PHARYNX
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
Potential Apertures in Pharyngeal Wall
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
GENERAL INFORMATION
Pharynx: 5-inch muscular tube from base of the skull to the lower border of the cricoid cartilage (C6)
Posterior portion of the pharynx lies against the prevertebral fascia
Lies posterior to the nasal and oral cavities and the larynx and thus is divided into 3 parts:
Responsible for properly conducting food to the esophagus and air to the lungs
Composed of:
• Cartilaginous part of the pharyngotympanic tube
The wall of the pharynx has 5 layers:
• Mucous membrane—the innermost layer
• Pharyngobasilar fascia—the fibrous layer attached to the skull anchoring the pharynx
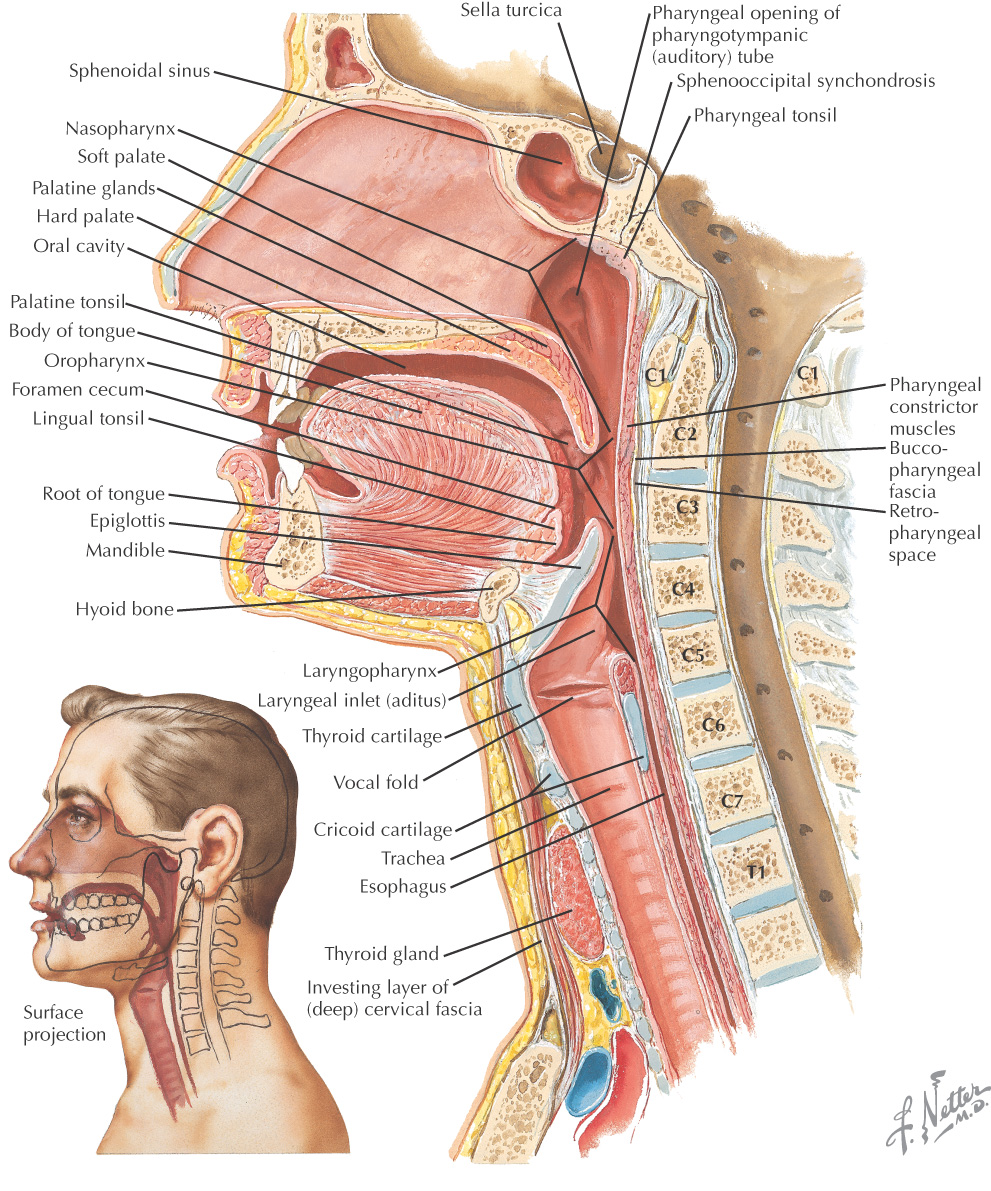
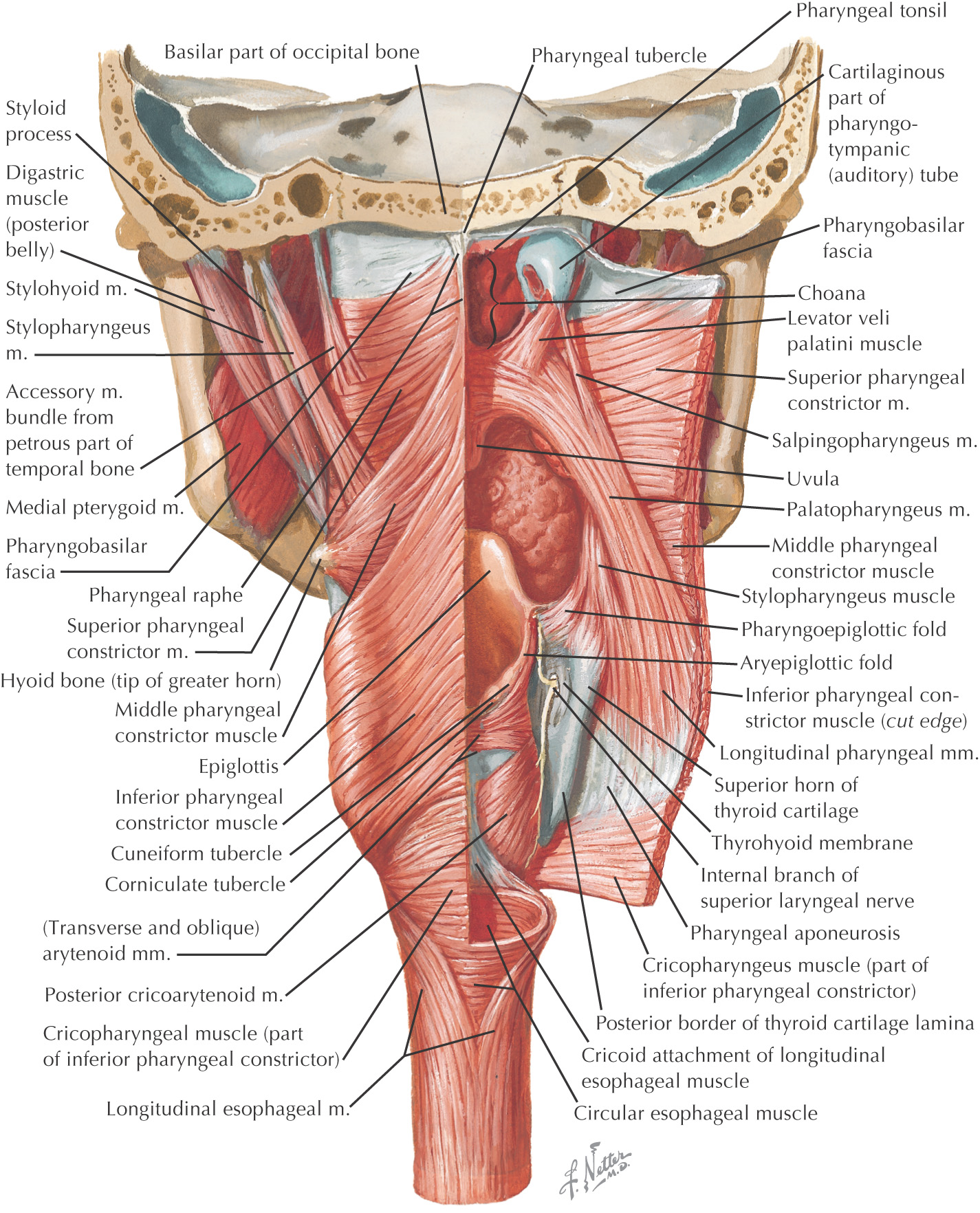
Parts of the Pharynx
NASOPHARYNX
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


