25 Swellings: Hereditary conditions, drug-induced swellings
Figure 25.1 Swelling diagnosis.
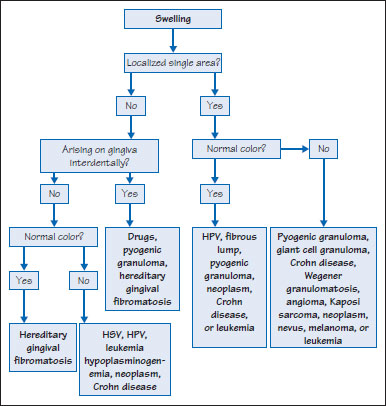
Figure 25.2 Fibrous lump.
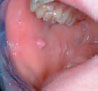
Figure 25.3 Venous malformation (cavernous hemangioma).
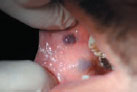
Figure 25.4 Pyogenic granuloma.
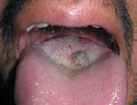
Figure 25.5 Idiopathic gingival fibromatosis.
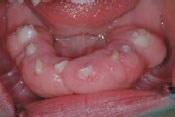
Figure 25.6 Gingival overgrowth from hydantoins.
Table 25.1 Causes of orofacial soft tissue swelling.
| Hereditary conditions | Hereditary gingival fibromatosis C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency (hereditary angioedema) | |
| Acquired conditions | Fluid accumulations | Allergic angioedema |
| Hematoma | ||
| Surgical emphysema | ||
| Traumatic edema | ||
| Inflammation | Insect bites/stings | |
| Cutaneous or oral infections | ||
| Granulomatous disorders | Crohn disease (and orofacial granulomatosis) | |
| Leprosy | ||
| Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome | ||
| Sarcoidosis | ||
| Tuberculosis | ||
| Wegener granulomatosis | ||
| Drug-induced and other reactive lesions | Denture-induced hyperplasia | |
| Drug-induced swelling | ||
| Fibrous lumps | ||
| Giant cell lesions | ||
| Pyogenic granulomas | ||
| Cysts, hamartomas and neoplasms | Angiomas | |
| Lymphangiomas | ||
| Various cysts | ||
| Various neoplasms | ||
| Foreign bodies | Any | |
| Endocrine, metabolic and deposits | Acromegaly | |
| Amyloidosis | ||
| Myxedema | ||
| Nephrotic syndrome | ||
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


