Limits of the panoramic image
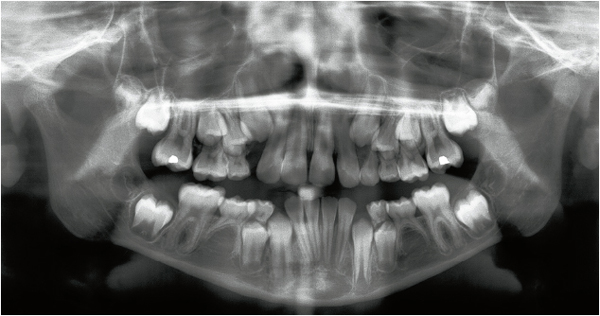
The panoramic radiograph represents a two-dimensional image of anatomic structures located in the three dimensions of space (Fig 3-1). The arrangement of these structures may therefore be assessed in the sagittal and coronal (vertical) planes. Conversely, the images do not show the buccolingual (or axial) component. Panoramic radiography is a type of curved rotating scanning tomography that uses slices of variable thickness. The slices are thicker in the posterior area of the dental arches than in the anterior area (Pajoni).
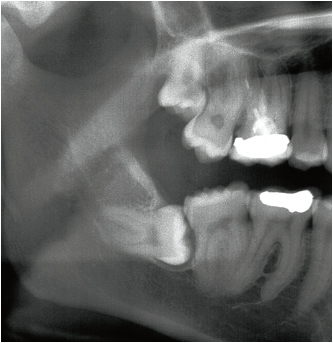
Therefore, the relationship between several superimposed anatomic components is difficult to interpret with the panoramic radiograph (Fig 3-2a).
Finally, the magnifying ratio, which may vary according to the device used, does not allow precise measurement to be made from this type of radiograph, except in the case of the Scanora.
Evaluation of the position and morphology of the third molar
Accurate interpretation of radiographs is only possible if the palatal plane is strictly horizontal. The slightest bending or extension of the patient’s head during the radiographic procedure will lead to distortions, thus making the radiographic image incomprehensible (Pajoni).
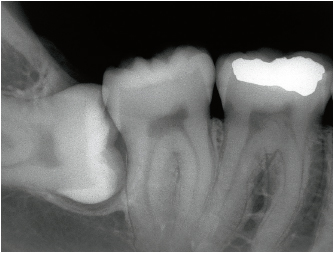
3-2b The periapical film indicates an incomplete image of the right mandibular third molar. This film cannot replace the panoramic image but it may provide additional information. The position of the crown in relation to the root of the adjacent second molar is clearly shown. The bone tissue and attachment of the periodontal ligament to the distal root are still intact.
Interpretation of the panoramic radiograph is carried out methodically in the two dimensions of space, sagittal and coronal. This analysis refers to the classifications described in chapter 4. Conversely, in the buccolingual dimension, superimposition of the roots and anatomic structures—mandibular canal and sinus—cannot be interpreted. A three-dimensional examination is often required (see below).
| Plane | Mandible | Maxilla |
|---|---|---|
| Sagittal | Inclination of the tooth Space between second molar and ramus | Inclination of the tooth Relationship with the sinus Tuberosity form |
| Vertical or coronal | Depth of the impaction | Depth of the impaction | ||
| Root morphology | • Number | Morphology of the buccal roots | ||
| • Length | ||||
| • Curve | ||||
| • Thickness of the inter-root septum | ||||
| Mandibular canal | – Distant from – Contacting – Superimposed |
Sinus inferior wall |
– Distant from – Contacting – Superimposed |
|
| Transversal or axial | Mandibular canal and roots | Superimposed structures | Sinu/> | |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses