The radiographic examination should show:
• The condition and situation of the tooth
• The orientation of its great axis
• Its skeletal relationships with the ramus and the mandibular body
• Its dental relationships with the second molar
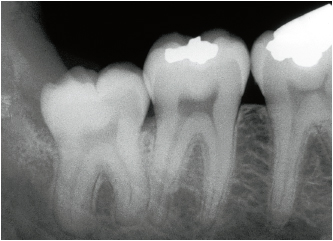
The shape of the crown of the third mandibular molar, either impacted or partially erupted, can be a source of problems, more due to its position than to its volume. Conversely, the anatomy of the roots is an important potential complication that the clinician must assess carefully from the radiographs. The whole tooth must be visible on the film and its position in relation to the mandibular canal must be clear. The anatomy of the roots, their orientation, the apex configuration, and the aspect of the inter-root septum should be clearly defined.
The type of surgical protocol may then be decided upon depending on the following three conditions:
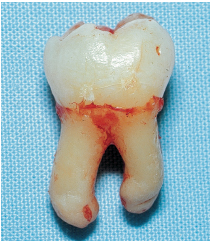
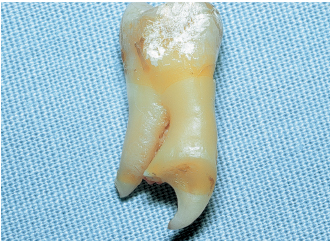
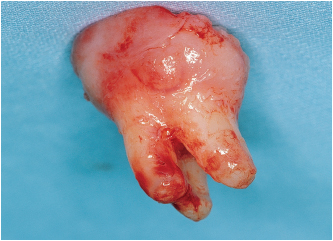
• The tooth is likely to be removed all in one block (Figs 4-1a and 4-1b). Despite a slight root convergence, a thick septum does not always prevent extraction. A septum that is thin and has become trapped between the roots is removed during extraction.
• The application point of the elevator is selected according to root orientation.
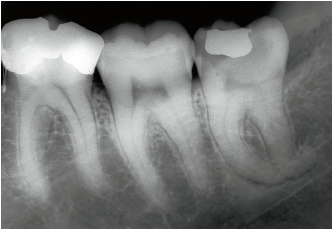
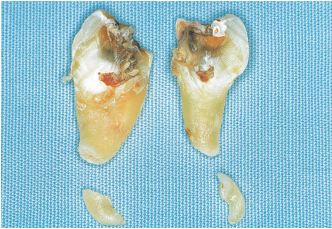
• Root form and orientation indicate the need for root separation (Figs 4-2a to 4-2d). This can be done using an overall sectioning of the tooth or following the horizontal section of the previously extracted crown. This separation is necessary if the roots are convergent or divergent and in cases where the root tips are severely angled (Figs 4-3 to 4-7). It is also recommended if the roots cross the mandibular canal.
The anatomic situation of the tooth
It is important to visualize the anatomic arrangement, both skeletal and dental, in order to plan the surgery and preempt any presurgical problems. From this stage the impacted tooth is classified according to its anteroposterior and vertical dimensions. The classification, which was proposed several decades ago, is intended to determine:
• The orientation of the great axis of the tooth
• The relationship of the tooth with the ramus
• The depth of impaction
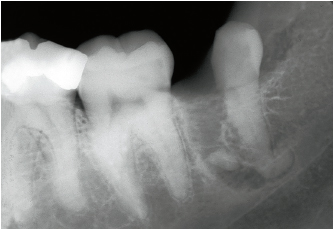
4-2b During the procedure, despite root separation, the mesial apex is fractured. The marked curvature of the apices does not depend on the position of the tooth or its effect on the mandibular body.
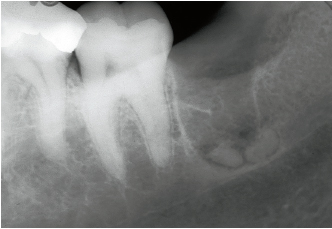
4-2c A new radiograph reveals the position of the two fractured apices.
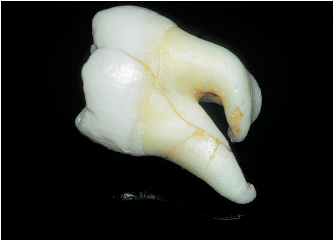
4-4 Sectioning of this tooth was carried out using chisels.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses