27 Swellings: Granulomatous conditions
Figure 27.1a Granulomatous cheilitis (Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome).
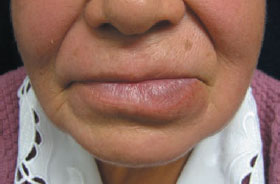
Figure 27.1b Granulomatous cheilitis (Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome).
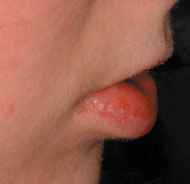
Figure 27.2 Cobblestone pattern in Crohn disease.
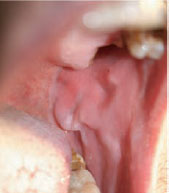
Figure 27.3 Orofacial granulomatosis.
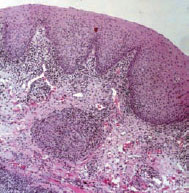
A granuloma is an organized collection of macrophages, with lymphocytes, giant cells and fibrosis, sometimes necrosis, which arises as a reaction to an antigen.
The term “granulomatous” refers to inflammatory diseases or reactions characterized by granulomas. In the mouth, these include:
- Granulomatous reactions to:
— unknown antigens (e.g. sarcoidosis, Crohn disease and orofacial granulomatosis (OFG))— foreign bodies (e.g. to silicone used as esthetic filler in lips)— infections (e.g. tuberculosis and mycoses)
- Wegener granulomatosis – a granulomatous reaction with necrotizing vasculitis, and infiltrating neutrophils, eosinophils and lymphocytes.
The term granuloma is also used in oral lesions such as pyogenic granuloma, giant cell granuloma and periapical granuloma but is then inappropriate, since none are granulomatous reactions.
Sarcoidosis
This presents with cervical lymphadenopathy, enlarged salivary glands and xerostomia. Heerfordt syndrome (salivary and lacrimal swelling, facial palsy and uveitis), mucosal nodules, gingival or labial swelling are rare. Diagnosis is by biopsy (minor salivary gland biopsy reveals granulomas in 20%), chest radiography, gallium scan, raised serum angiotensin converting enzyme (SACE) and adenosine deaminase. Management is with intralesional corticosteroids; systemic corticosteroids if lung or eye are involved.
Crohn disease and orofacial granulomatosis
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


