30 Swellings: Malignant neoplasms, lymphoma, metastatic neoplasms
Figure 30.1 Lymphoma.
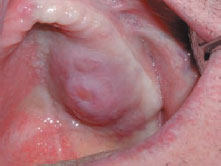
Figure 30.2 Lymphoma (from Bagan JV, Scully C. Medicina y Patoiogia Oral, 2006).
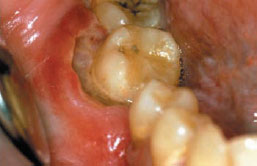
Figure 30.3a Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

Figure 30.3b Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
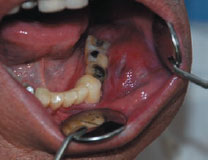
Figure 30.3c Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
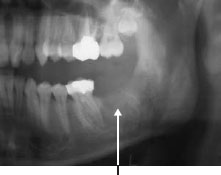
Figure 30.3d Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
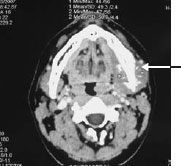
Figure 30.4 Metastasis of carcinoma.
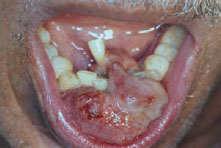
Figure 30.5 Metastasis of renal cell carcinoma.
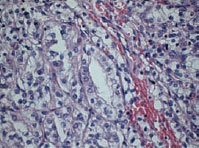
Lymphomas
Definition: Malignant neoplasm arising from lymphocytes; based on the “Revised European-American Lymphoma classification” (REAL), the WHO (2001, updated 2008) classified lymphomas in three broad groups (B, T or NK (natural killer)) according to cell type, plus less common groups e.g. Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
Prevalence (approximate): Lymphomas are rare but, with the increase in HIV disease, are becoming more common.
Age mainly affected: Young adults. However, African Burkitt lymphoma typically affects children < 12–13 years age.
Gender mainly affected: M > F.
Etiopathogenesis: Lymphomas affecting the oral cavity are mainly B-cell lymphomas. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is more common in immunosuppression/HIV and autoimmune disease and often associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV; human herpesvirus-4). Plasmablastic lymphoma (polymorphic immunoblastic B lymphoproliferative disease) is predisposed by HIV disease and may be EBV-related, as is African Burkitt lymphoma (BL).
HL affects males predominantly and may have a family history, history of EBV inf/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


