2 Unerupted upper central incisor
Summary
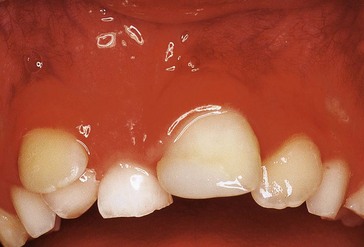
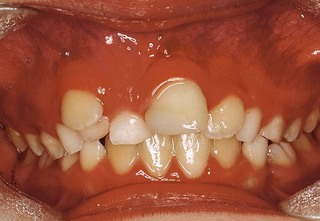
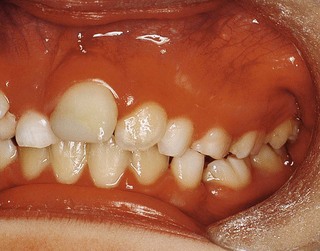
Neil, a 9-year-old boy, presents with 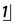 unerupted (Fig. 2.1). What are the possible causes and how would you manage the problem?
unerupted (Fig. 2.1). What are the possible causes and how would you manage the problem?
Examination
Intraoral examination
 Why are the centrelines displaced?
Why are the centrelines displaced?
The lower centreline shift is due to early unbalanced loss of 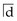 in a potentially crowded arch.
in a potentially crowded arch.
 What are the possible causes of the unerupted
What are the possible causes of the unerupted 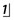 ?
?
 How would you rate the likelihood in this case of each of the potential causes of unerupted
How would you rate the likelihood in this case of each of the potential causes of unerupted 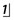 listed in Box 2.1?
listed in Box 2.1?
Congenital absence of 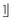 is highly unlikely. It would be very rare for
is highly unlikely. It would be very rare for 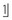 to be absent without other congenitally missing teeth.
to be absent without other congenitally missing teeth.
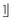 is highly unlikely. It would be very rare for
is highly unlikely. It would be very rare for 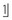 to be absent without other congenitally missing teeth.
to be absent without other congenitally missing teeth.Ectopic position of the tooth germ is a possibility but is more likely to be secondary to some pathological cause or the presence of a supernumerary tooth.
Dilaceration and/or displacement due to trauma can be excluded due to the absence of a relevant history.
A supernumerary tooth (Box 2.2) is the most likely cause of unerupted 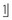 . With an incidence of 1–3% in the premaxilla, supernumerary teeth (particularly the late-forming tuberculate type) are associated with delay or non-eruption of an upper permanent central incisor.
. With an incidence of 1–3% in the premaxilla, supernumerary teeth (particularly the late-forming tuberculate type) are associated with delay or non-eruption of an upper permanent central incisor.
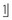 . With an incidence of 1–3% in the premaxilla, supernumerary teeth (particularly the late-forming tuberculate type) are associated with delay or non-eruption of an upper permanent central incisor.
. With an incidence of 1–3% in the premaxilla, supernumerary teeth (particularly the late-forming tuberculate type) are associated with delay or non-eruption of an upper permanent central incisor.Crowding is an unlikely cause. Although the upper labial segment is crowded, only very severe crowding would prevent 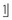 erupting 2 years following its expected eruption time.
erupting 2 years following its expected eruption time.
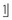 erupting 2 years following its expected eruption time.
erupting 2 years following its expected eruption time.Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 as he is 9 years old and the tooth has not yet appeared;
as he is 9 years old and the tooth has not yet appeared;  is also erupting over
is also erupting over  and she dislikes the appearance.
and she dislikes the appearance.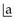 was lost at about 6 years and
was lost at about 6 years and 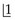 erupted normally at 6.5 years. Unfortunately, Neil fell over while playing soccer with his class team 4 months ago and fractured
erupted normally at 6.5 years. Unfortunately, Neil fell over while playing soccer with his class team 4 months ago and fractured 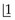 , exposing the pulp, which was treated by a coronal pulpotomy and placement of calcium hydroxide.
, exposing the pulp, which was treated by a coronal pulpotomy and placement of calcium hydroxide.
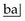 .
.
 .
. present.
present. , which also appears to be darker than the other incisors.
, which also appears to be darker than the other incisors.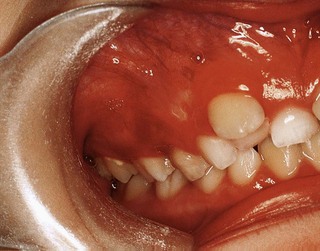
 is considerably smaller than an
is considerably smaller than an  ) has promoted the upper centreline shift, but this has been aggravated by inherent upper arch crowding.
) has promoted the upper centreline shift, but this has been aggravated by inherent upper arch crowding.
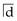 , the lower centreline should have been monitored at review visits.
, the lower centreline should have been monitored at review visits. 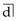 should have been extracted to balance for loss of
should have been extracted to balance for loss of 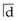 when the centreline appeared to be migrating.
when the centreline appeared to be migrating. can be excluded as there is no history of
can be excluded as there is no history of  having erupted or of incisor trauma.
having erupted or of incisor trauma. can be excluded also.
can be excluded also. , a supernumerary or odontome. Other rarer lesions would need to be excluded.
, a supernumerary or odontome. Other rarer lesions would need to be excluded. and may produce no effect, a median diastema, incisor rotation or failure of
and may produce no effect, a median diastema, incisor rotation or failure of 