Chapter 2 Periodontal disease
Susceptibility to periodontal disease
Susceptibility of an individual patient is determined by relating three things:
A young patient with severe disease whose plaque control is good would be regarded as having a high susceptibility whilst an elderly patient with poor plaque control and little evidence of disease would be regarded as having a low susceptibility. Susceptibility is thus a very individual concept relating to each patient. It must be appreciated that a patient’s innate susceptibility cannot be changed as this is partly genetically determined. Recognition of this has led to the realization that risk recognition and control forms an essential part of periodontal management, particularly in patients with higher susceptibility.
The concept of risk
Risk recognition begins at the stage of taking thorough histories from patients.
Taking histories from patients with periodontal disease
Medical history
This serves three main functions:
Dental history
Assessment of periodontal disease
The clinical assessment
The basic periodontal examination (BPE)
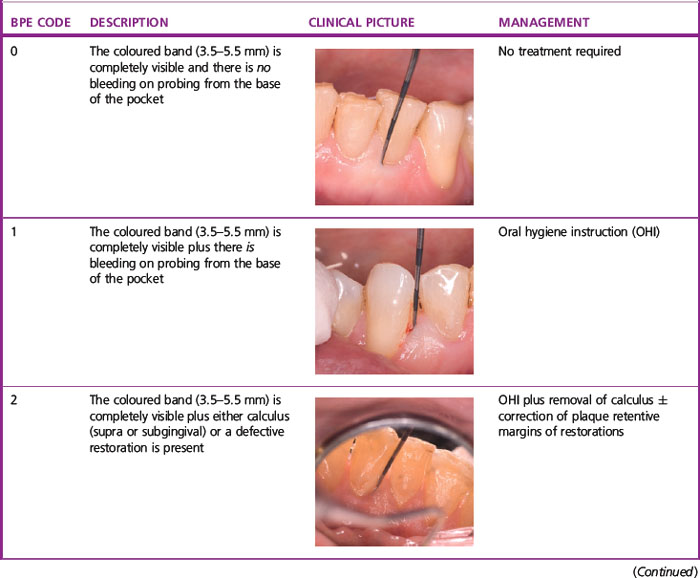
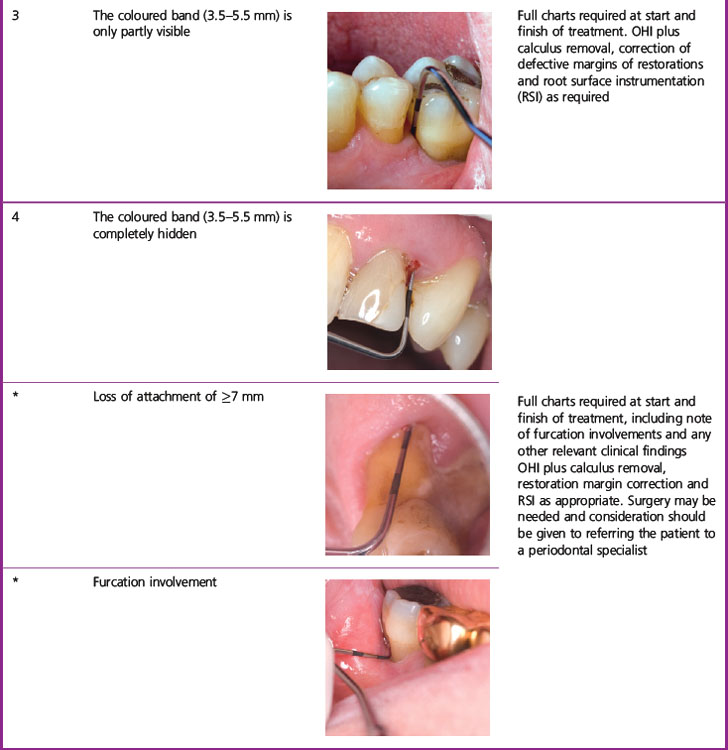
The BPE (Table 2.1) is a screening tool to enable practitioners to determine whether or not their patient has significant periodontal disease. This examination should be used to screen:
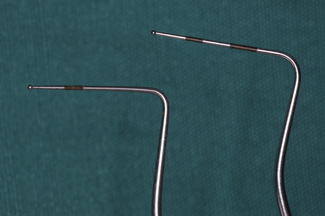
The BPE can only be performed using a WHO probe and the probing force applied should be 20–25 g. There are two common variants of the WHO probe in use: the WHO-E (epidemiological) type probe and the WHO-C (clinical) type probe (Figure 2.1). The key elements to note on each are a ball-shaped probe tip of diameter 0.5 mm and a coloured band extending from 3.5 to 5.5 mm. The WHO-C probe has, in addition, a second coloured band extending from 8.5 to 11.5 mm.
To carry out a BPE, the dentition is divided into sextants (first premolar to second molar and canine to canine). The probe tip is gently placed in the base of the gingival crevice/pocket and ‘walked’ around all the teeth in the entire sextant. One code is assigned per sextant and this is the highest encountered anywhere within it. Table 2.1 shows the criteria used for assigning the BPE codes and the corresponding management for each sextant.
| X | 4 | 3 |
| * | 1 | 2 |
As with any system, the BPE has both advantages and disadvantages (Table 2.2) and the reader should be aware of these if the system is to be correctly applied and interpreted.
Table 2.2 Advantages and disadvantages of the BPE
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses