BASIC NEUROANATOMY AND CRANIAL NERVES
Nervous Tissue
GENERAL INFORMATION
Nervous tissue is divided into 2 major cell types:
• Neurons
• Neuroglial cells (the neuroglia)
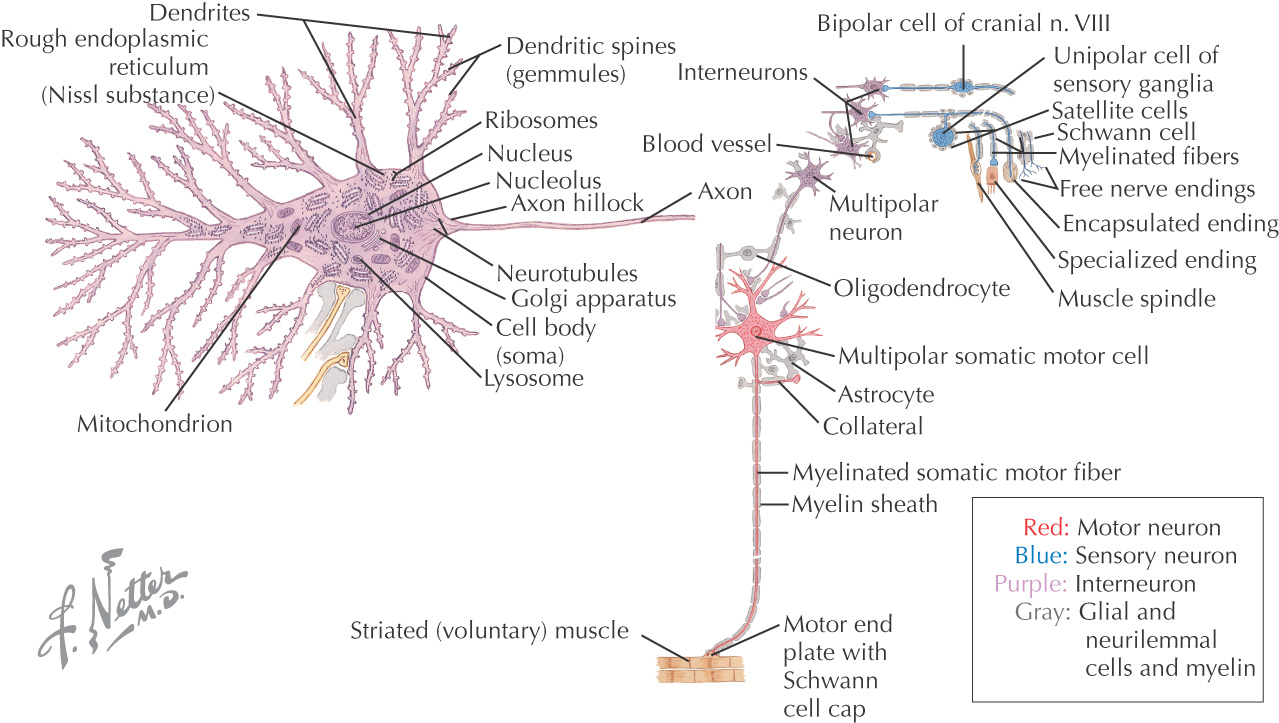
NEURONS
The structural and functional cells in the nervous system
Respond to a nervous stimulus and conduct the stimulus along the length of the cell
A neuron’s cell body is called the perikaryon, or soma
Cell bodies are classified by their location:
Neuron’s cell bodies contain typical cellular organelles within their cytoplasm:
• Nucleus
• Rough endoplasmic reticulum (Nissl substance)
Neurons have 2 types of processes that extend from the nerve cell body:
• Axon—process that carries nerve impulses away from the nerve cell body; neurons can have only 1 axon
3 major types of neurons:
• Unipolar—has only 1 process from the cell body (sensory neurons)
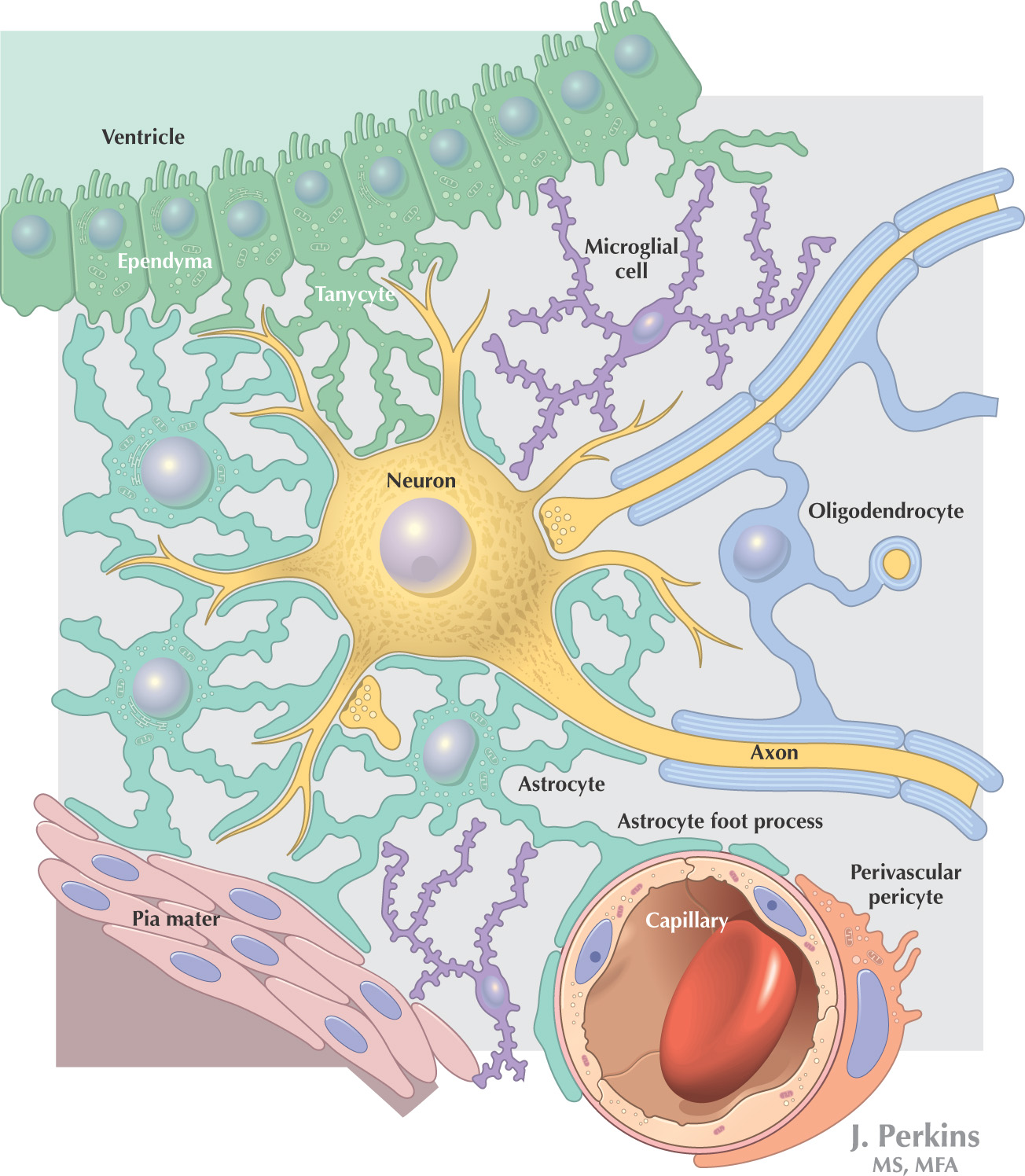
NEUROGLIA
Neuroglia is the supporting nervous tissue for neurons, although neuroglial cells also have assistive roles in neuron function
Neuroglial cells have only 1 type of process
Classification:
• Microglia—located in the central nervous system; responsible for phagocytosis to remove waste
• Satellite cells—located in the peripheral nervous system; surround the nerve cell bodies of ganglia
Central Nervous System
GENERAL INFORMATION
The central nervous system is composed of the:
• Brain
BRAIN
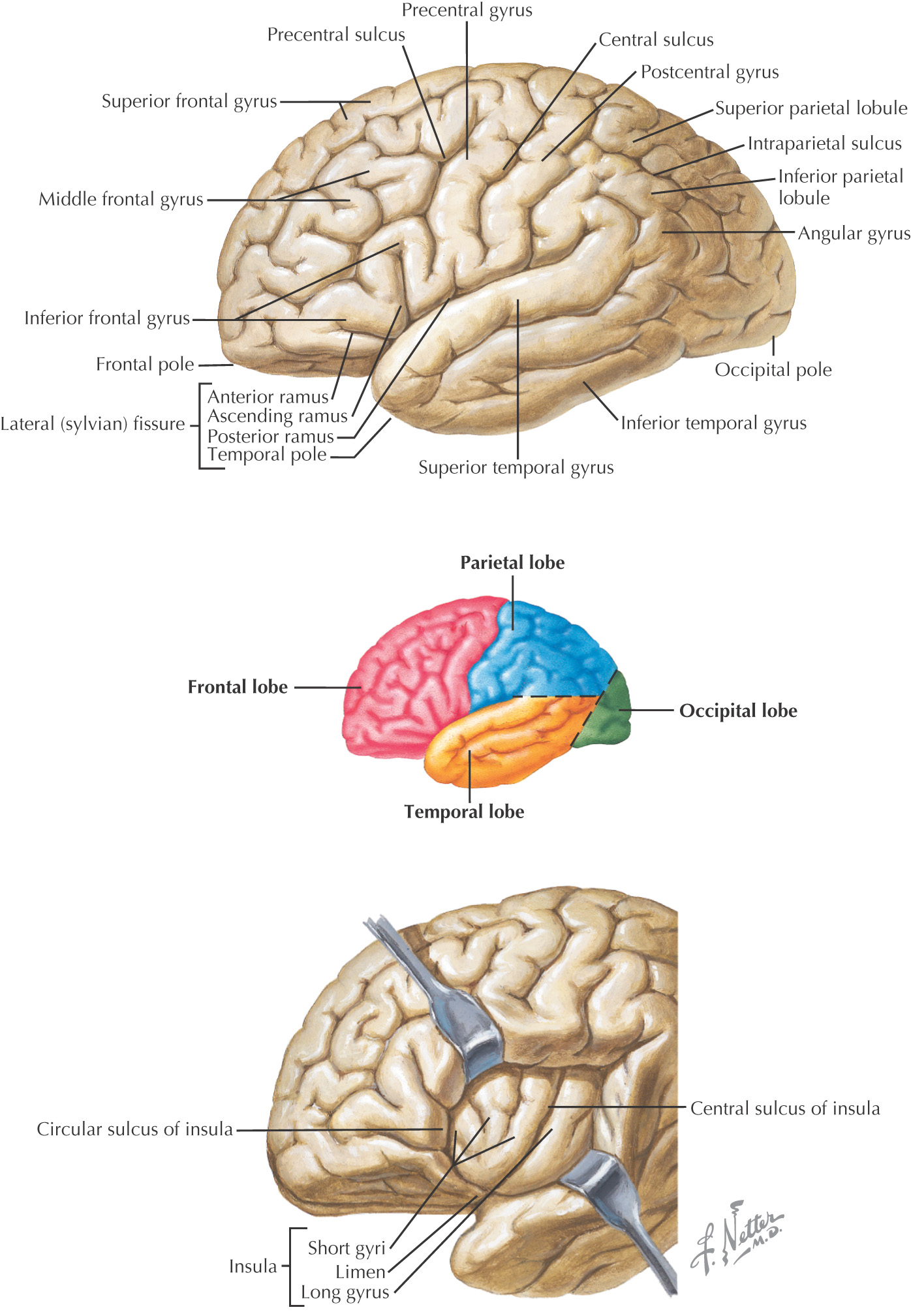
CEREBRUM
The surface of the cerebral cortex of the brain is divided by:
• Gyri (singular gyrus)—the elevations of brain tissue on the surface
• Sulci (singular sulcus)—the grooves or fissures located between the gyri
There are 3 large sulci that help divide the cerebral hemispheres into 4 of its lobes:
• Central sulcus (of Rolando)—divides frontal lobe from parietal lobe
• Lateral sulcus (of Sylvius)—divides the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe
• Parieto-occipital sulcus—divides the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe
The brain is divided into 5 lobes:
• Temporal—auditory perceptions, learning, and memory
• Insula—associated with visceral functions including taste
DIENCEPHALON
Composed of 4 parts:
• Thalamus—major relay center of the somatosensory system and parts of the motor system
• Hypothalamus—controls the autonomic nervous system and endocrine system
BRAINSTEM
Composed of 3 parts:
• Midbrain
• Pons
• Medulla
CEREBELLUM
Part of the motor system
Receives sensory input of all forms that use the deep cerebellar nuclei
Associated with:
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


