OSTEOLOGY
Overview
GENERAL INFORMATION
Most complicated bony structure in the human body
The complete bony framework of the head; includes the mandible
28 individual bones make up the skull:
• 11 are paired
• 6 are single
Wormian bones, or sutural bones, are irregularly shaped small bones found along sutures that occur naturally
FUNCTIONS
Most important function: to protect the brain
Also protects the 5 organs of special sense:
• Vision
• Taste
DIVISIONS
Two major ways to divide the bones of the skull:
• Regional
Regionally, the skull is divided into the mandible (lower jaw) and cranium (skull without the mandible)
Cranium is further divided into:
• Cranial vault–upper portion of the skull
• Cranial base–inferior portion of the skull
• Cranial cavity–interior of the skull
• Facial skeleton–bones that make up the face
• Acoustic skeleton–ear ossicles
Developmentally, the skull is divided into:
• Viscerocranium–the portion of the skull related to the digestive and respiratory systems
• Neurocranium–the portion of the skull that protects the brain and the 5 organs of special sense
Cranial cavity divisions:
• Anterior cranial fossa–contains the frontal lobe of the brain
• Middle cranial fossa–contains the temporal lobe of the brain
• Posterior cranial fossa–contains the cerebellum
Skull is depicted by observing it from 5 views:
• Norma frontalis–the anterior view
• Norma lateralis–the lateral view
• Norma occipitalis–the posterior view
• Norma basalis–the inferior view
• Norma verticalis–the superior view
ARTICULATIONS
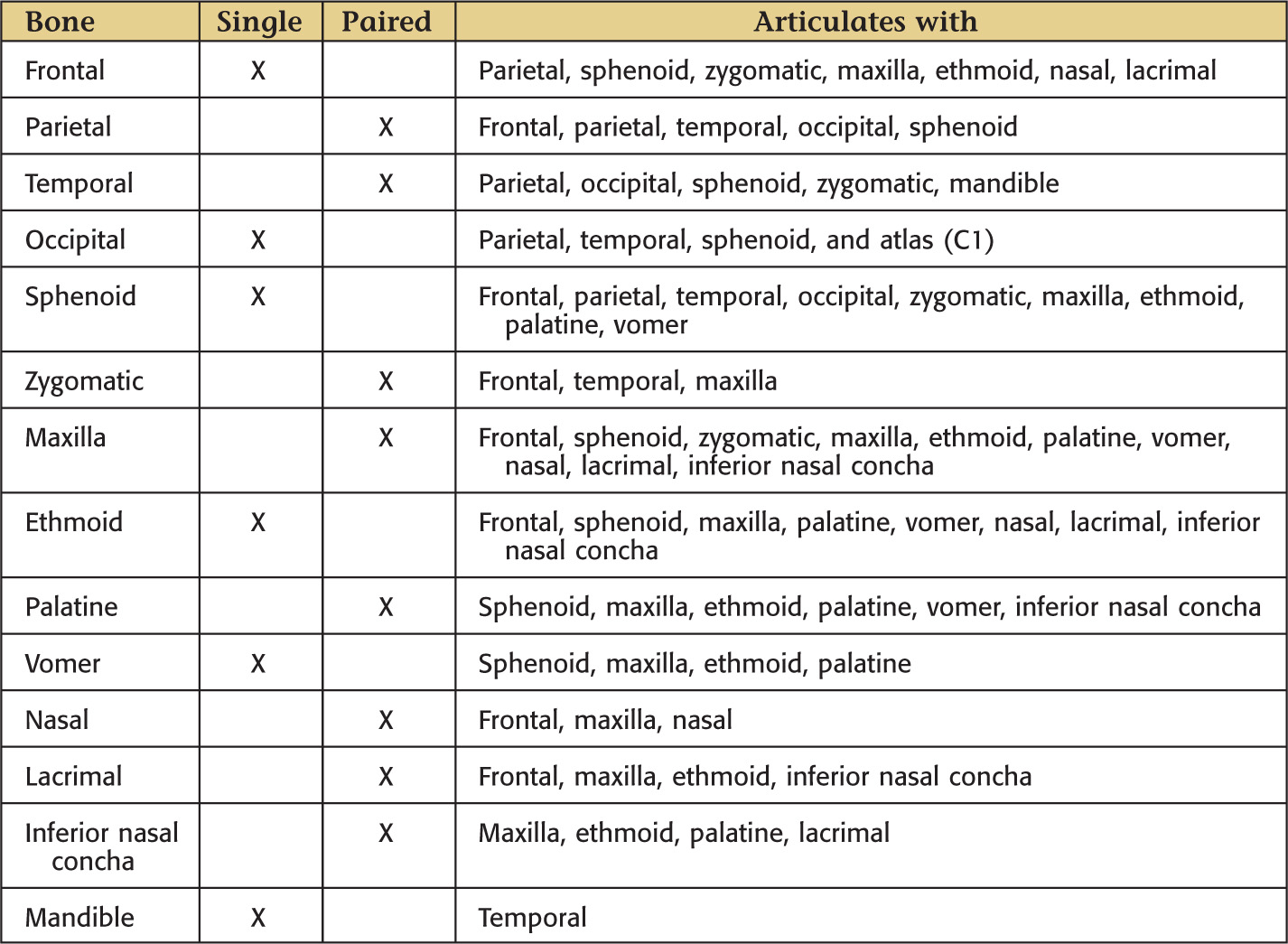
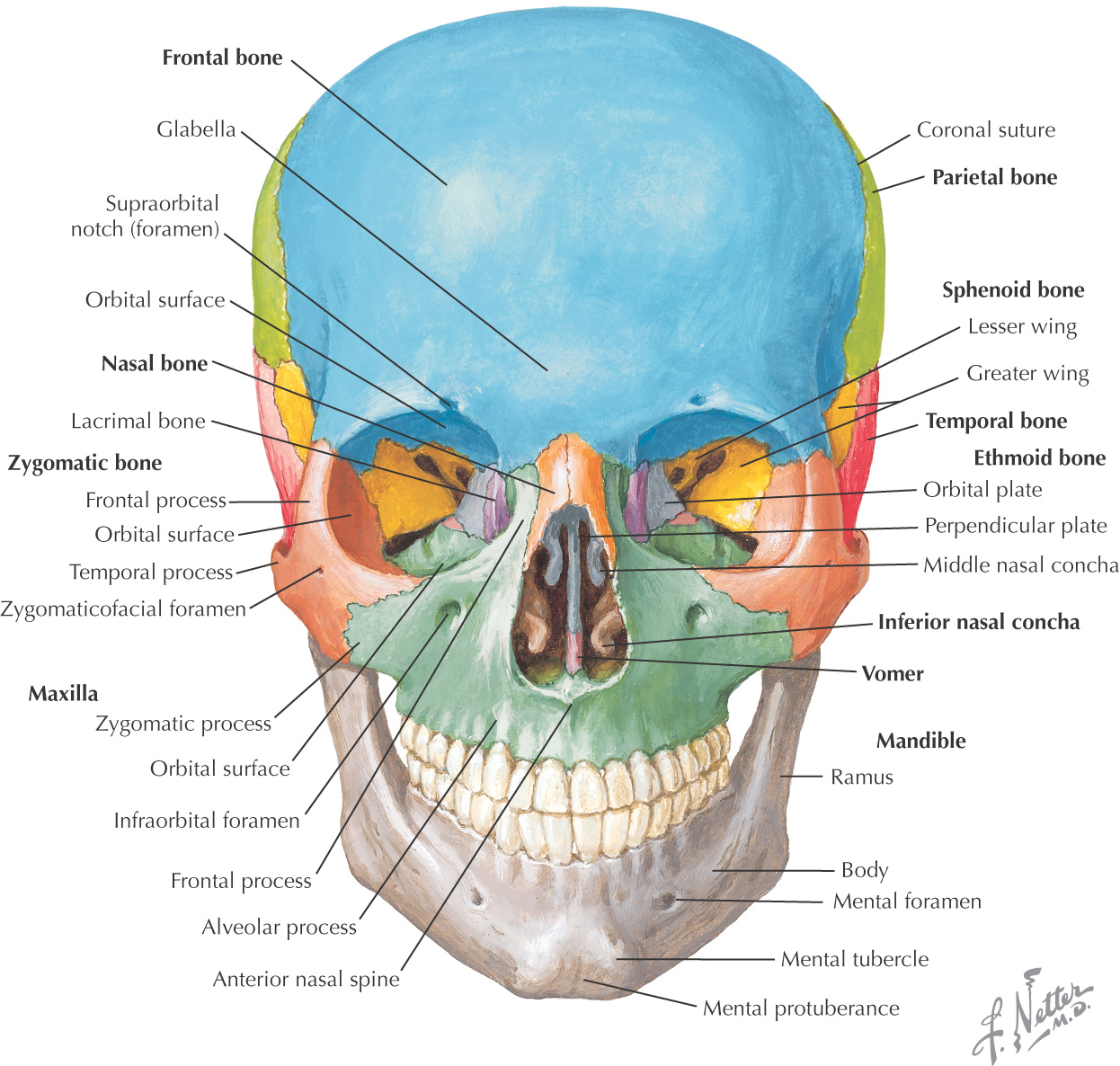
Bones of the Skull
FRONTAL BONE
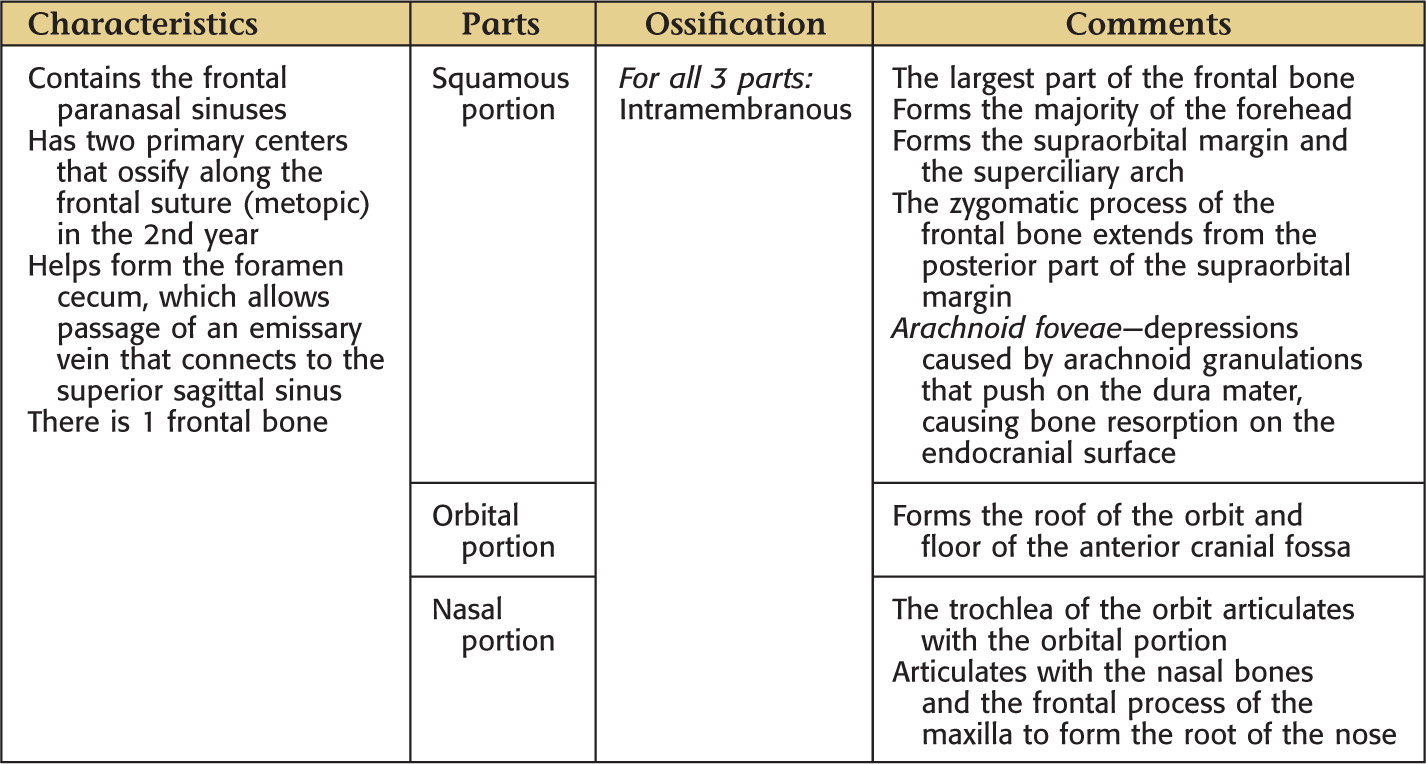
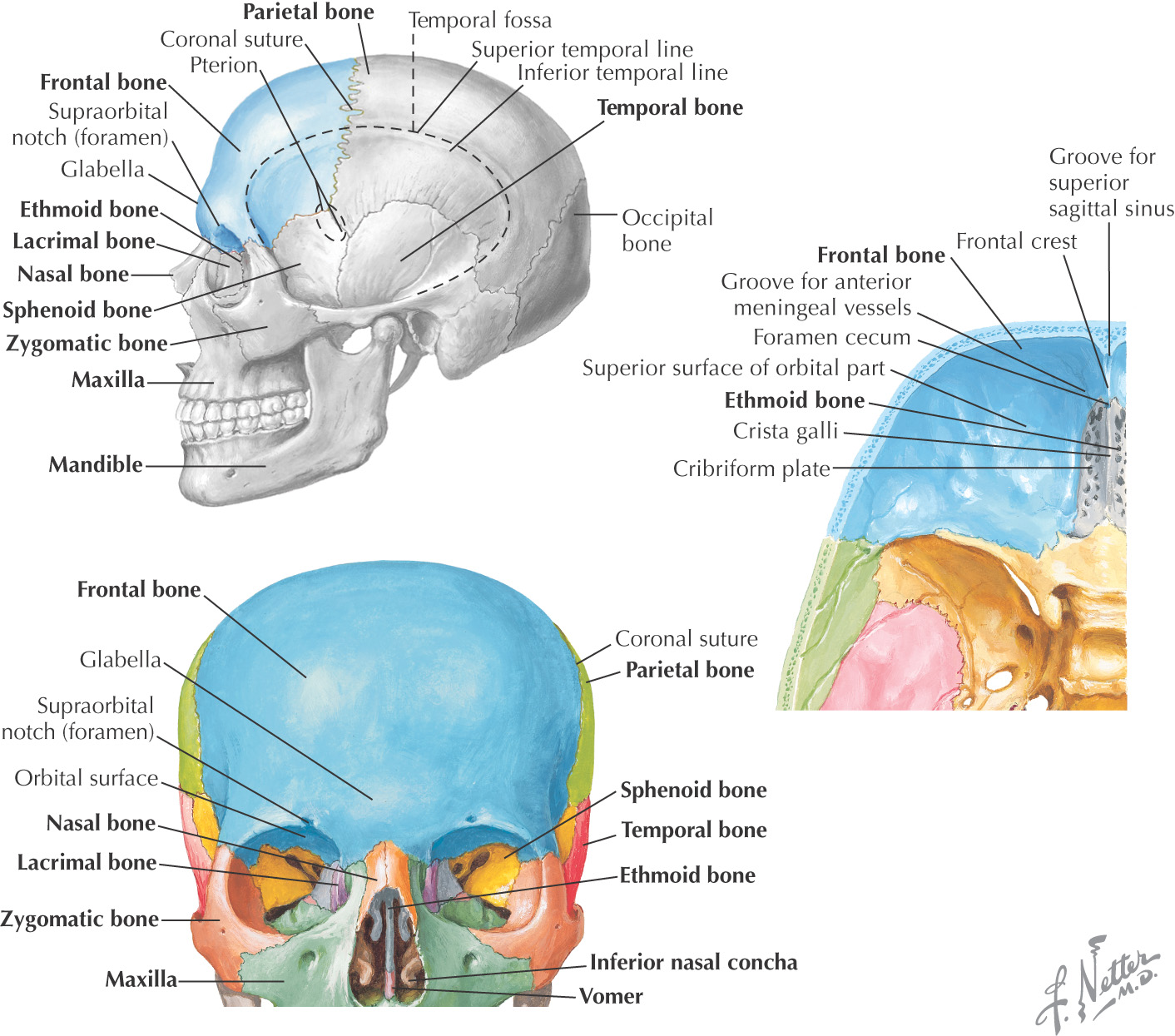
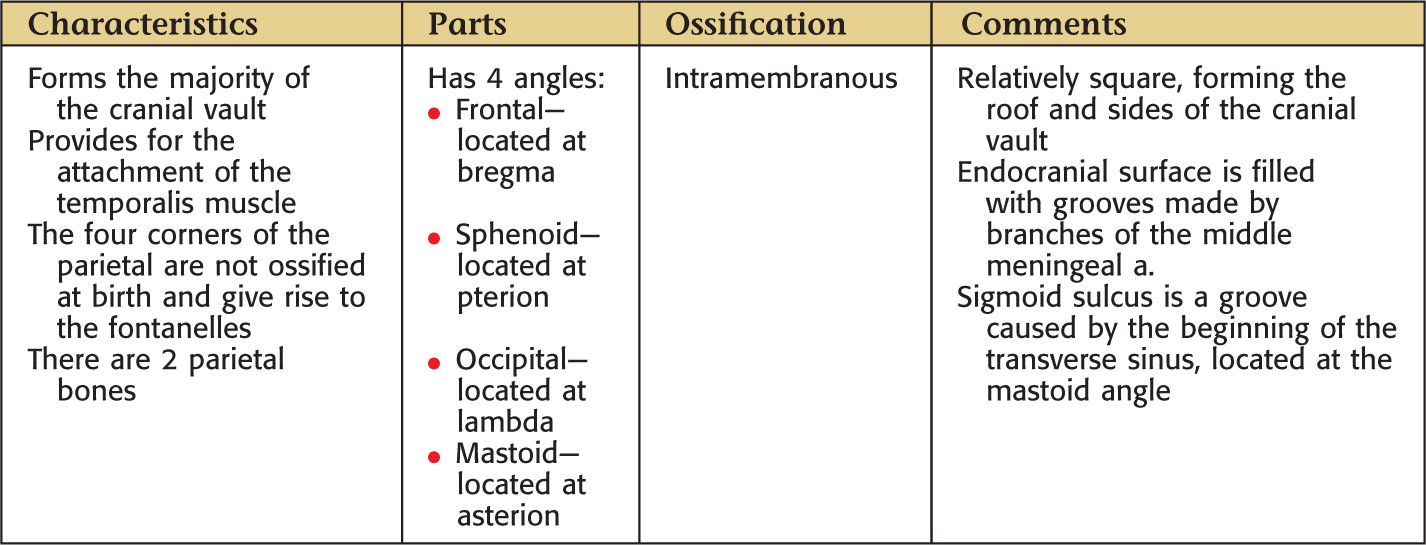
PARIETAL BONE
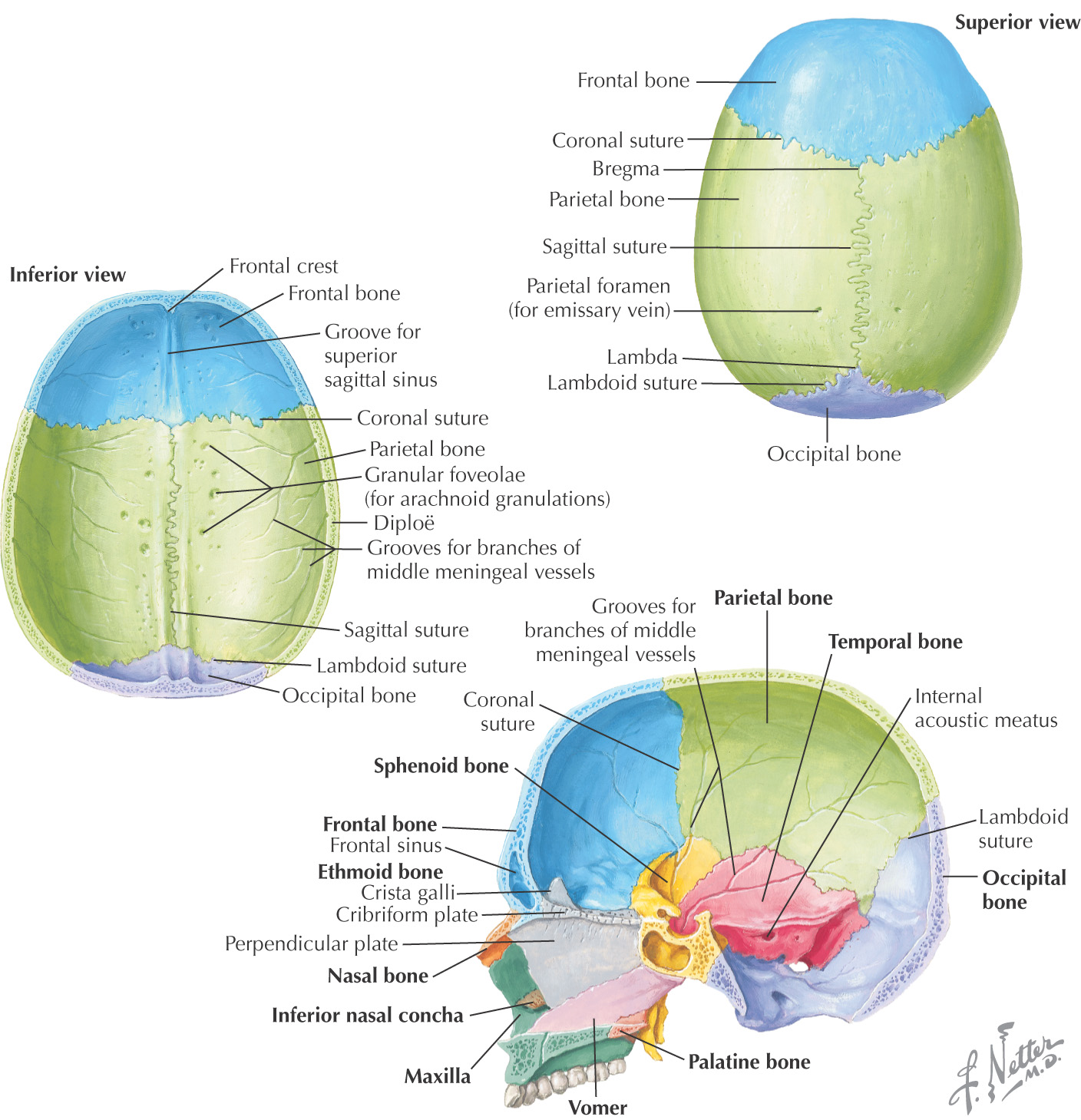
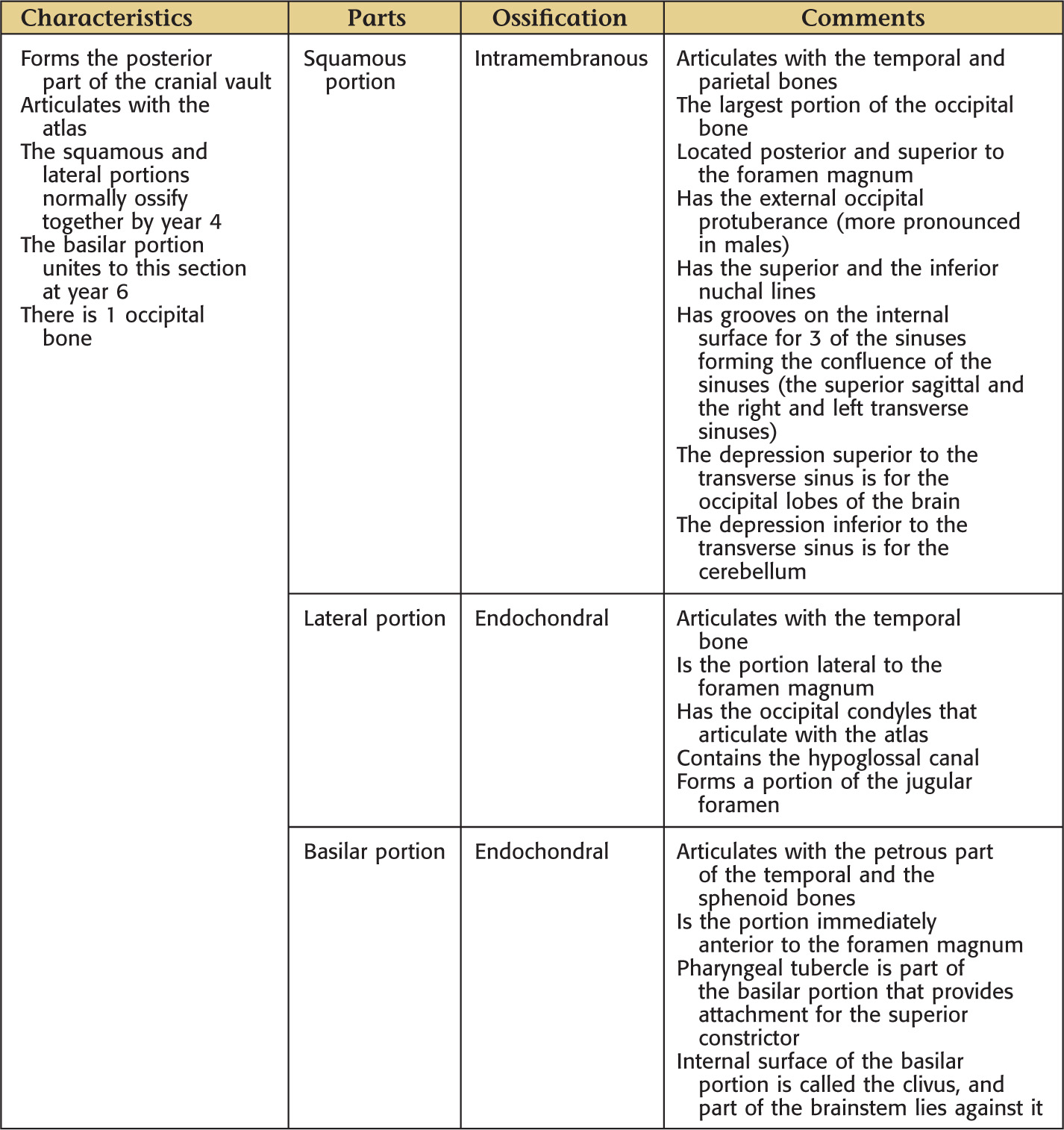
OCCIPITAL BONE
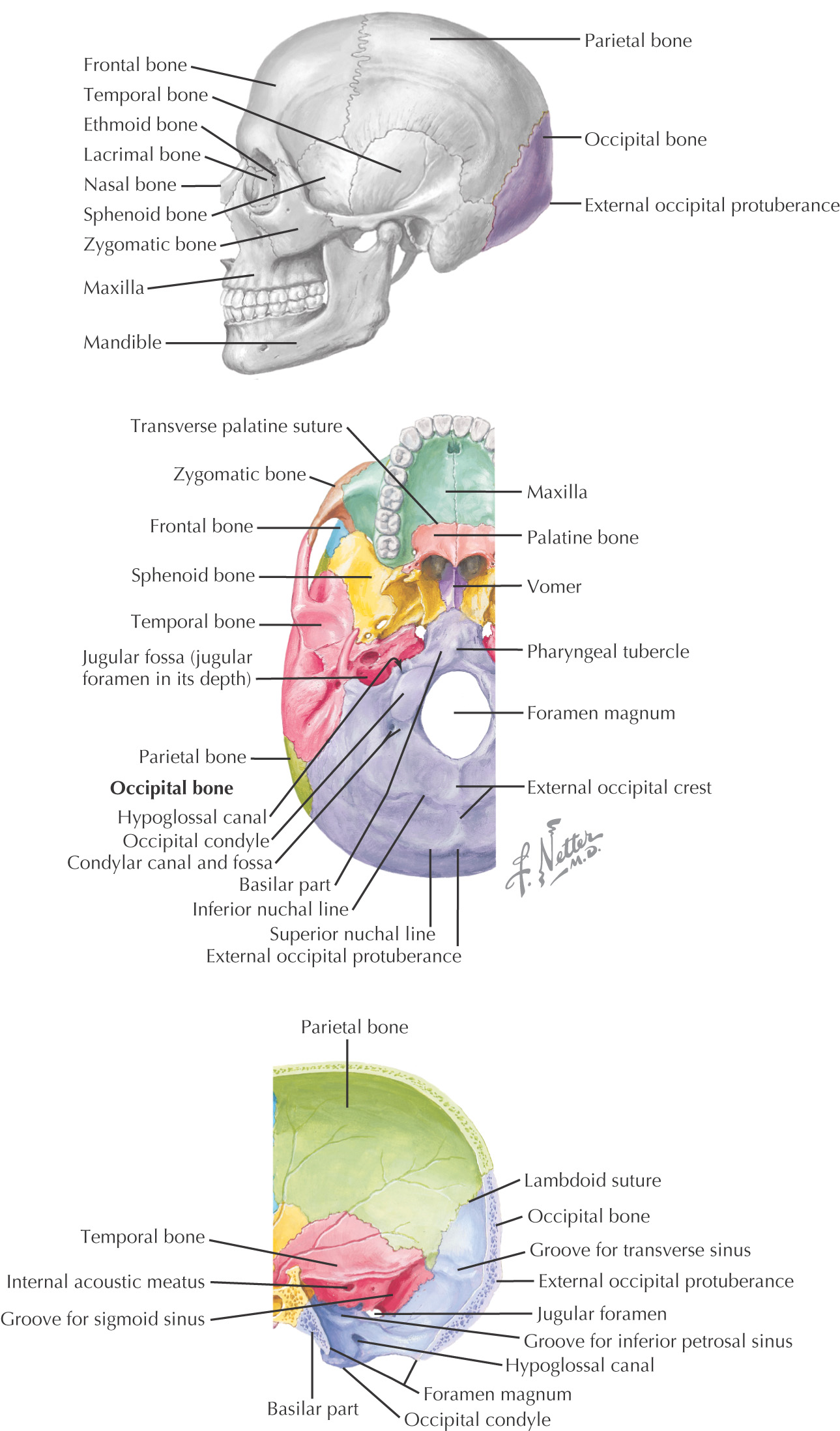
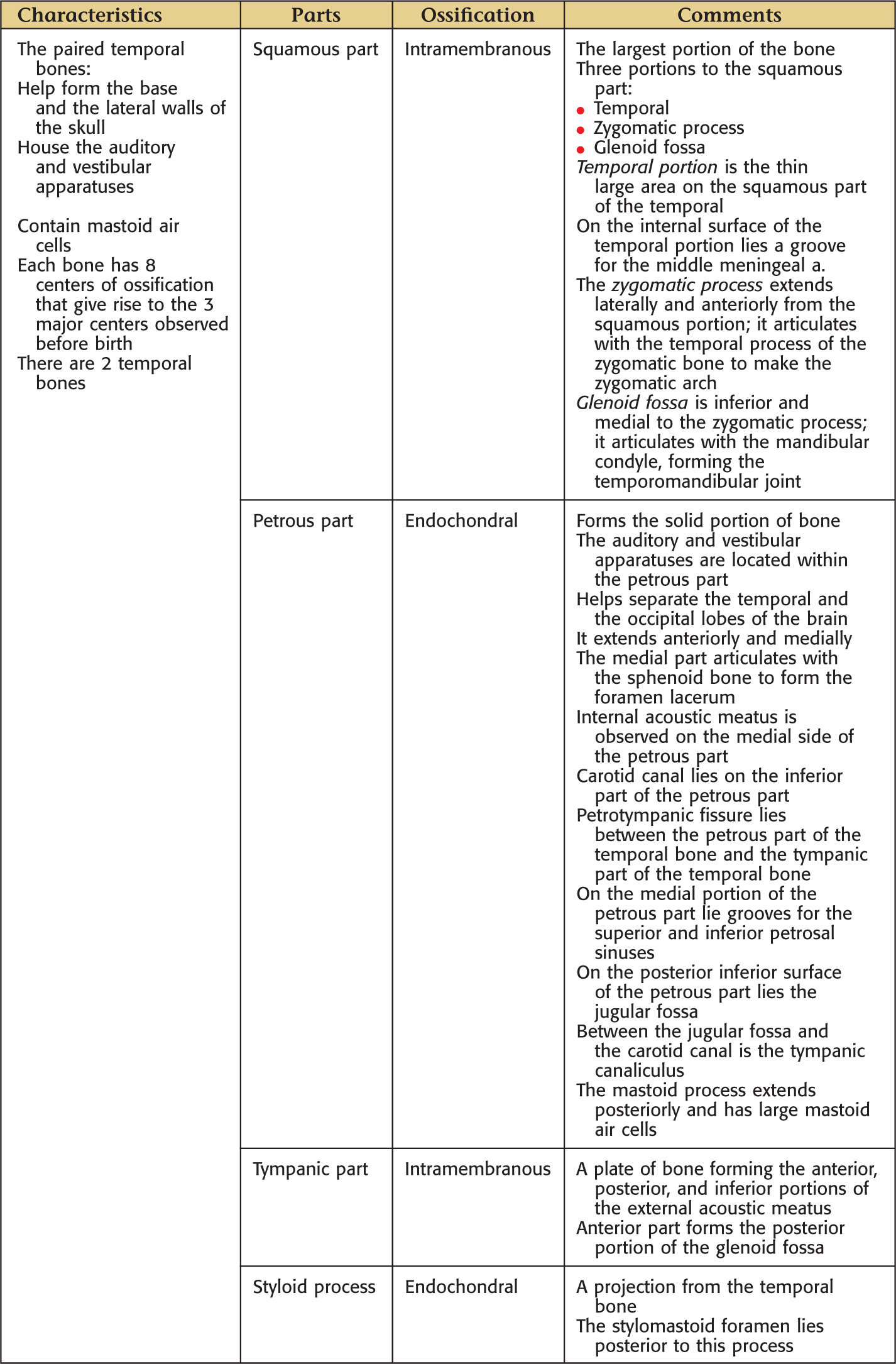
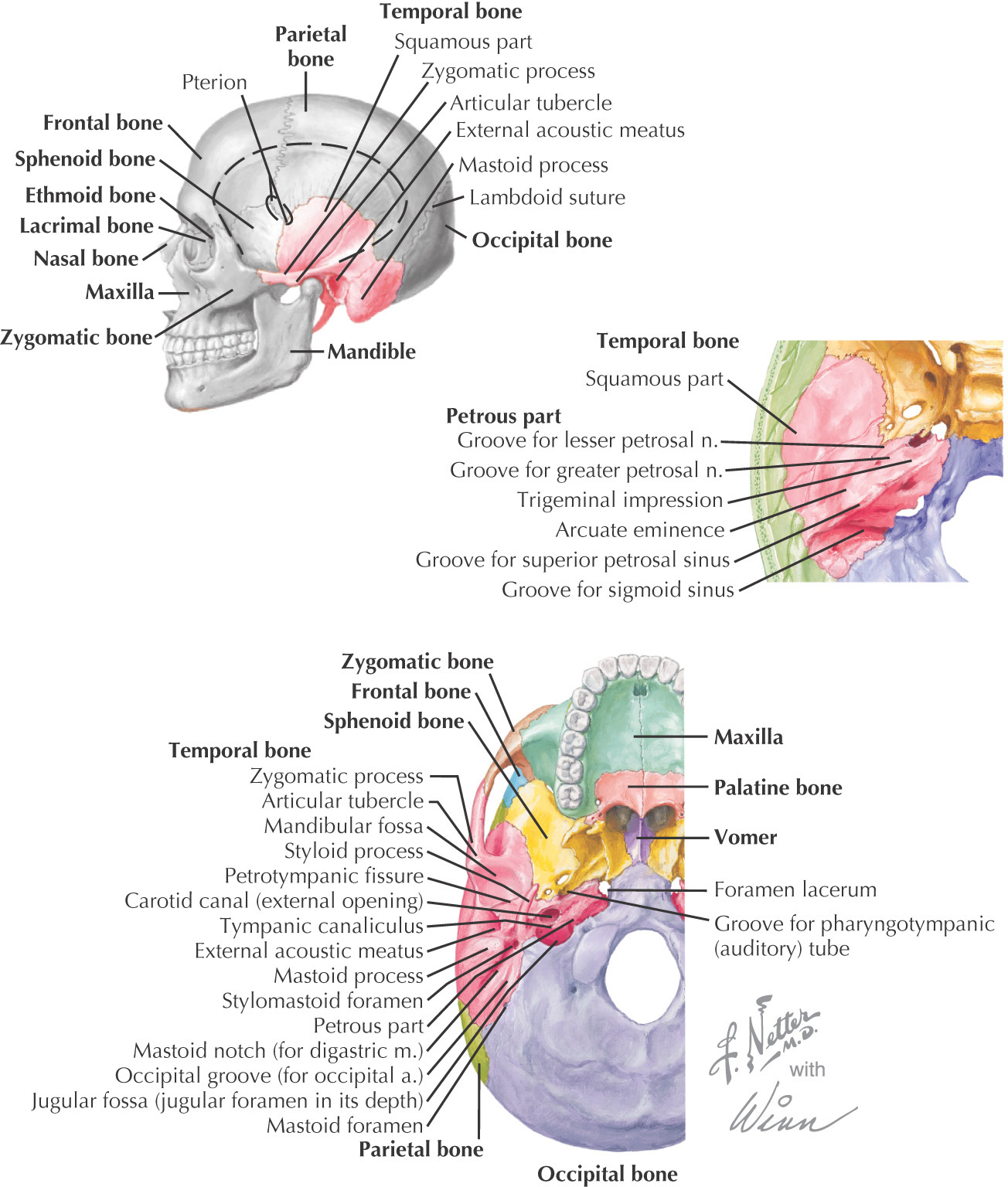
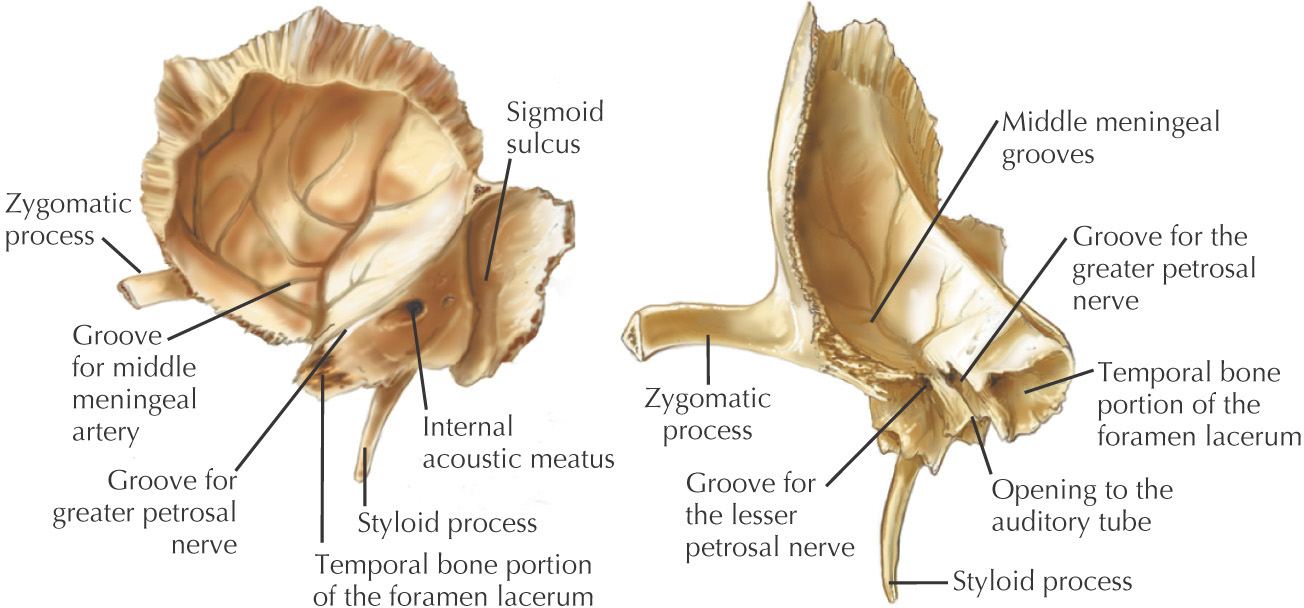
TEMPORAL BONE
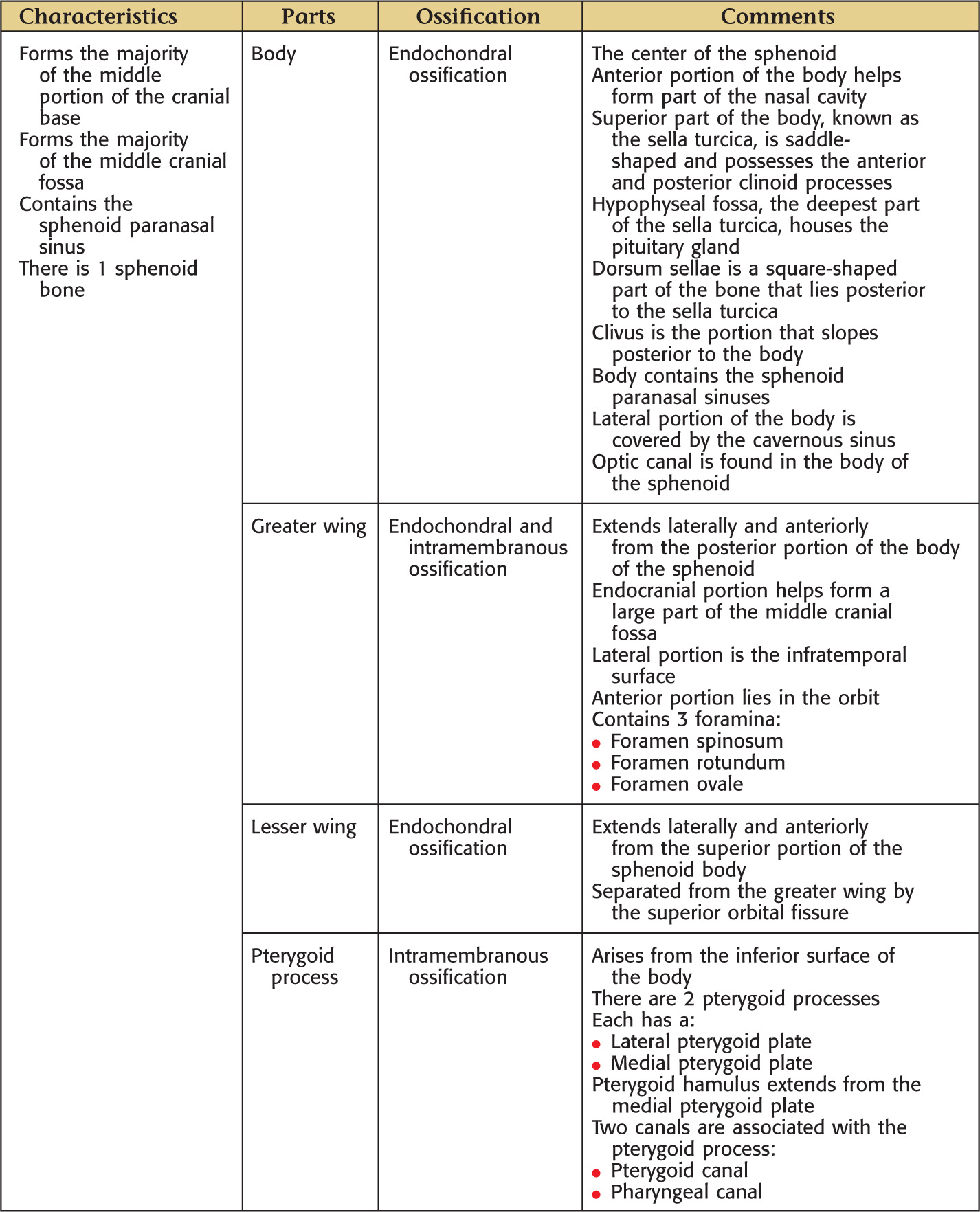
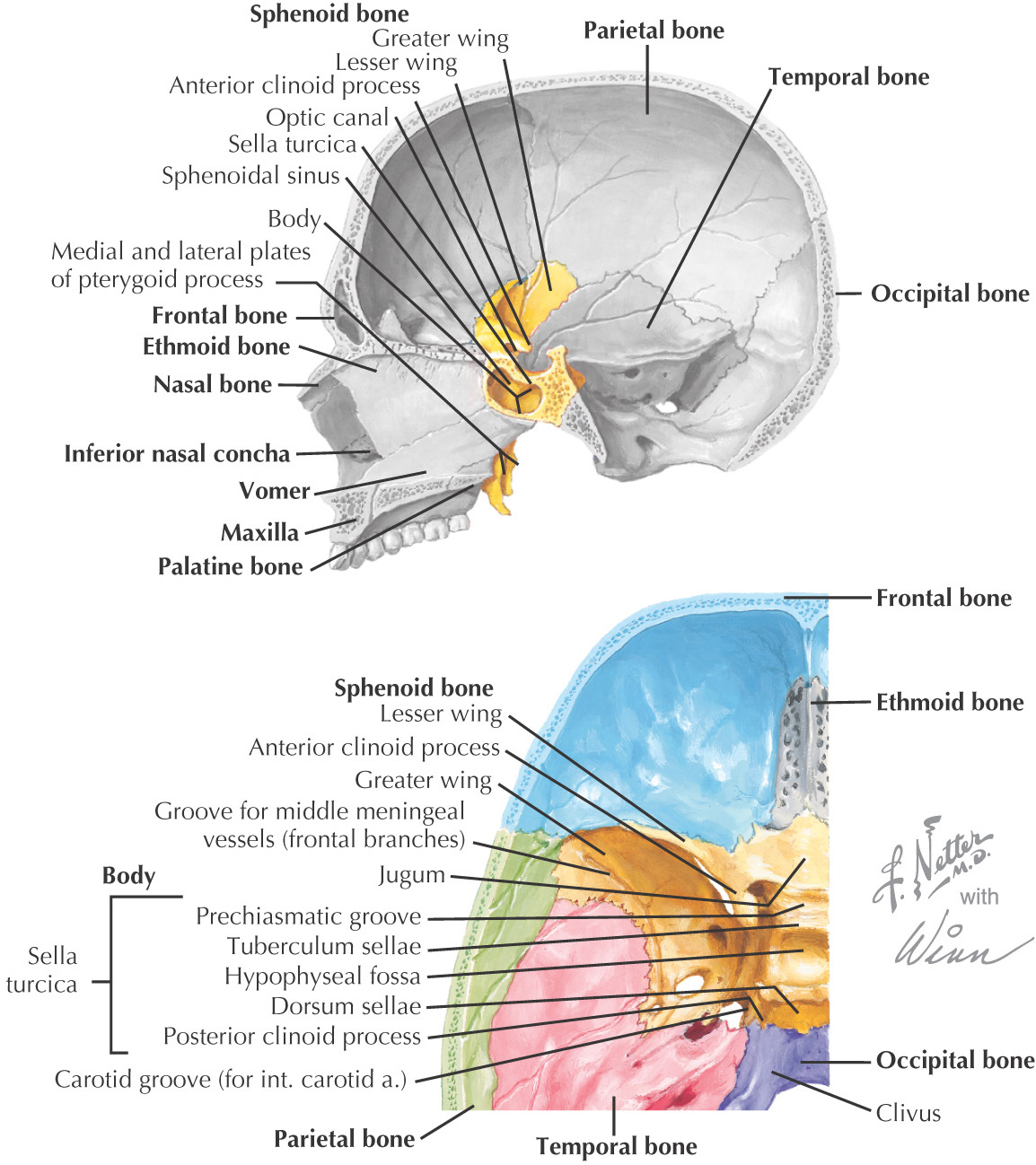
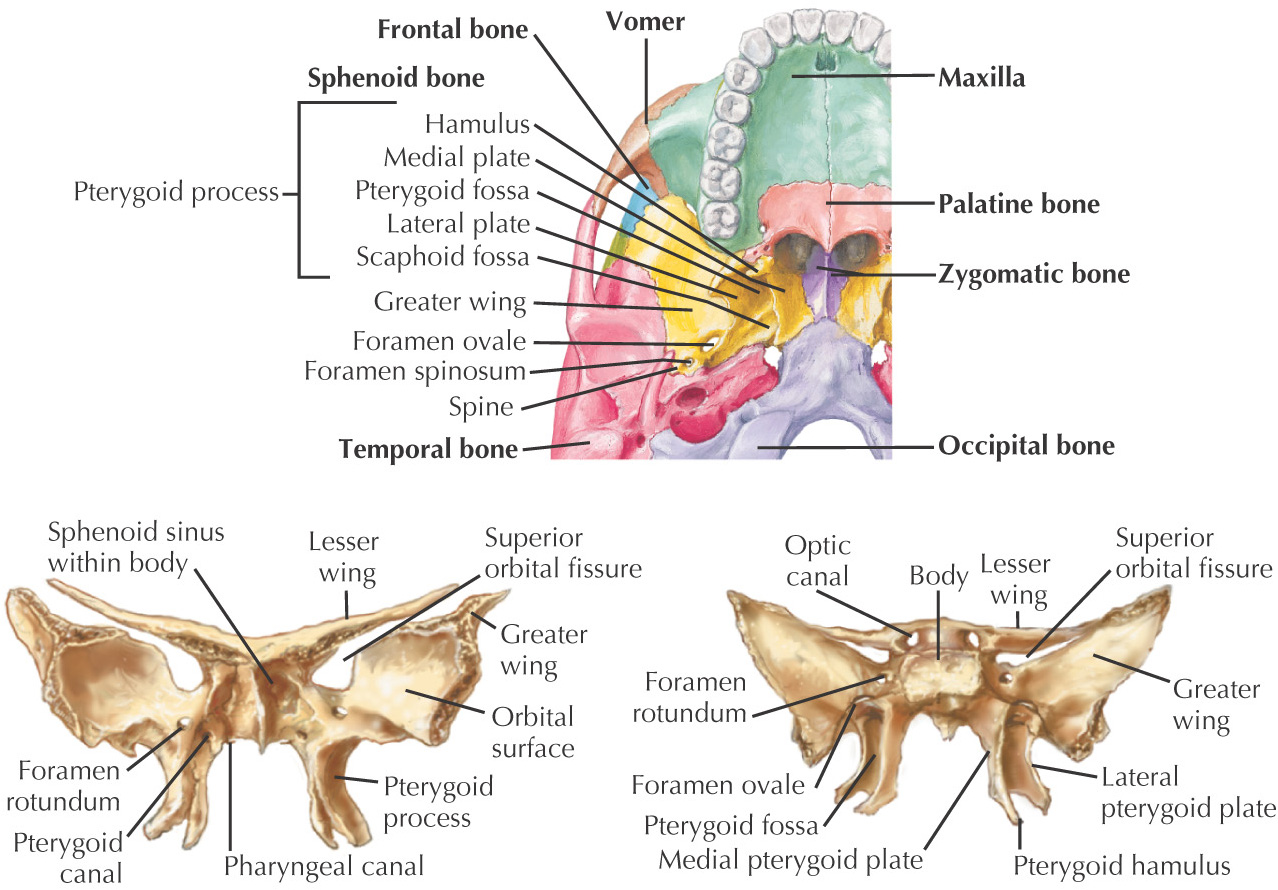
SPHENOID BONE
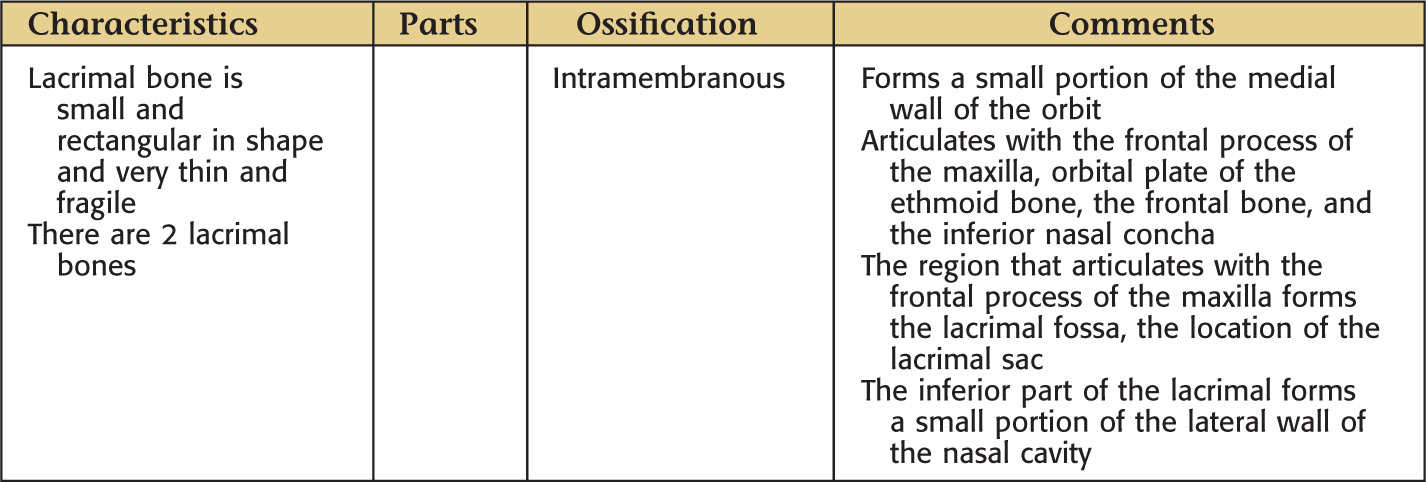
LACRIMAL BONE
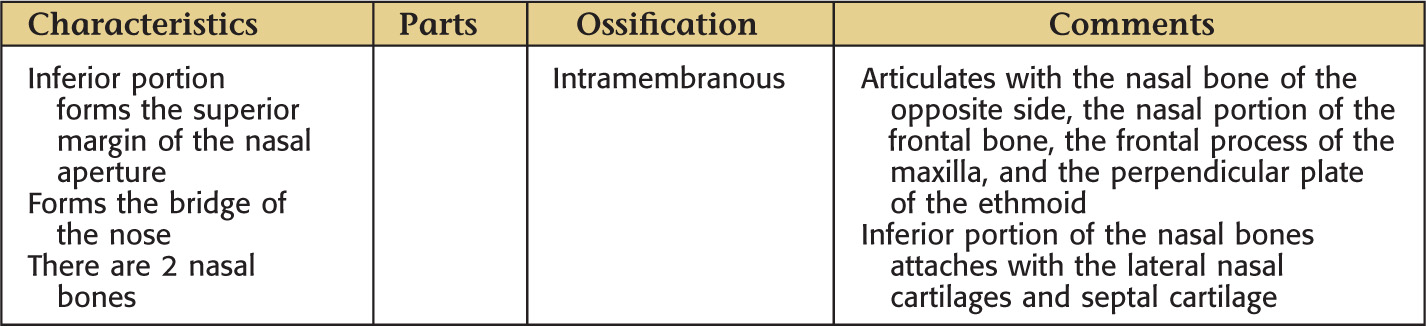
NASAL BONE
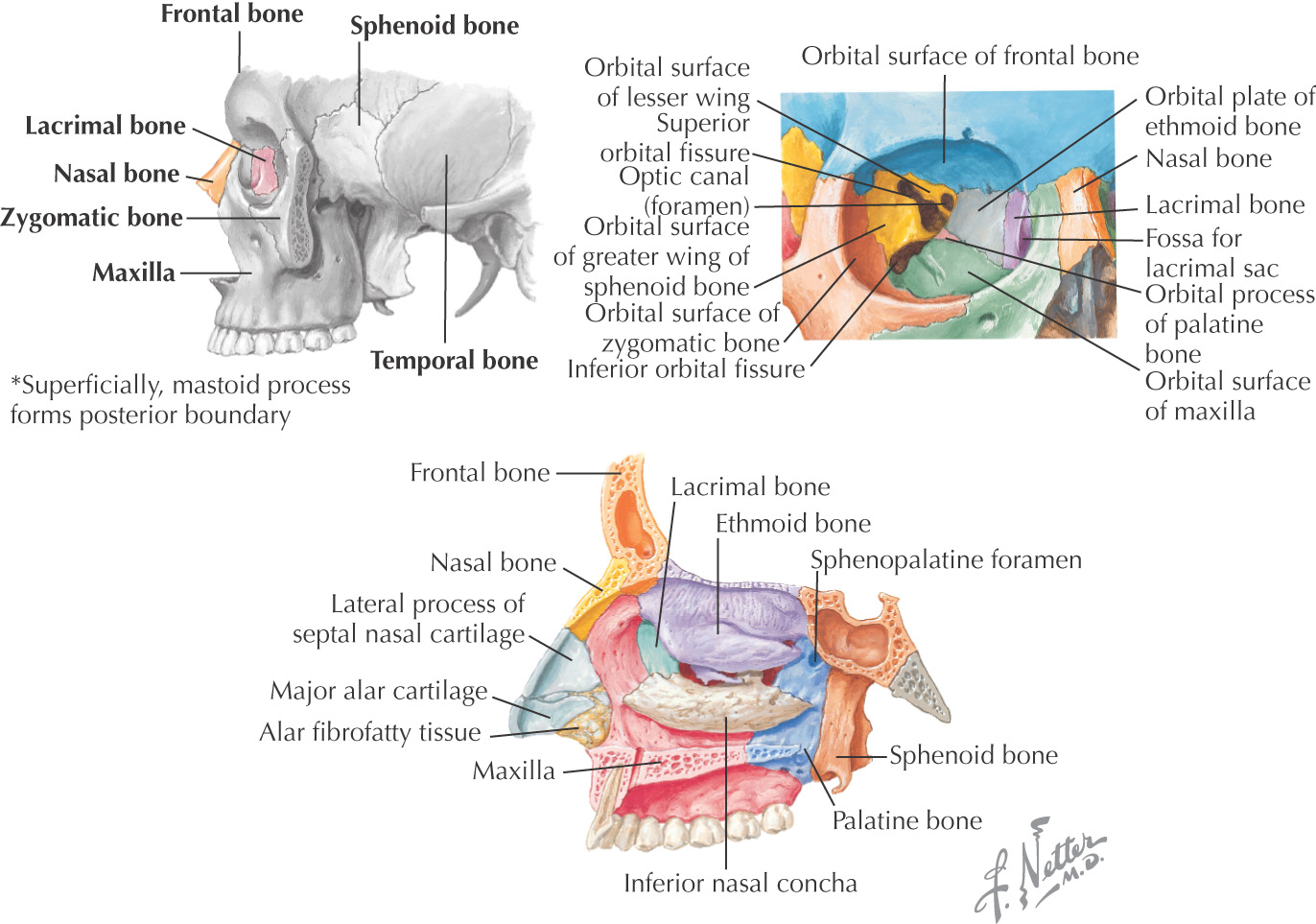
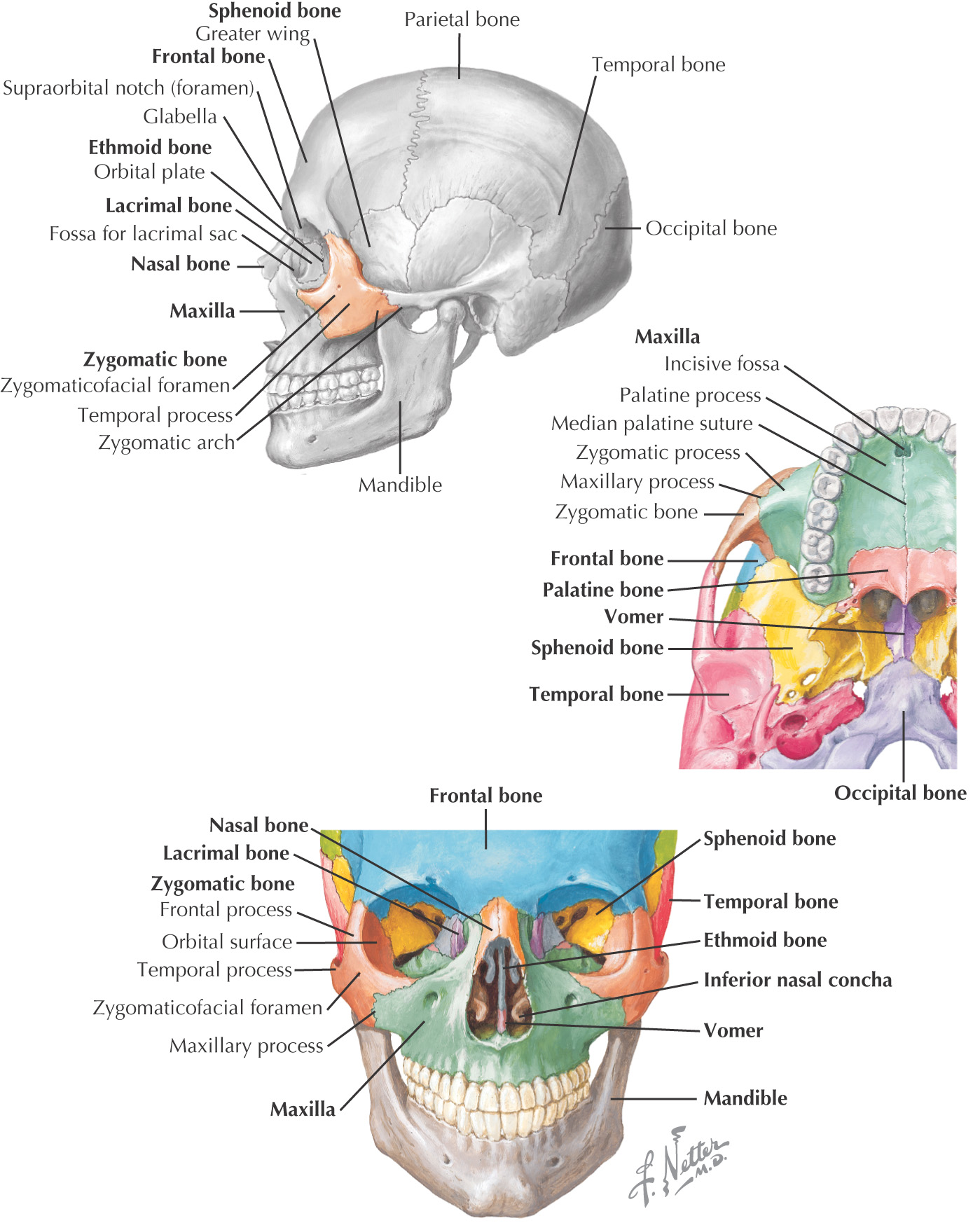
ZYGOMATIC BONE (ZYGOMA)
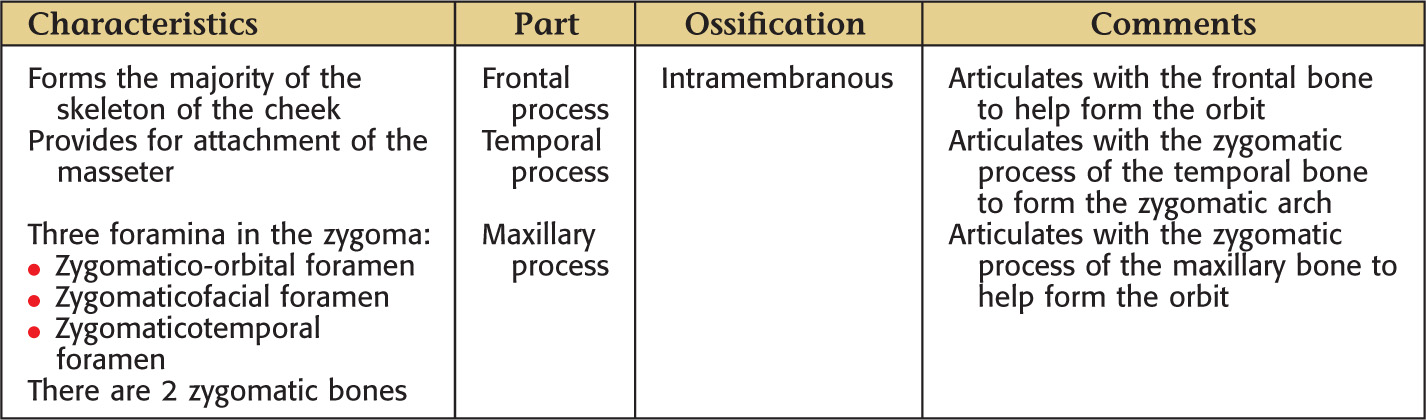
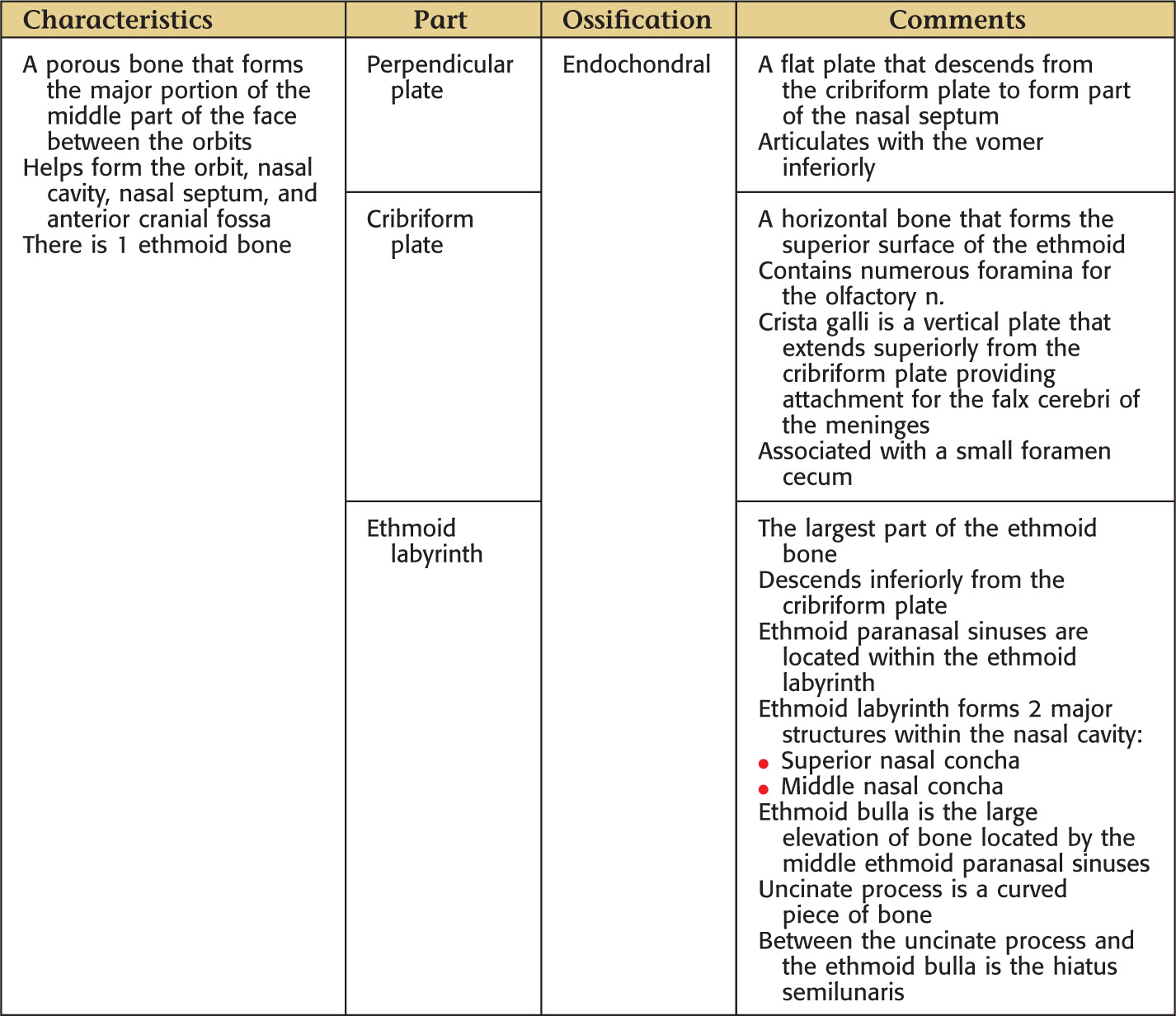
ETHMOID BONE
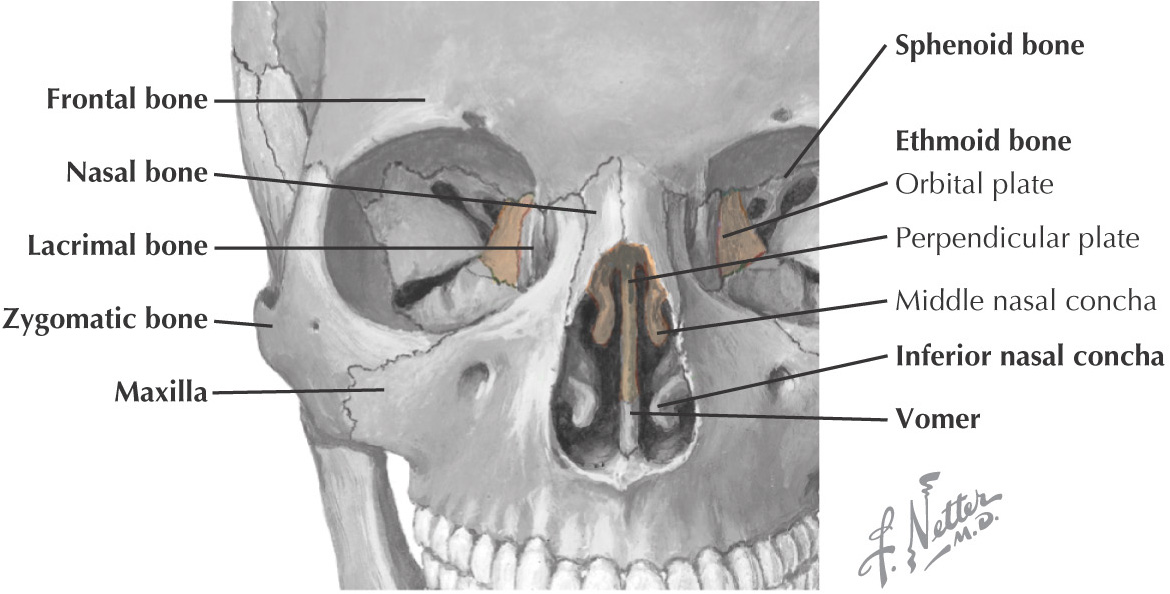
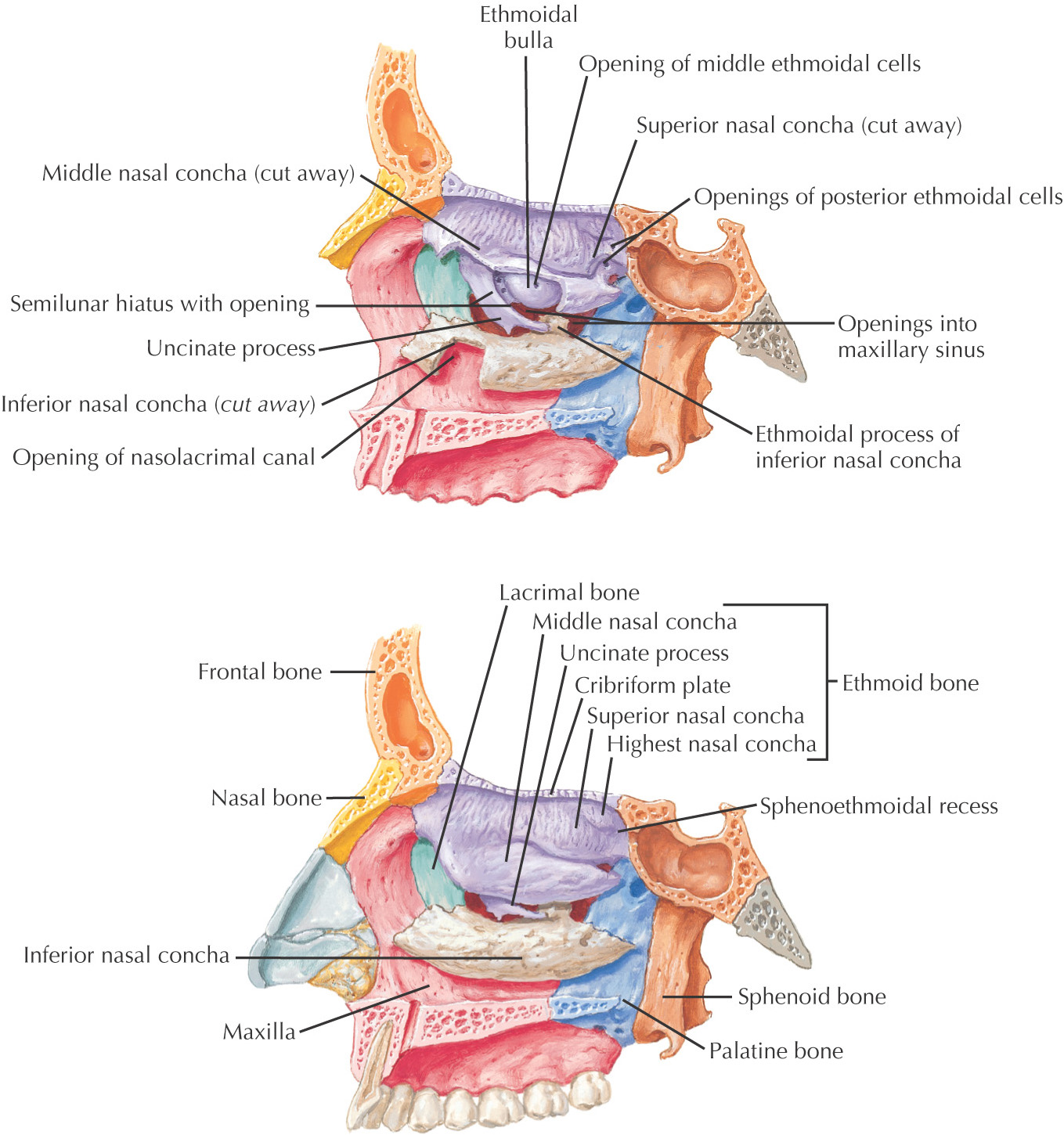
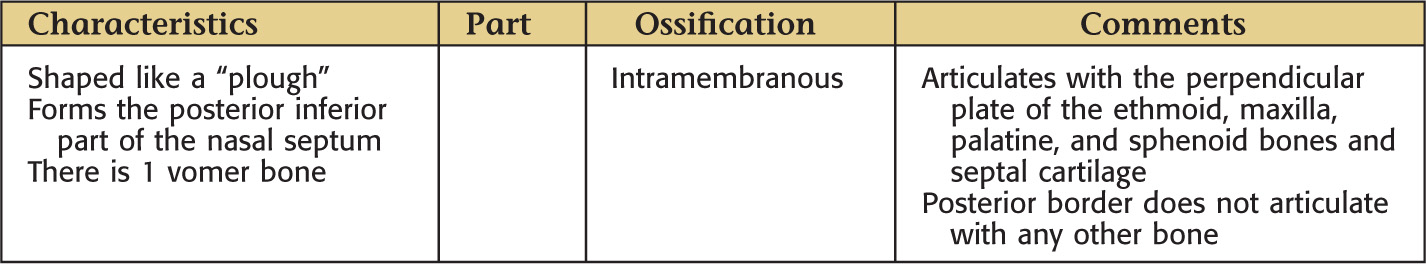
VOMER
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


