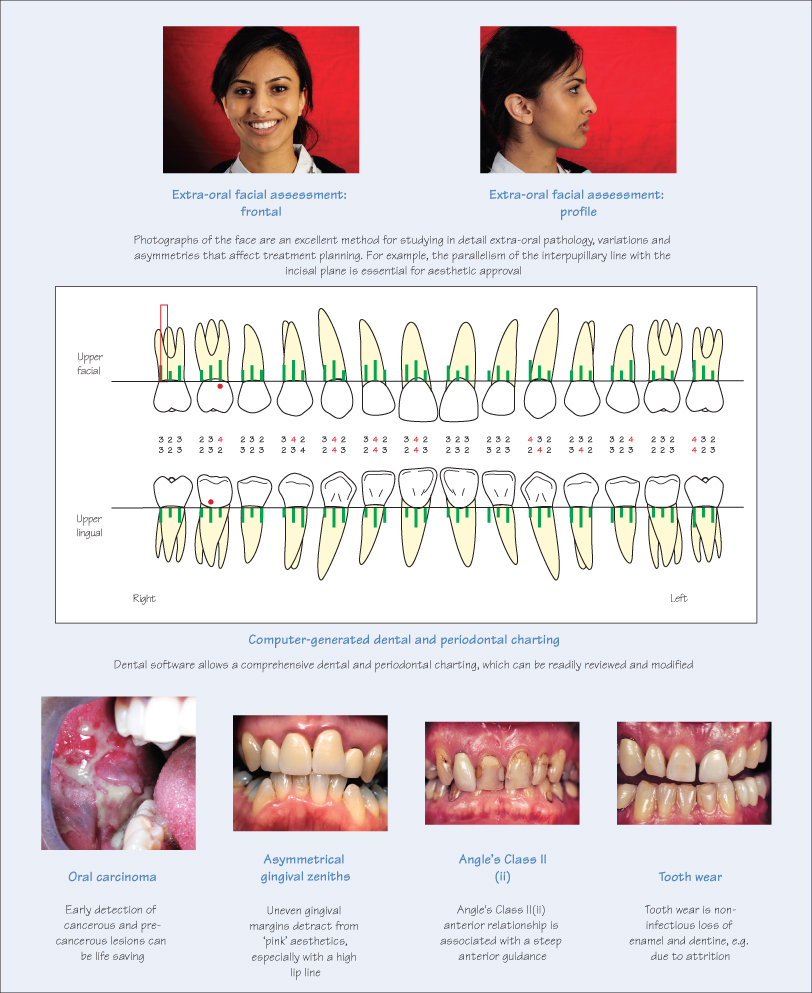
The initial consultation is to assess the patient’s current dental status and determine which, if any, detailed investigations or referral are necessary before arriving at a diagnosis.
Initial Complaint
The first point to ascertain is the reason for attending, which can be pain, dissatisfaction with previous dentists, referral, coercion by family, friends and colleagues regarding poor dental health and/or appearance, second opinion, or a personal desire to improve dental health and aesthetics.
Dental History
Dental history taking includes the following:
- Attitude to oral health;
- Regular or occasional attender;
- Dental records, models, photographs and radiographs from previous dentist(s);
- Dental phobias;
- Hobbies or habits that affect the dentition, e.g. playing a wind instrument;
- Sports, occupational hazards, or other risky activities;
- Persona and expectations about dental treatment;
- Financial status.
Extra-oral Examination
The extra-oral examination consists of a visual and tactile assessment. The skeletal structure, tegumental (skin) structure and the musculature are scrutinised, and deviations from the norm or pathological changes are noted.
- Skeletal: facial shape (ovoid, tapering, rectangular or square), facial profile (class I, II or III base), zygomata (prominent, receding), angle of mandible (prominent, receding), temporomandibular joint (TMJ) (deviation and/or clicking during movement, hypo- and hyperplasia of condyles) and maxilla (parallelism, prominent, receding, canting).
- Tegumental: swellings, lacerations, bruising, scarring (e.g. healing of previous disease or surgery, or result of facial cosmetic procedures), indelible tattoos, suppuratio/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


