8
Implant microstructure: implant surfaces
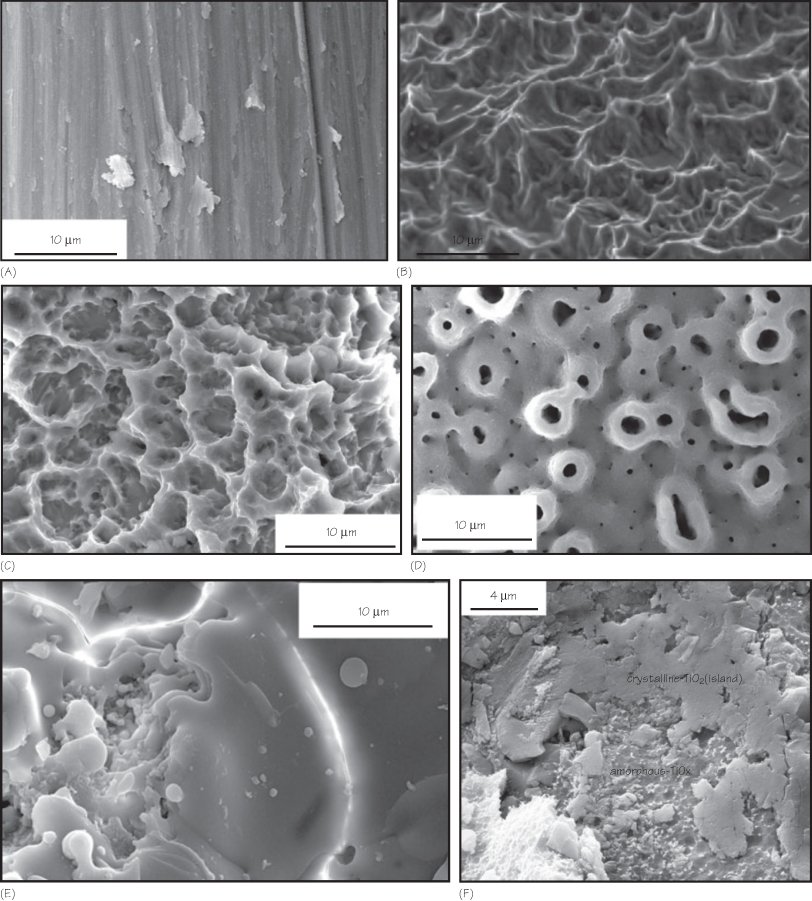
Titanium is commonly used for dental implants. There is ongoing development to obtain better anchorage and surface properties. The first generation of dental implants had smooth machined (turned) surfaces (Fig. 8.1A). The extensive use of dental implants has led to more and more challenging clinical situations, i.e. implant placement in fresh extraction sockets, grafted bone, low bone density, and immediate loading. The attachment of transitory structural proteins, such as fibrin, to the machined surfaces was quite poor, and increased failure rates were reported in challenging clinical situations.
Figure 8.1 Scanning electron microscopy images showing the surface morphology of some commercially available implants. (A) Machined surface
(Jamar et al., 2008).
(B) Osseotite™ surface
(data from www.biomet3i.com.br/implantenanotite_pg04.asp).
(C) SLA™ surface
(Jamar et al., 2008).
(D) TiUnite™ surface
(Jamar et al., 2008).
(E) HA-coated surface
(Jamar et al., 2008).
(F) OsseoSpeed™ surface
(Jamar et al., 2008).
The employment of microtextured-surf/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


