ORAL CAVITY
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
Vascular Supply of the Oral Cavity
Nerve Supply of the Oral Cavity
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
GENERAL INFORMATION
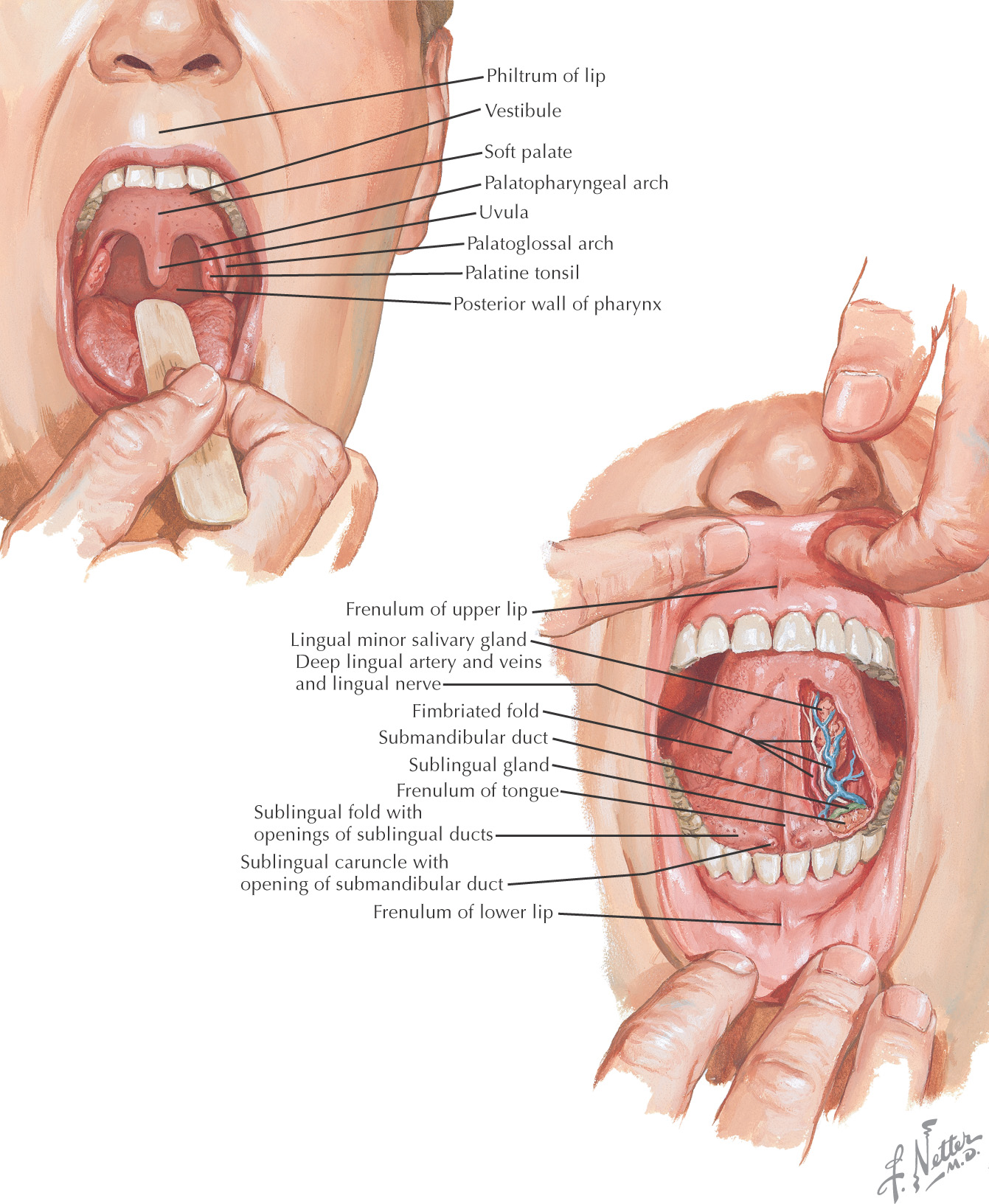
Oral cavity: the space located between the lips and cheeks on the external surface to the palatoglossal fold on the internal surface
The oral cavity is important in mastication, tasting, and talking
The area of the oral cavity can be divided into:
• Vestibule—the area between the teeth and lips or cheek
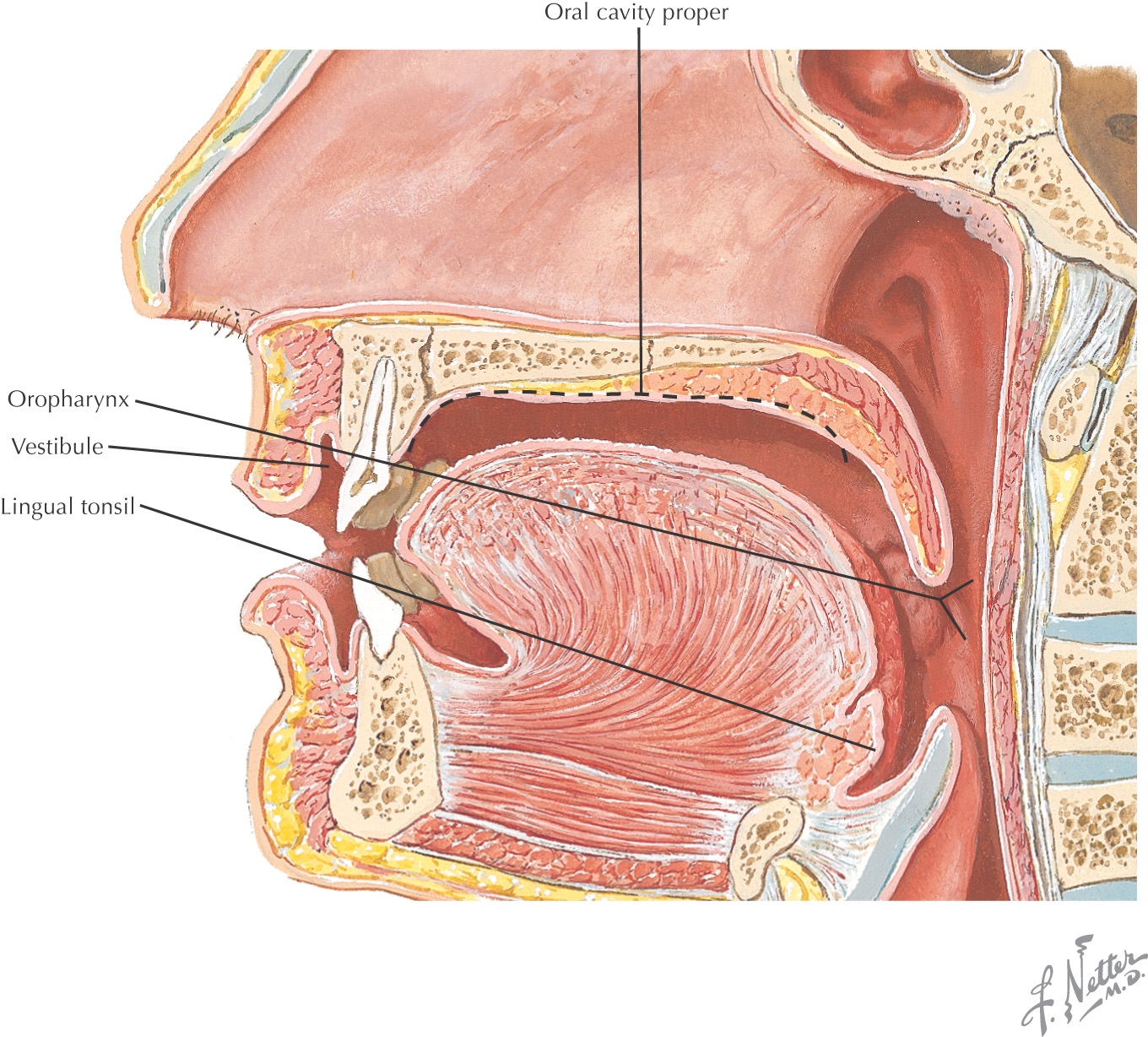
• Oral cavity proper—the area located internal to the teeth
Posteriorly, the oral cavity is continuous with the oropharynx
The hard palate and the soft palate are important boundaries within the oral cavity
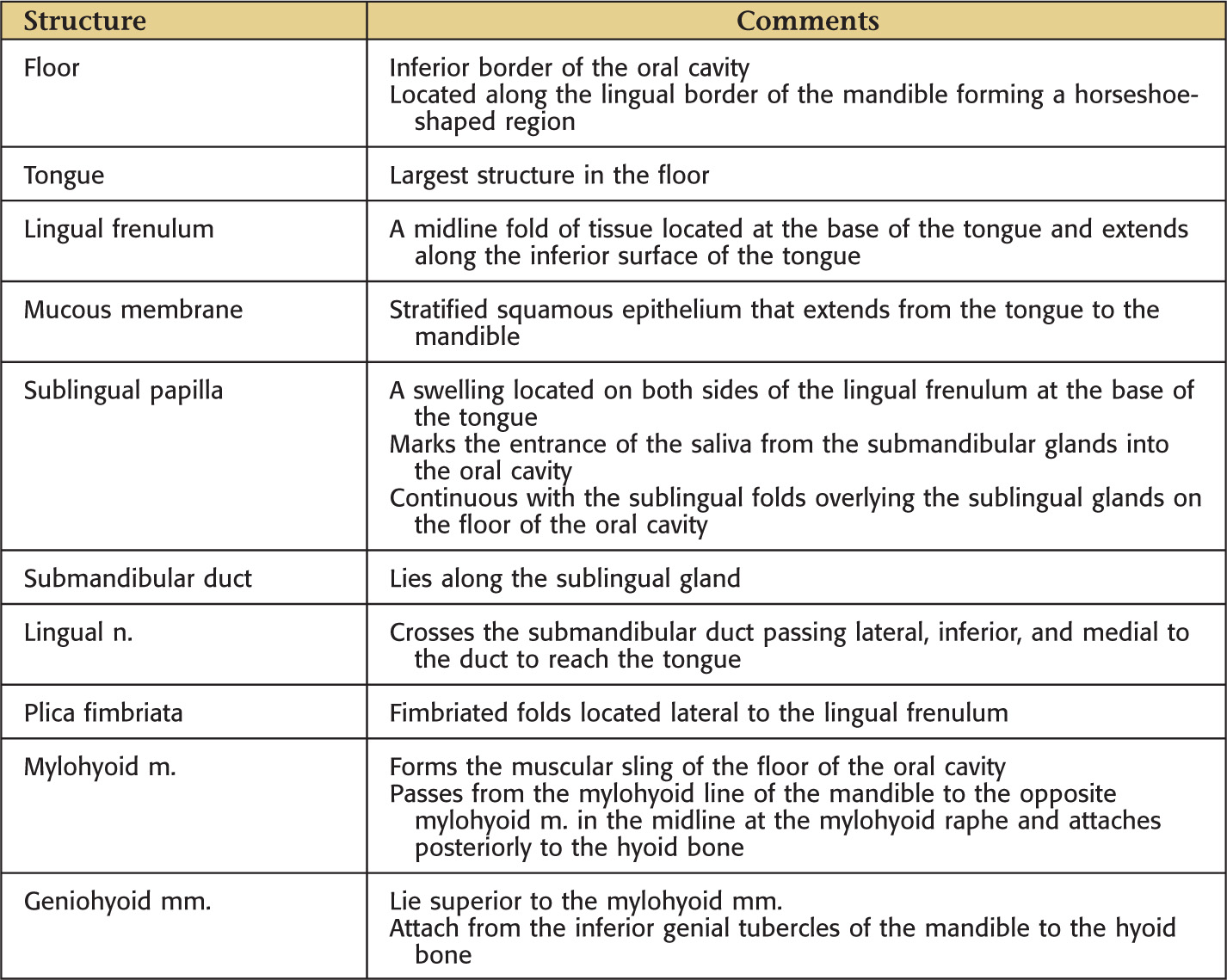
The tongue is a major structure located on the oral cavity floor
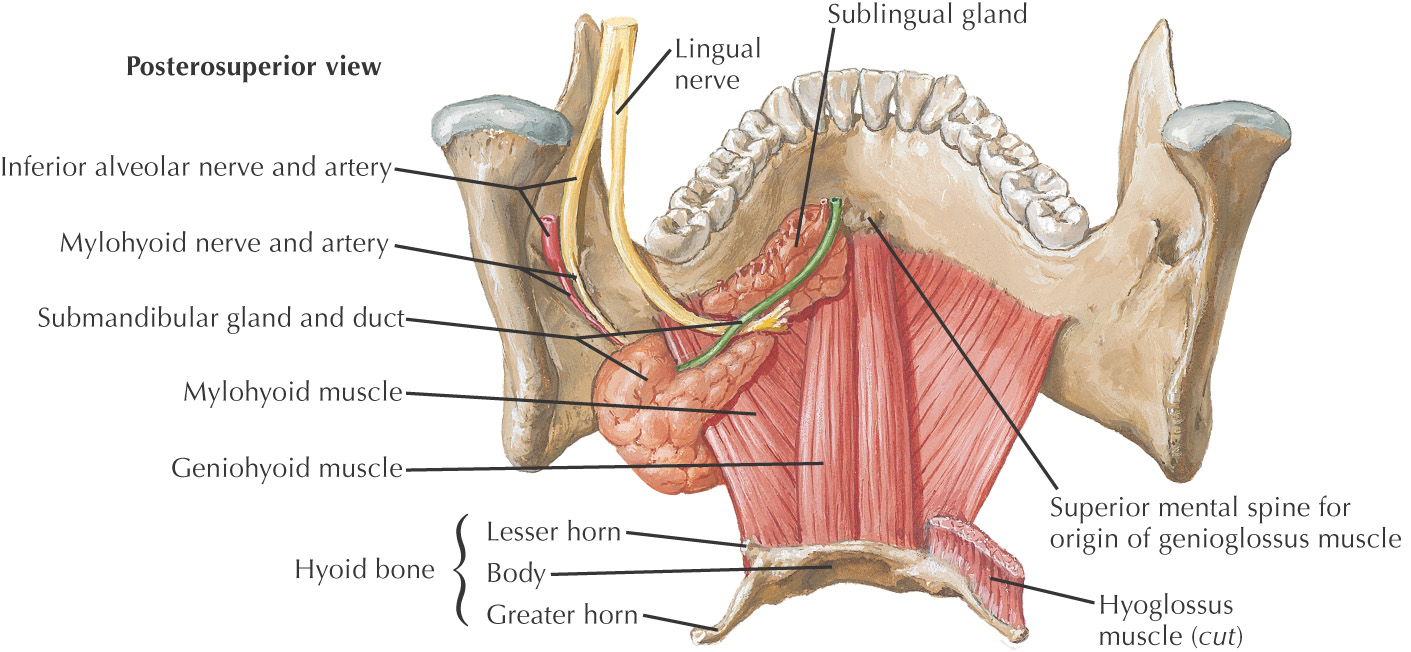
All of the major salivary glands—parotid, submandibular, and sublingual—drain into the oral cavity
External Anatomy
EXTERNAL FEATURES
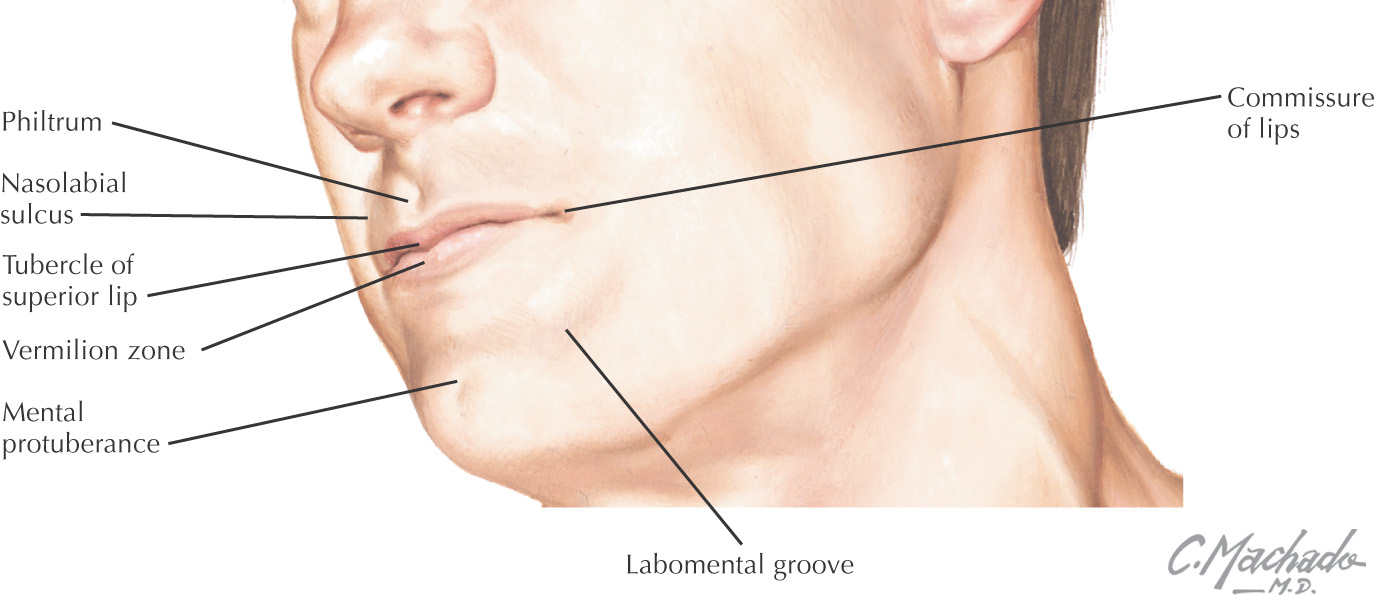
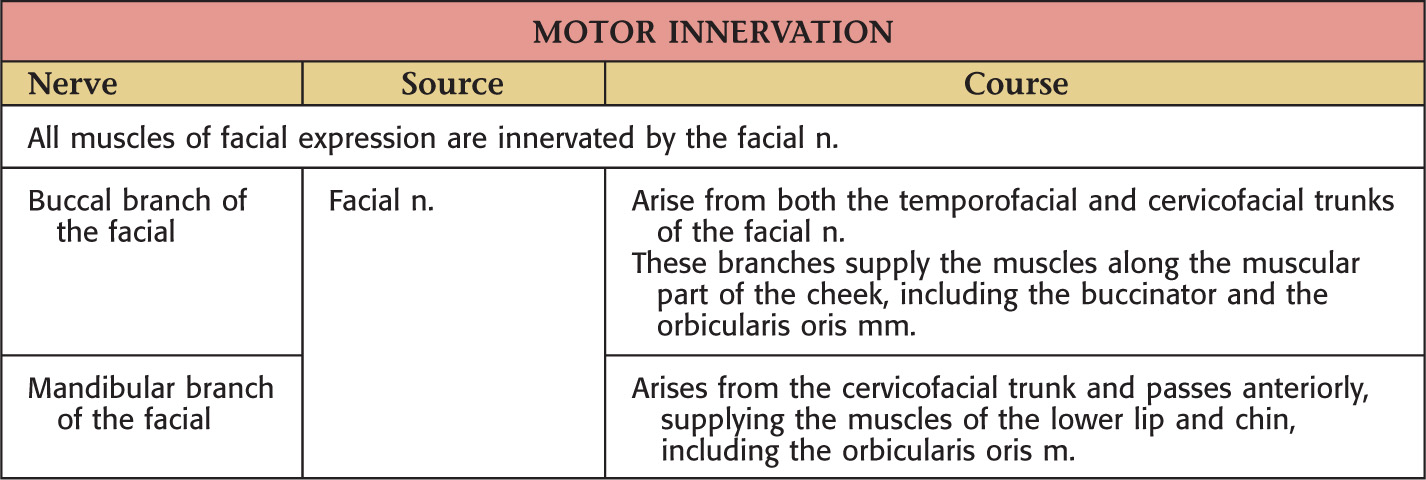
VASCULAR SUPPLY OF THE LIPS AND CHEEK
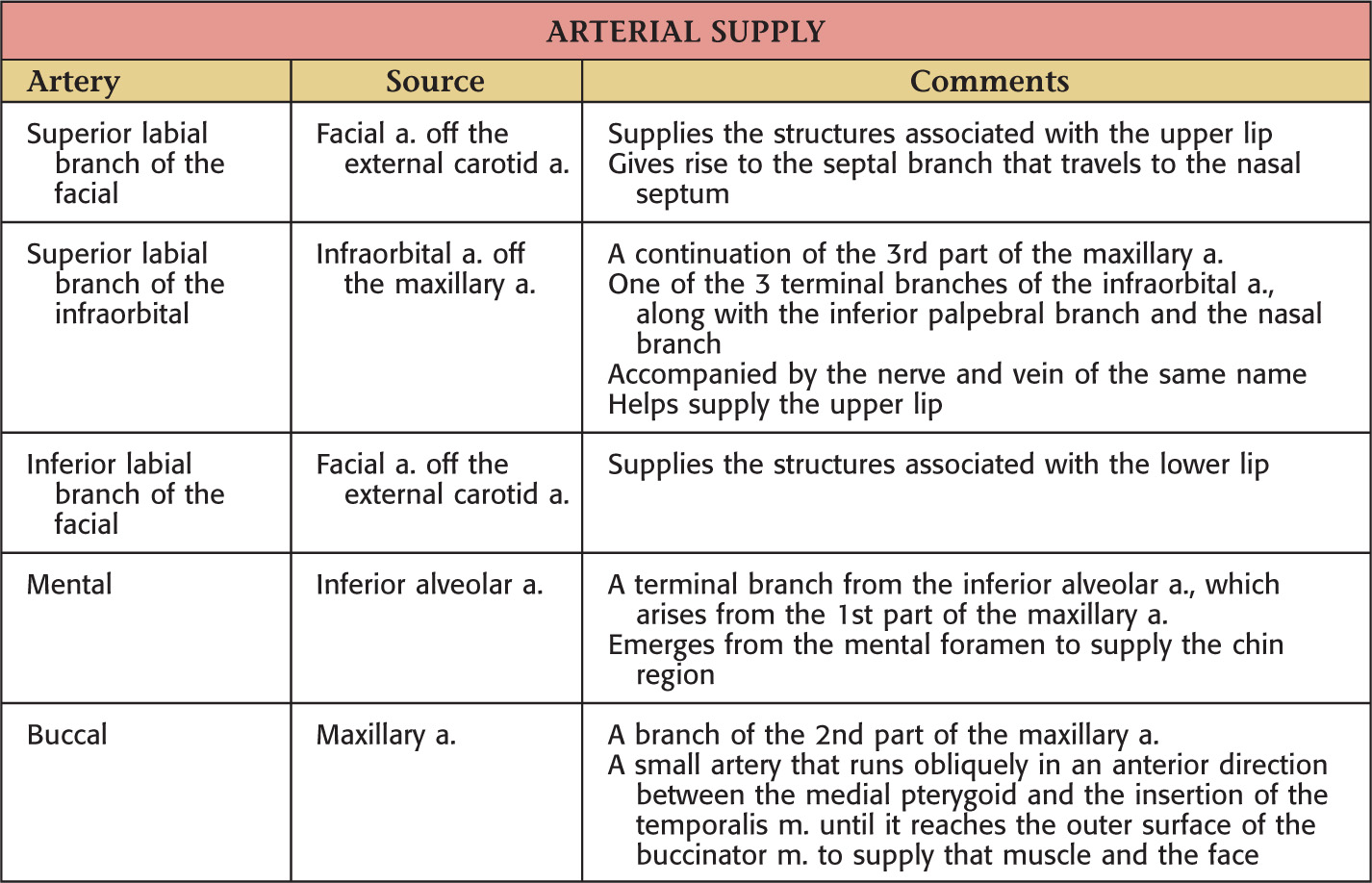
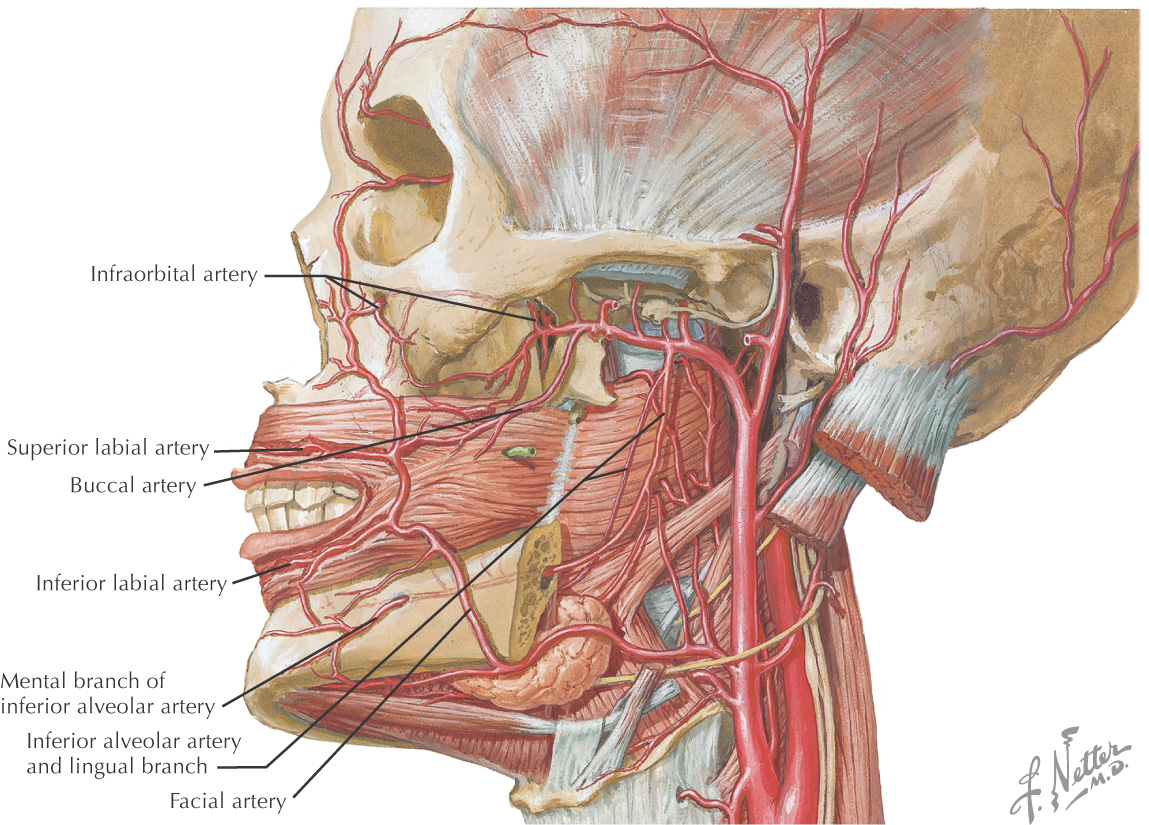
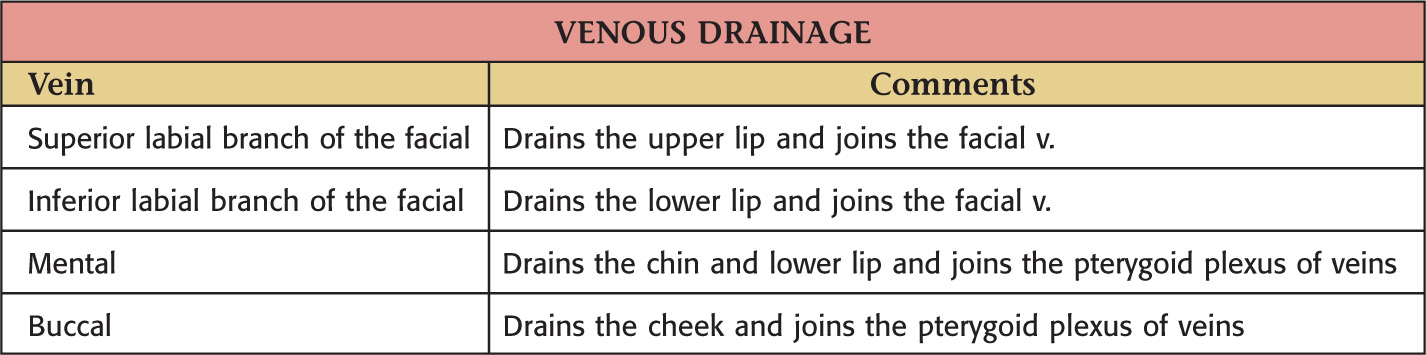
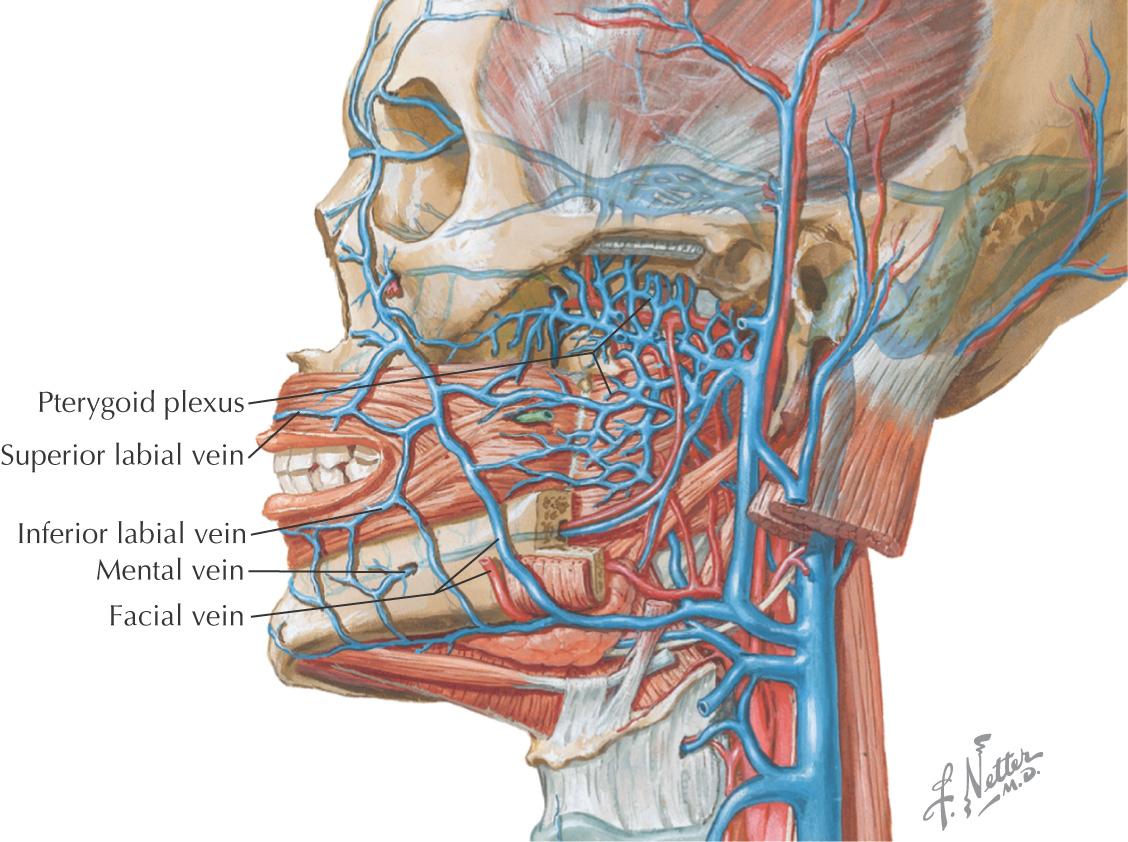
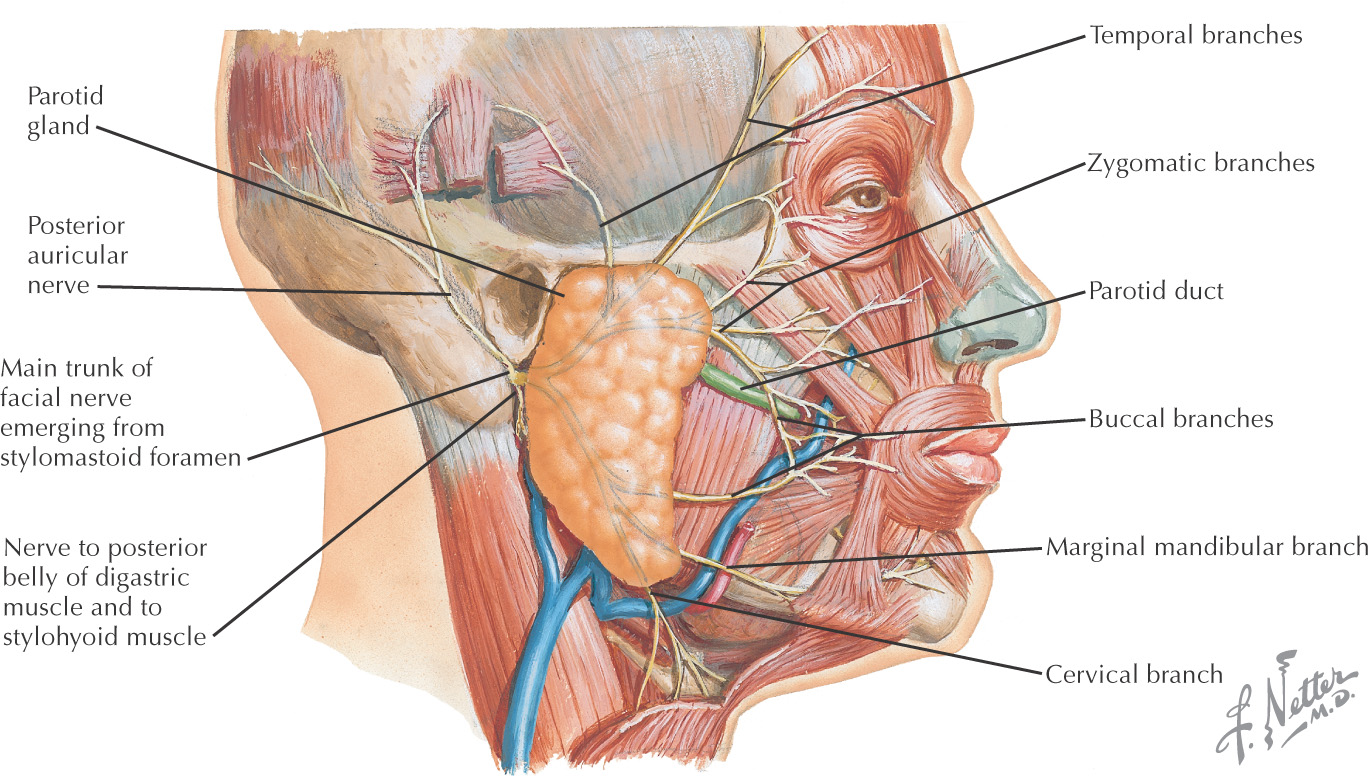
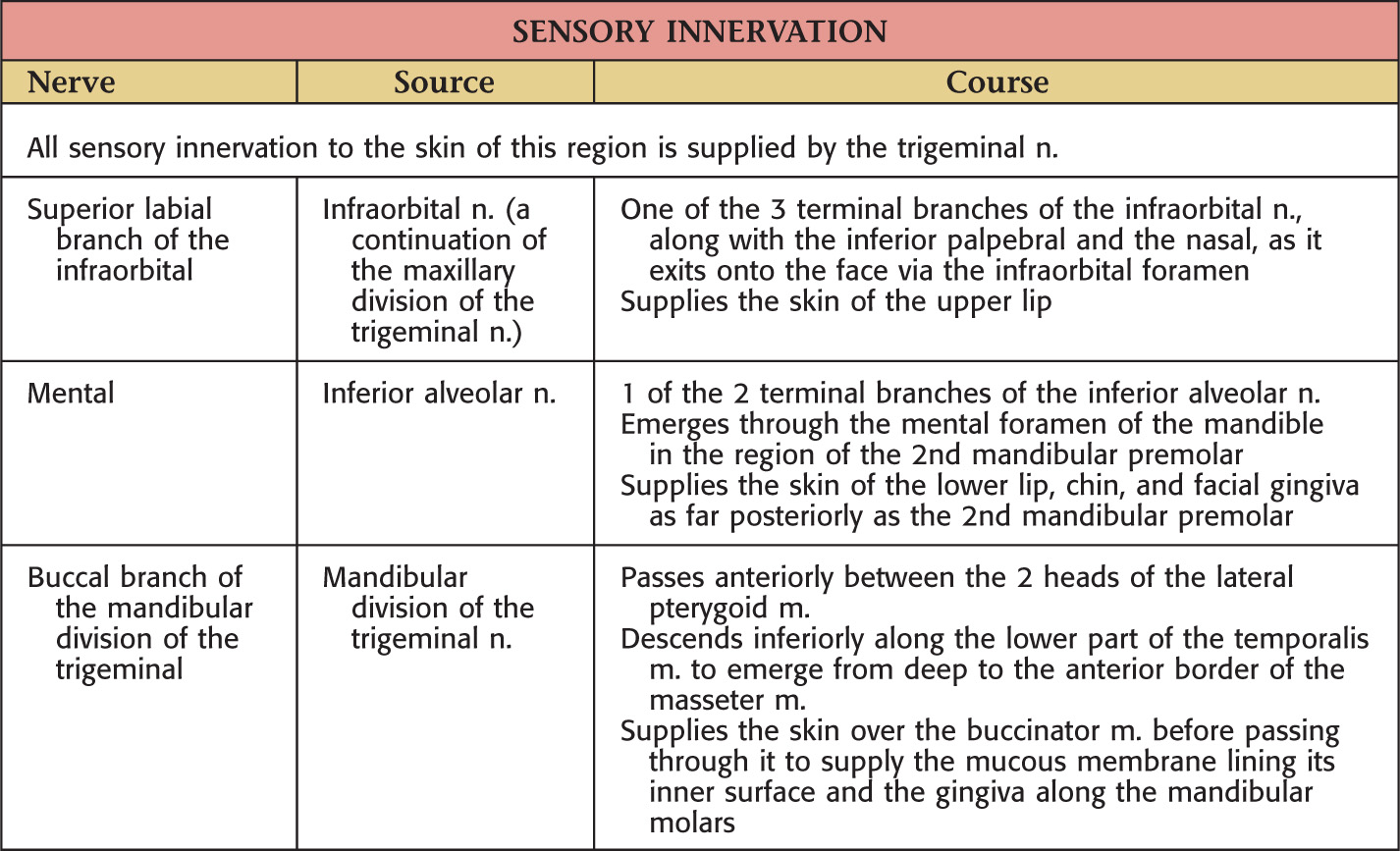
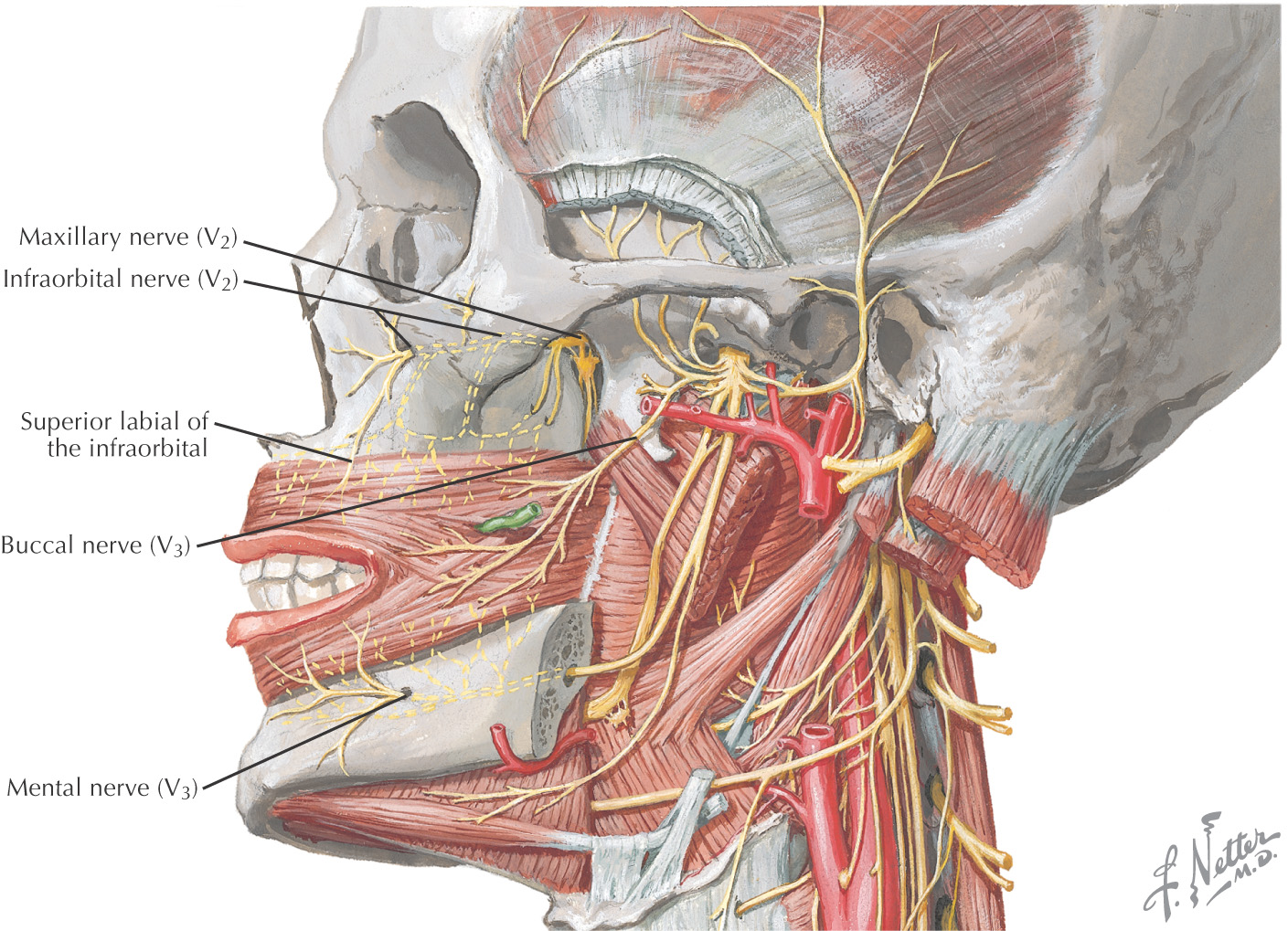
NERVE SUPPLY
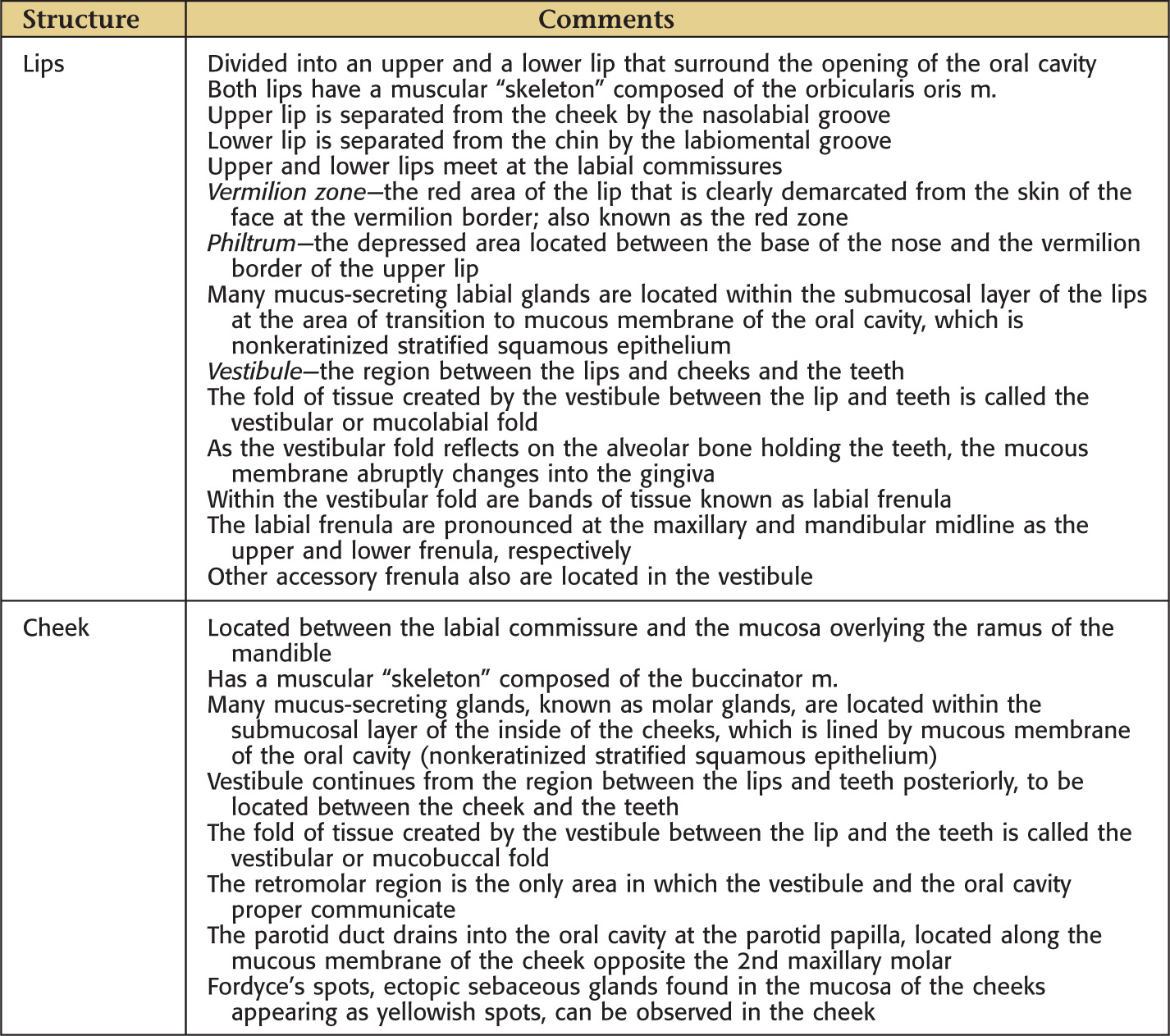
Boundaries of the Oral Cavity
GENERAL INFORMATION
|
Boundary |
Structure |
|
Superior |
The roof is the hard palate |
|
Posterosuperior |
Soft palate |
|
Lateral |
Cheeks |
|
Inferior |
The floor is located along the lingual border of the mandible forming a horseshoe-shaped region |
SUPERIOR BORDER: HARD PALATE
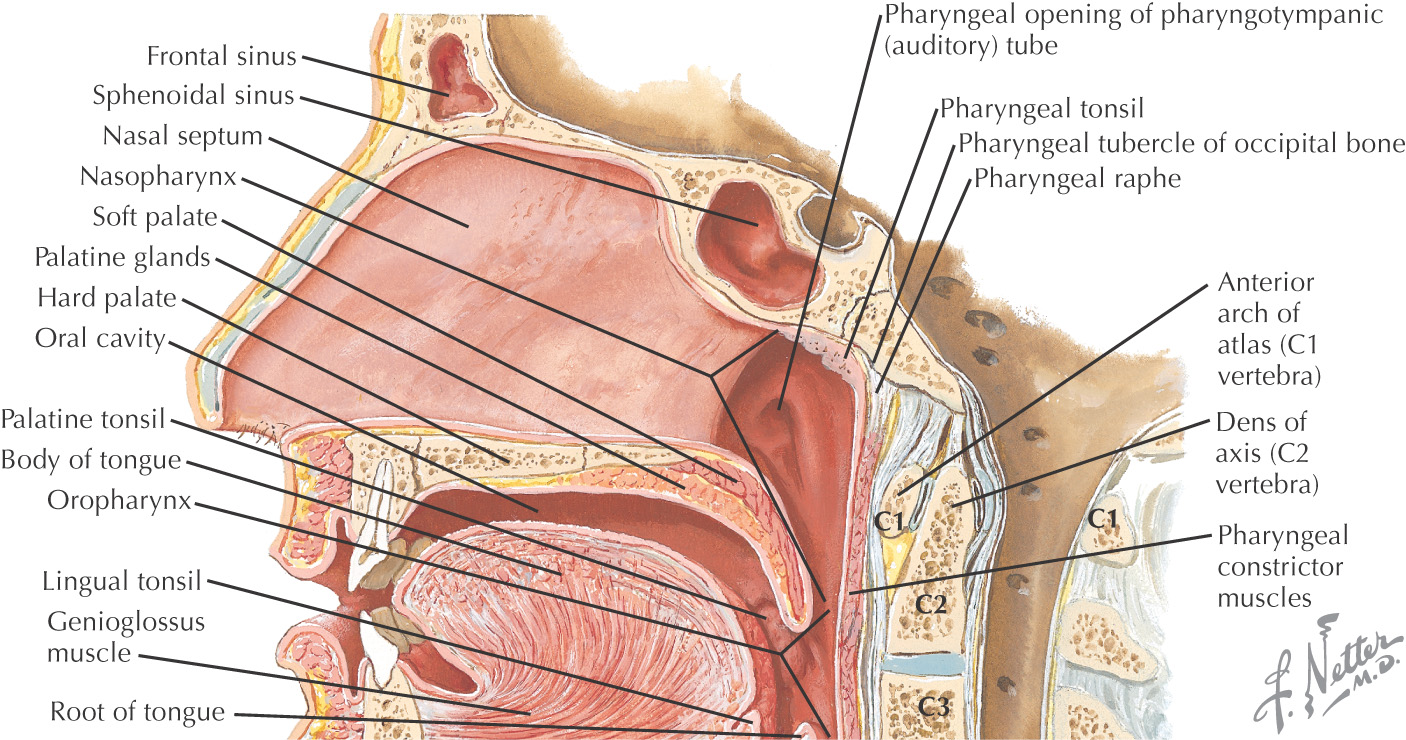
The superior border (or roof) of the oral cavity is the hard palate, comprising the anterior 2/3 of the entire palate
Separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity
Composed of:
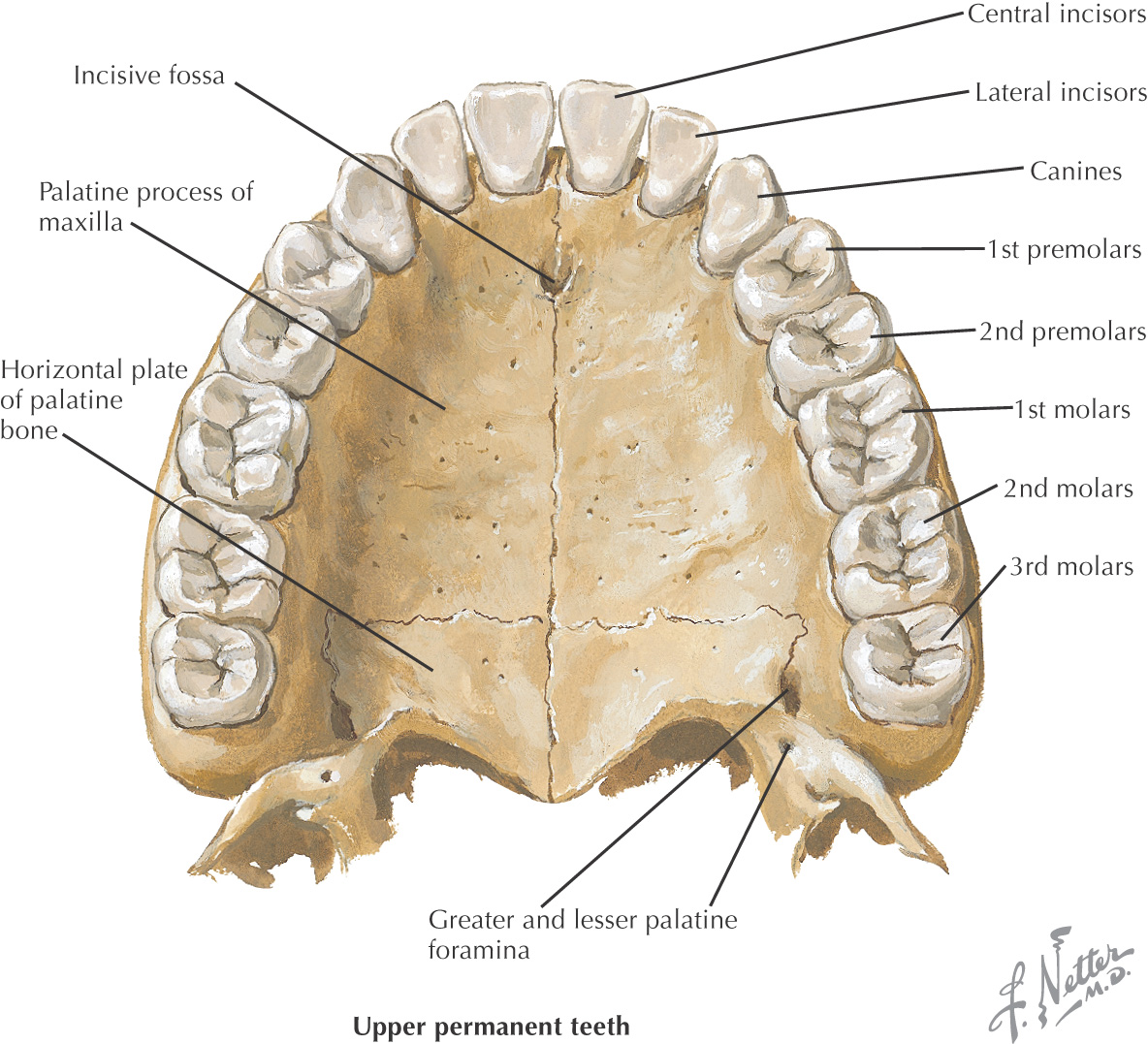
• Palatal process of the maxilla
• Horizontal process of the palatine
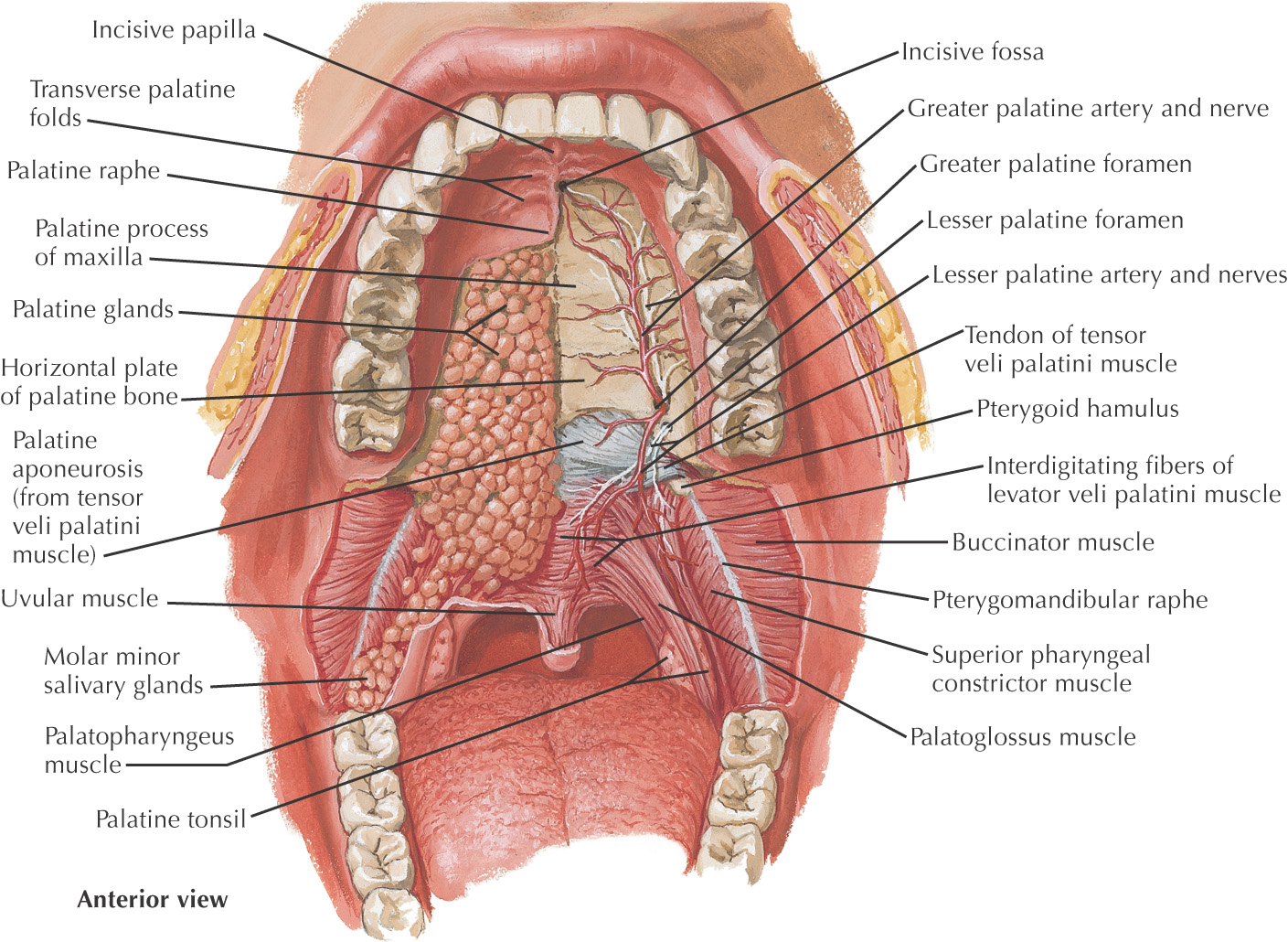
In the anterior midline, an incisive foramen is located on the right and left sides that transmits the terminal branches of the nasopalatine nerve and sphenopalatine vessels
In the posterolateral region of the hard palate, the greater and lesser palatine foramina are located on the right and left sides; these openings transmit the greater and lesser palatine nn. and vessels
The bones of the hard palate are covered by a thick mucous membrane
The mucous membrane has a small elevation in the anterior midline called the incisive papilla that overlies the incisive foramen
Moving posteriorly from the incisive papilla, the mucous membrane has a thick midline palatal raphe
Lateral transverse ridges called transverse rugae (plicae) are located along the mucous membrane of the hard palate
Deep to the mucous membrane of the hard palate are numerous mucus-secreting glands called palatal glands
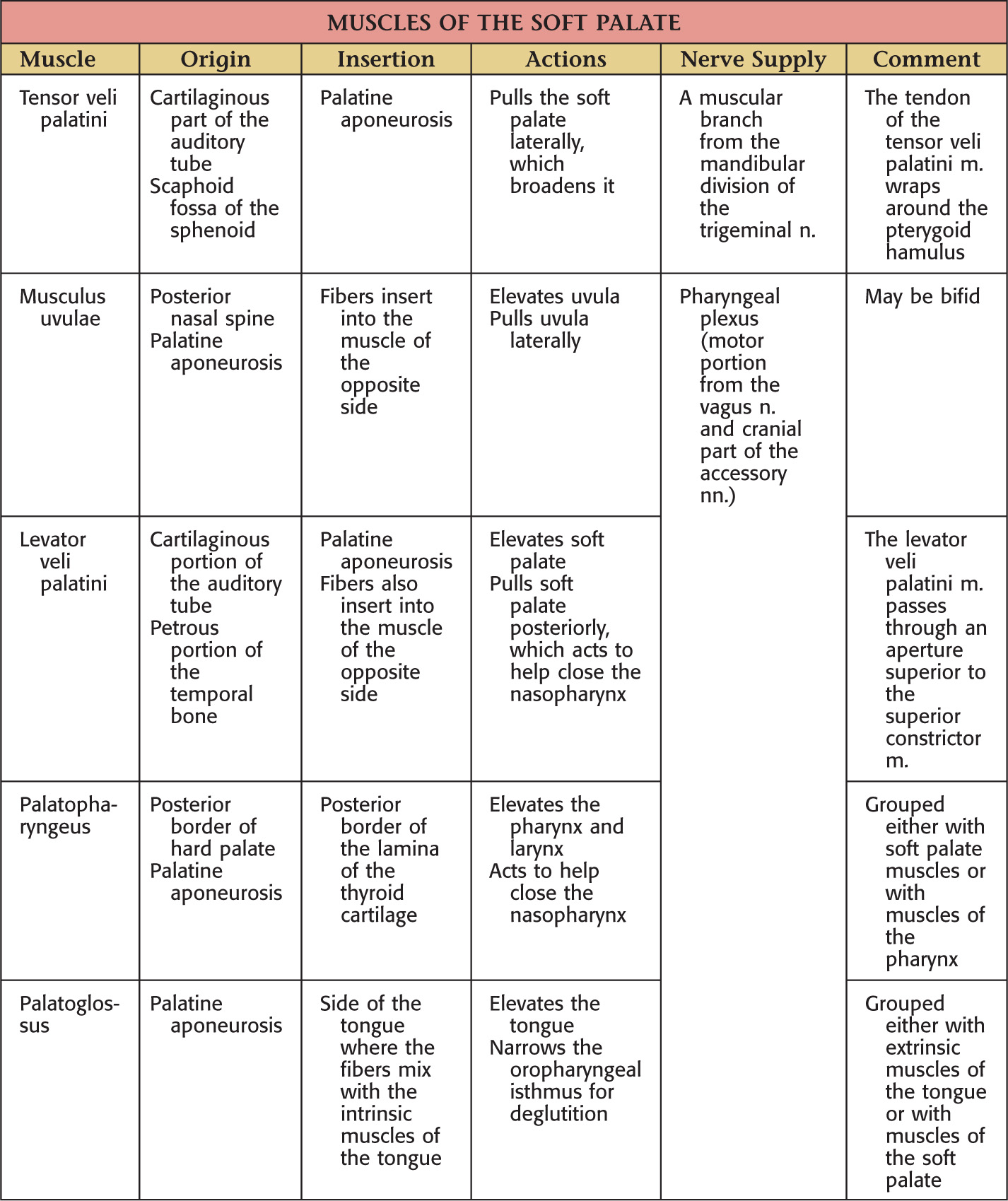
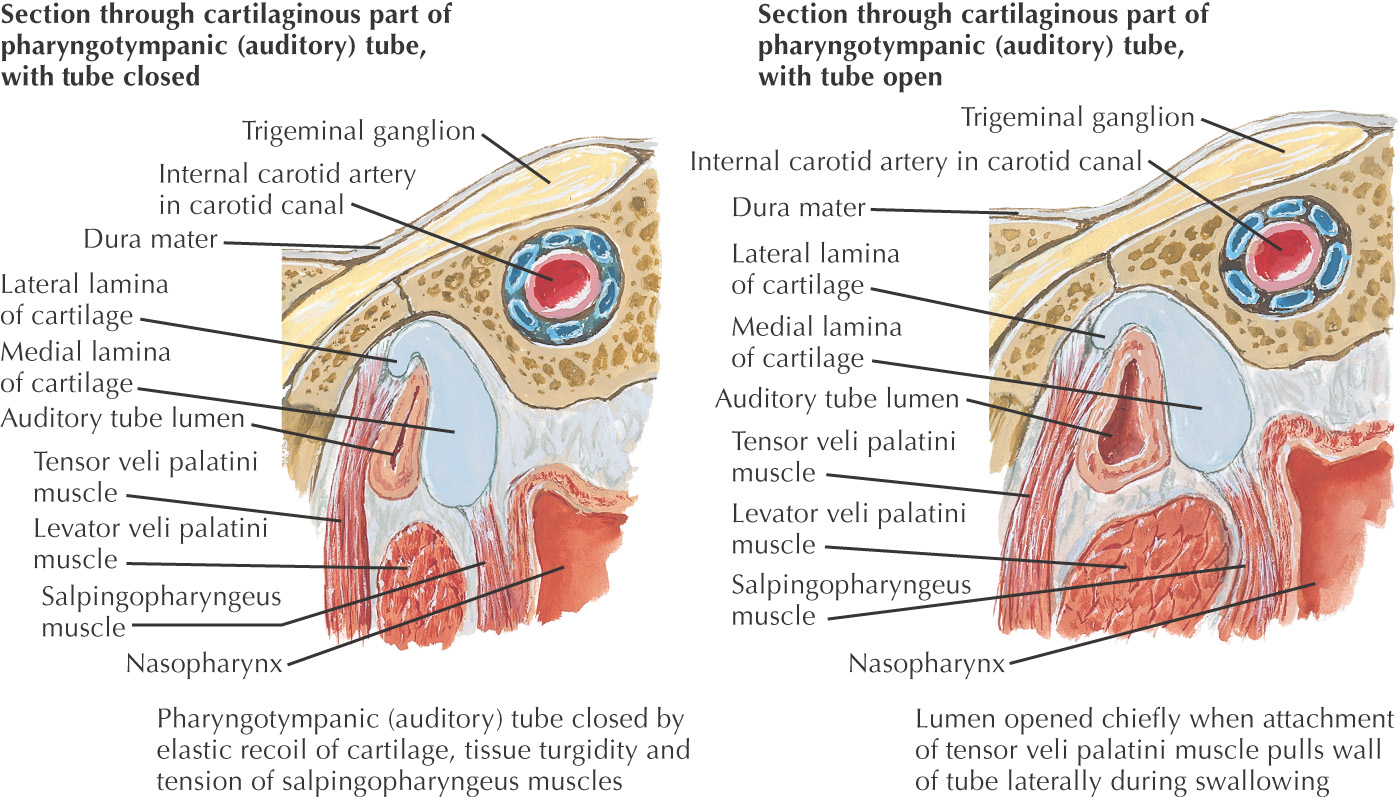
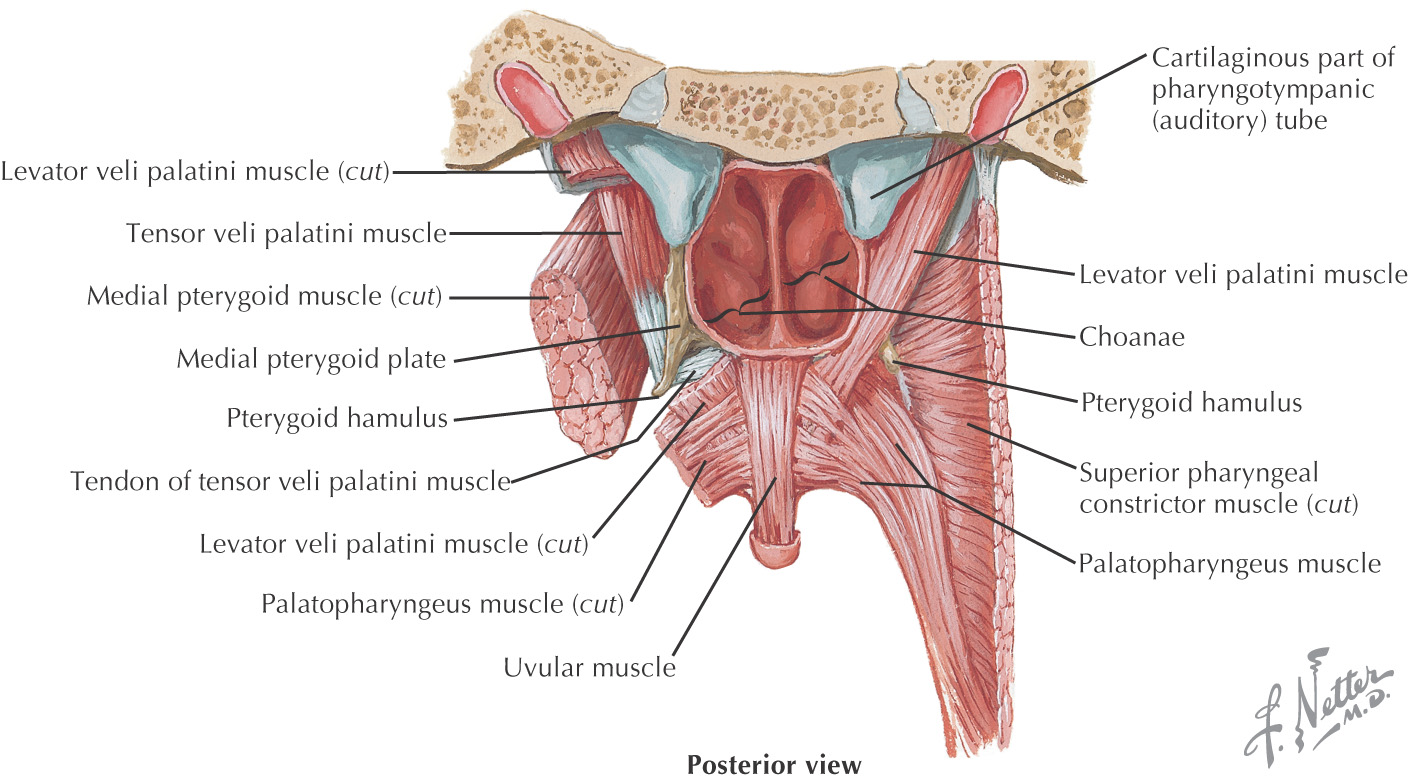
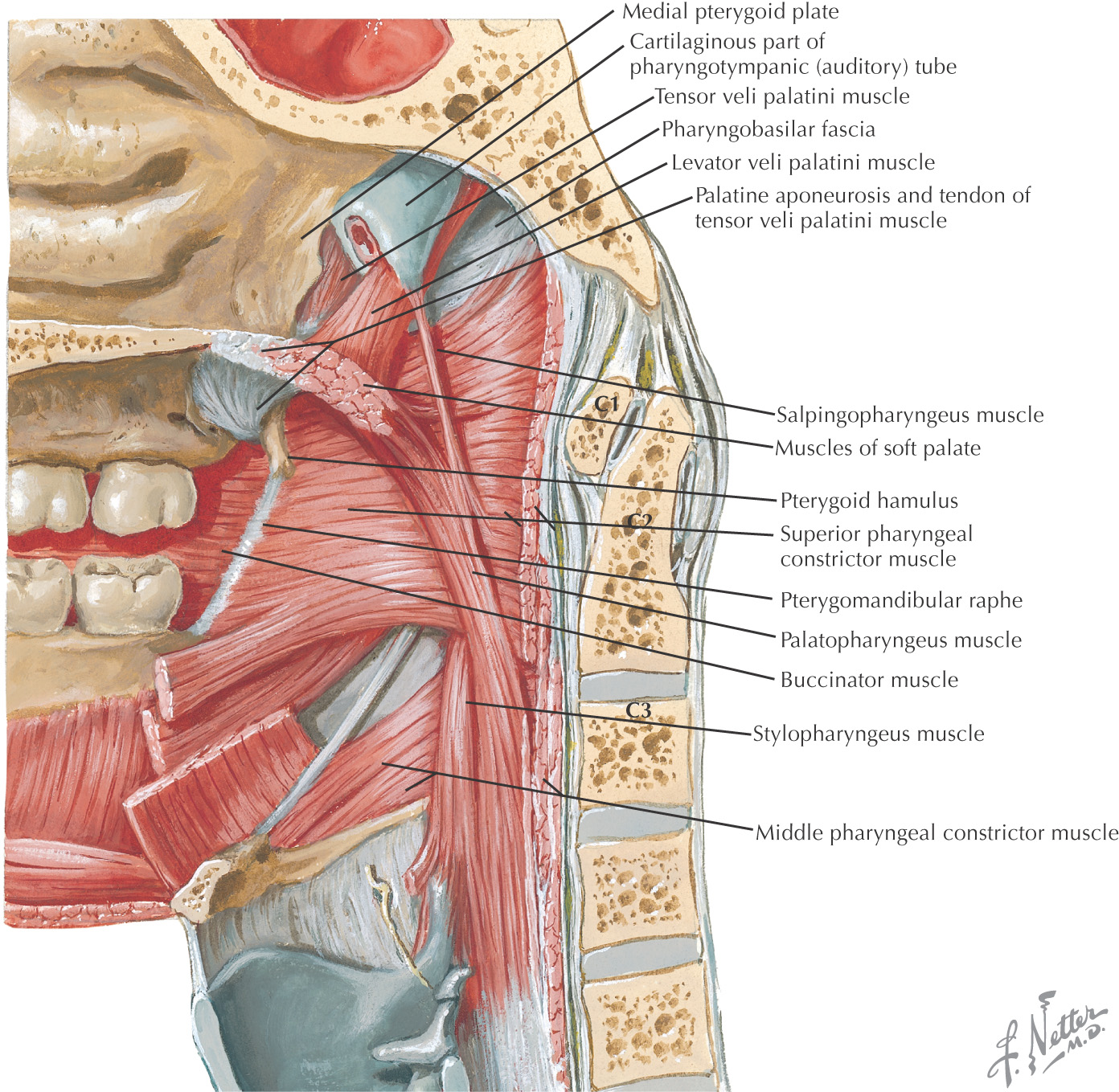
POSTEROSUPERIOR BORDER: SOFT PALATE
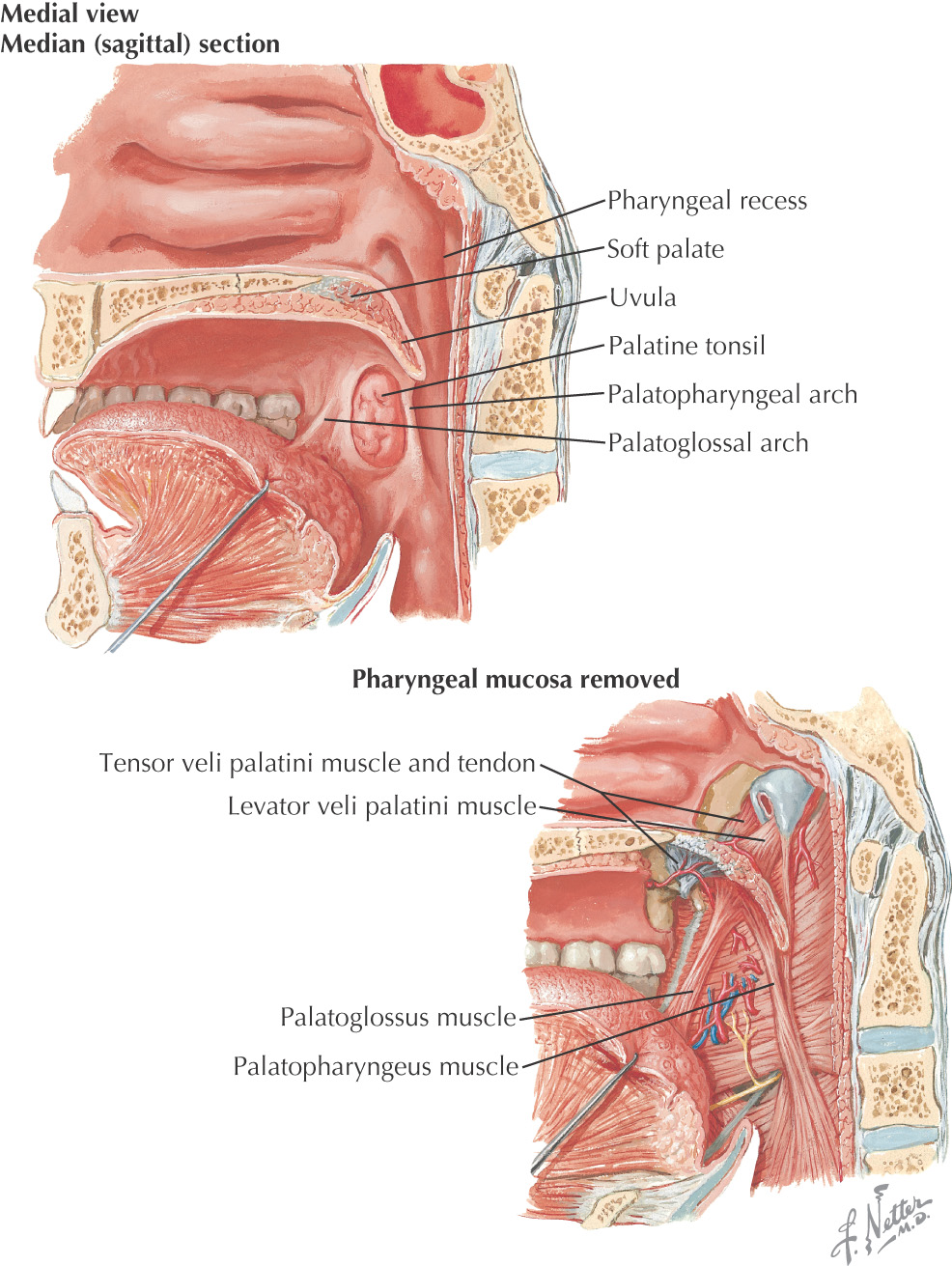
The posterosuperior border of the oral cavity is the soft palate
The soft palate is the continuation of the palate posteriorly and makes up approximately 1/3 of the entire palate
The soft palate separates the oral cavity from the nasopharynx
An abundance of mucus-secreting palatal glands, which are continuous with the hard palate, are located in the soft palate
The soft palate has 3 margins:
• Anteriorly, it is continuous with the hard palate at the vibrating line
• Posterolaterally, it forms the superior portion of the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds
• Posteriorly, the uvula hangs in the center of the posterior free margin
The thick palatine aponeurosis forms the foundation of the soft palate
The soft palate is composed of 5 muscles:
• Palatoglossus (sometimes considered in the grouping of tongue muscles)
The soft palate helps close off the nasopharynx during deglutition by forming a seal at the fold of Passavant
LATERAL BORDER: CHEEK
The lateral border of the oral cavity extends anteriorly from the labial commissure, posteriorly to the ramus of the mandible
Superior limit of the cheek is the maxillary vestibule; inferior limit is the mandibular vestibule
Mucous membrane of the cheek is stratified squamous epithelium
Fordyce’s spots are ectopic sebaceous glands that may be observed on the inner surface of the cheek
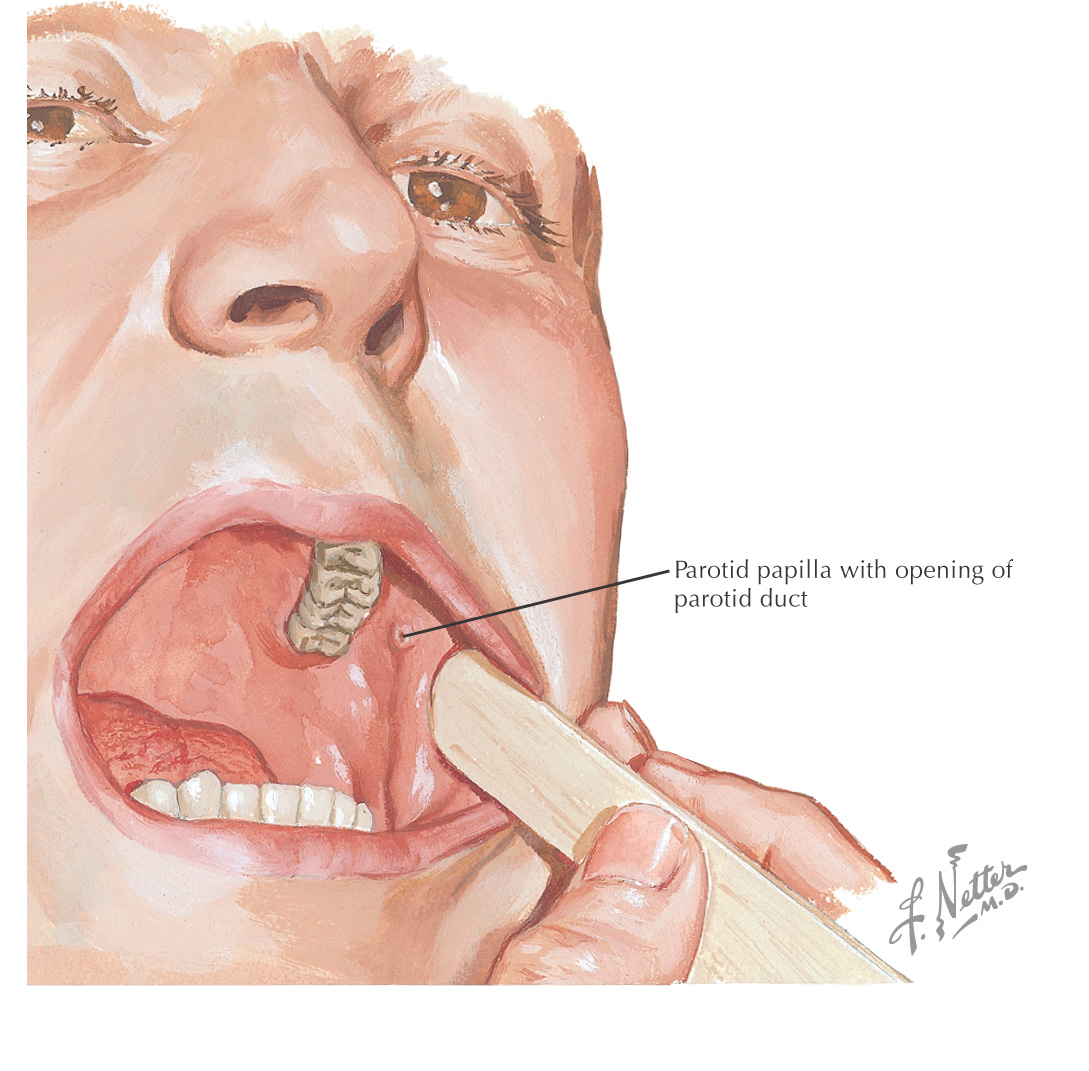
Parotid papilla is located in the cheek opposite the maxillary 2nd molar
Pterygomandibular raphe is located in the posterior portion and serves as a landmark for the pterygomandibular space
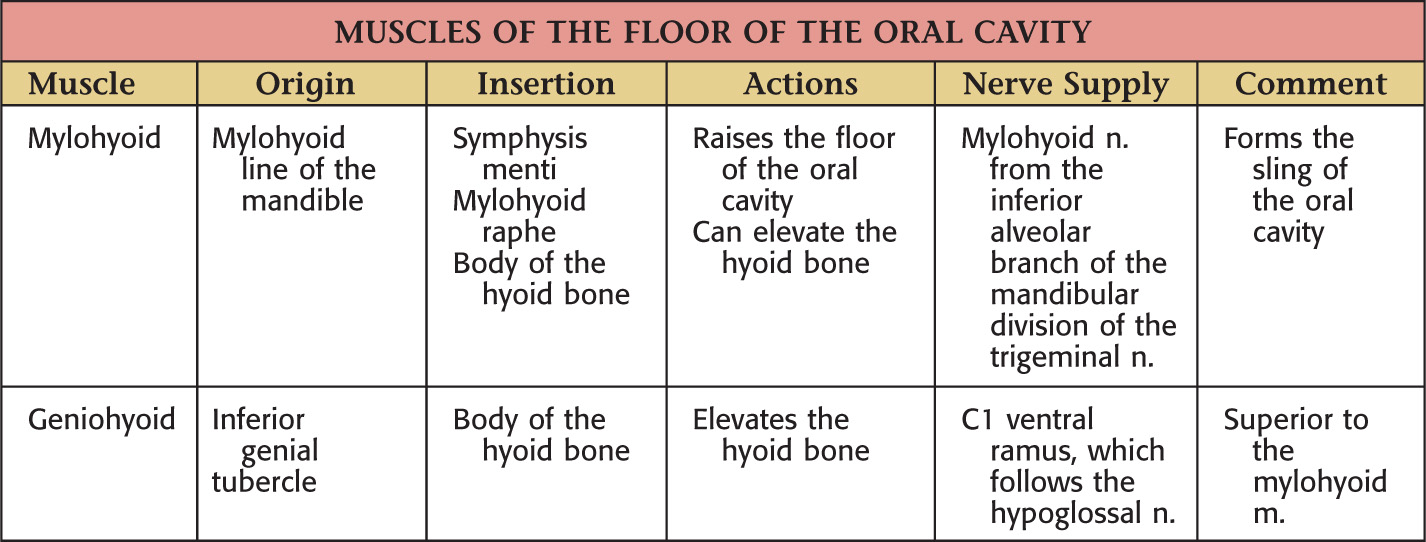
INFERIOR BORDER: FLOOR OF THE ORAL CAVITY
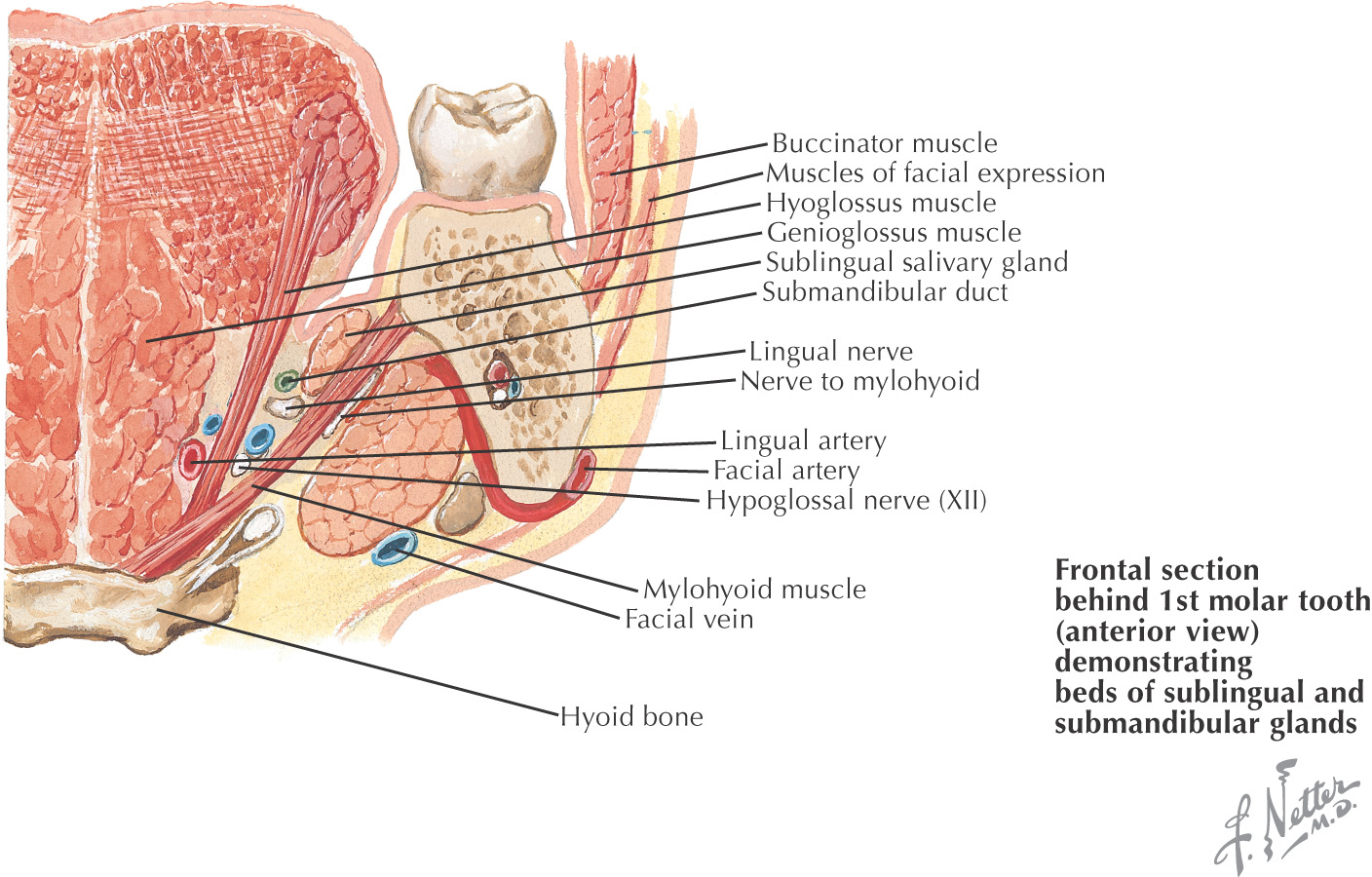
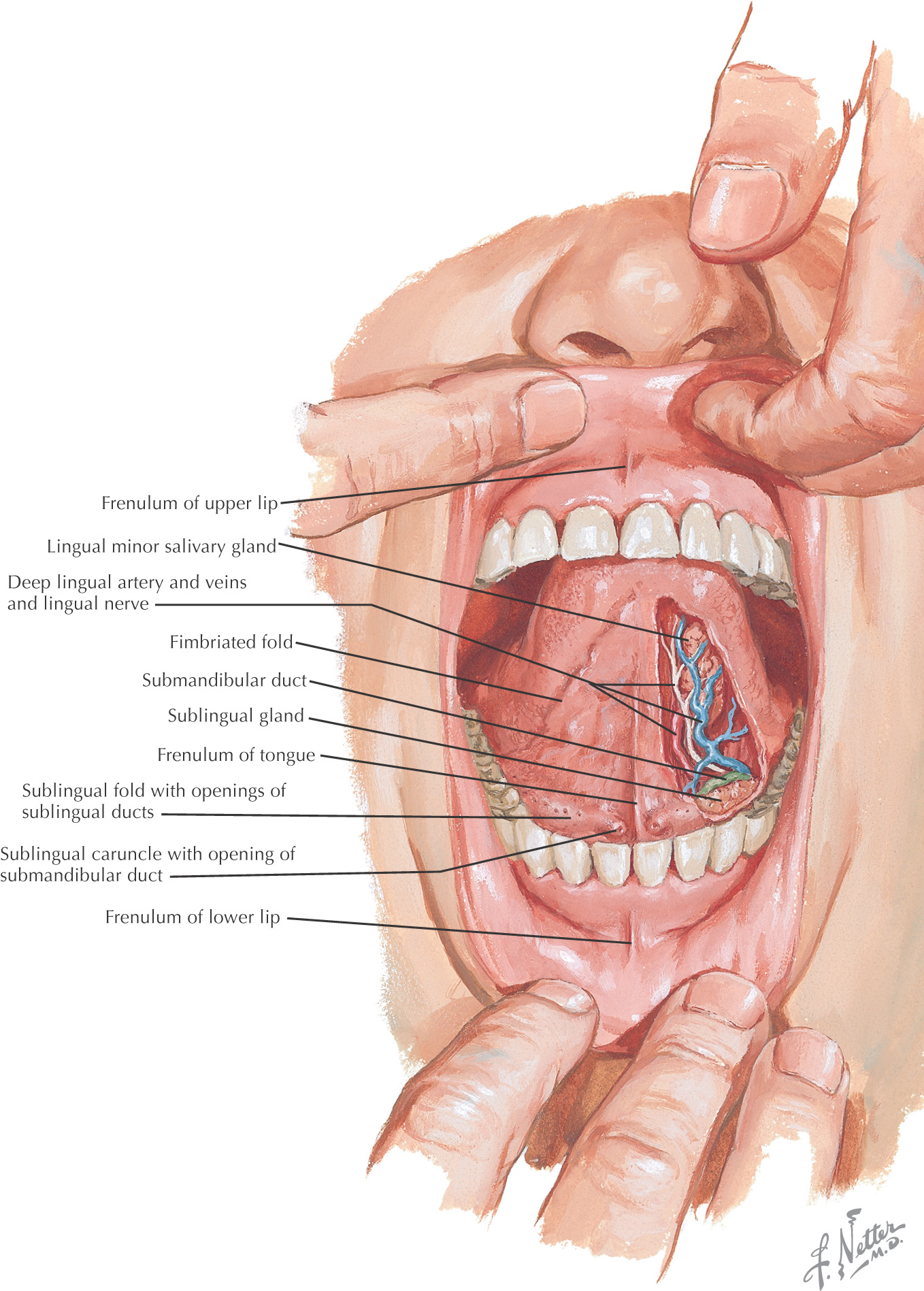
Teeth
GENERAL INFORMATION
Teeth are hard structures attached to the jaws and involved primarily in eating
2 arches contain the teeth:
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


