6 Palatal canines
Summary
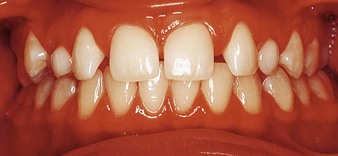
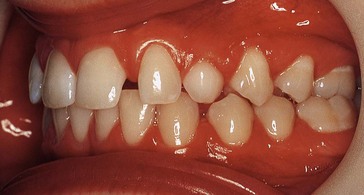
Diane, a 15-year-old girl, presents with both upper primary canines retained (Fig. 6.1). What is the cause and what treatment possibilities are there?
Examination
Intraoral
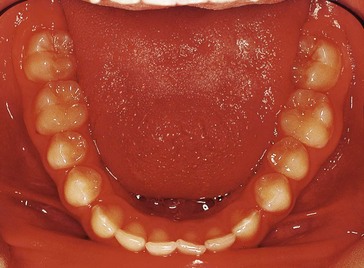
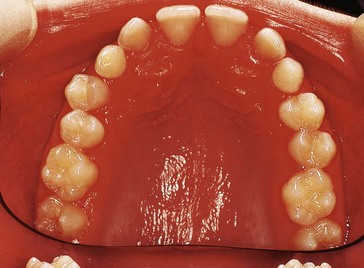
 The intraoral views are shown in Figures 6.1 and 6.2. Describe what you see.
The intraoral views are shown in Figures 6.1 and 6.2. Describe what you see.
Oral hygiene is fair with mild marginal gingival erythema related to 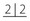 and the upper left buccal segment teeth.
and the upper left buccal segment teeth.
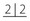 and the upper left buccal segment teeth.
and the upper left buccal segment teeth.No obvious buccal swellings in the c areas but there seem to be mucosal swellings palatal to  , perhaps indicating the position of unerupted 3’s.
, perhaps indicating the position of unerupted 3’s.
 , perhaps indicating the position of unerupted 3’s.
, perhaps indicating the position of unerupted 3’s.Mild lower labial segment crowding;  very slightly mesiolingually rotated; lower buccal segments spaced.
very slightly mesiolingually rotated; lower buccal segments spaced.
 very slightly mesiolingually rotated; lower buccal segments spaced.
very slightly mesiolingually rotated; lower buccal segments spaced.Class I incisor relationship with a centreline shift (clinically the lower centreline was 1.5 mm to the left).
 What factors are implicated in maxillary canine ectopia?
What factors are implicated in maxillary canine ectopia?
1 Genetic – palatally displaced 3 appears to result from a polygenic multifactorial mode of inheritance, with associated anomalies including incisor-premolar hypodontia and peg-shaped 2 (see below). Class II division 2 malocclusion is also associated with an increased incidence of palatal 3.
2 Crypt displacement – where the position of 3 is grossly displaced, this may be an aetiological factor.
4 Arch length discrepancy – palatal displacement of 3’s has been mostly associated with an uncrowded or spaced arch. Note the spacing present in Diane’s upper arch.
5 Trauma to the maxillary anterior area at an early stage of development – this has been suggested but there is no history of trauma in this case.
6 Peg-shaped, short-rooted 2’s or absent 2’s – guidance for 3 is reduced where these features are evident, doubling the incidence of palatal impaction of 3.
Quick-check method
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 is also slightly loose and she is worried in case it is lost, producing a big space.
is also slightly loose and she is worried in case it is lost, producing a big space. areas and all other primary teeth were lost naturally. All permanent teeth have erupted on schedule.
areas and all other primary teeth were lost naturally. All permanent teeth have erupted on schedule. has been loose intermittently for the past 18 months. It does not appear to have got looser in recent months. Diane is very keen to improve the appearance of her upper teeth.
has been loose intermittently for the past 18 months. It does not appear to have got looser in recent months. Diane is very keen to improve the appearance of her upper teeth.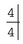 .
.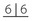 .
. erupted.
erupted.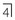 with
with 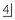 ; buccal crossbite of
; buccal crossbite of 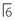 with
with 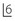 .
.

 ’s, indicating that
’s, indicating that 
 How would you assess for a TSD?
How would you assess for a TSD?
