Basics of Radiation Physics
Pioneers in Dental Radiology
Wilhelm Conrad Röentgen (1845–1923)
Publications on X-rays
1. ‘On a New Kind of Rays, A Preliminary Communication’. Journal of Würzburg Physical-Medical Society, December 28, 1985.
2. ‘On a New Kind of Rays, Continued’. Journal of Würzburg Physical-Medical Society, March 9, 1896.
3. ‘Further Observations on a New Kind of Rays’. Journal of Prussian Academy of Science, March 10, 1897.
William Herbert Rollins (1852–1929)
William Herbert Rollins was an American scientist and dentist. He was a pioneer in radiation protection and is known as the father of radiation protection. It is believed that he had published over 200 scientific articles regarding the hazards of radiation. Rollins, although a practicing dentist, also had a medical degree from Harvard Medical School. He called X-rays ‘X-light’ and documented them extensively in 1904. He is called the ‘Forgotten Man’ of dentistry. William Rollins proposed the use of filters to remove the low energy X-rays from the primary beam and introduced collimation. He recommended a long targetfilm distance to improve image quality. He pioneered the sandwiching of the X-ray film between two intensifying screens to increase the film speed. Dr Rollins advocated the need to determine a safe and harmless dose of radiation. In 1901, he advocated the use of leaded glasses for radiation personnel and a lead shield to cover all areas on the patient’s body that were not being imaged. Rollins also felt the need to construct a lead hood that would cover the X-ray tube head.
Fundamentals of Radiation Physics
Radiation
Radiation is the transmission of energy through space and matter. There are two basic forms of radiation, namely, particulate radiation and electromagnetic radiation.
Electromagnetic Radiation
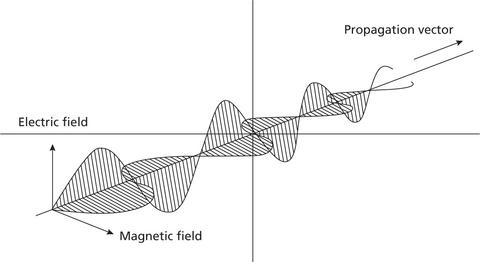
There are two concepts to understand electromagnetic radiation, namely, classical theory and modern quantum theory. According to the classical theory, the flow of energy at the universal speed of light through free space or through a material medium is in the form of the electric and magnetic fields that make up electromagnetic waves such as radio waves, visible light, and gamma rays. In such a wave, time-varying electric and magnetic fields are mutually linked with each other at right angles and perpendicular to the direction of motion (Figure 1).
Ionizing and Non-ionizing Radiation
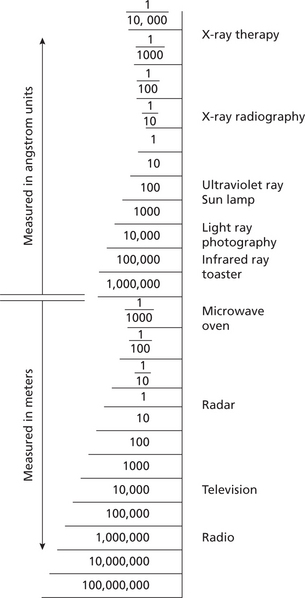
Radiation has a wide range of energies that form the electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 2). The spectrum has two major divisions:
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses