H
Drug Class:
Corticosteroid, synthetic topical
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Reduces or prevents tissue response to the inflammatory process.
Precautions and Contraindications
History of hypersensitivity to halcinonide or other corticosteroids
Serious Reactions
! The serious reactions of long-term therapy and the addition of occlusive dressings are reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing’s syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria.
Dental Considerations
Teach Patient/Family to:
Drug Class:
Topical corticosteroid, group VI potency
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Decreases or prevents tissue response to inflammatory process.
Pharmacokinetics
Variation in absorption among individuals and sites: scrotum 36%, forehead 7%, scalp 4%, forearm 1%.
haloperidol
(Apo-Haloperidol[can], Haldol, Haldol Decanoate, Novo-Peridol[can], Peridol[can], Serenace[aus])
Drug Class:
Indications and Dosages
Drug Interactions of Concern to Dentistry
• Increased sedation: other CNS depressants, alcohol, barbiturate anesthetics, opioid analgesics
• Hypotension, tachycardia: epinephrine
• Increased extrapyramidal effects: phenothiazines and related drugs (haloperidol, droperidol), metoclopramide
• Additive photosensitization: tetracyclines
• Increased anticholinergic effects: anticholinergics
• Suspected increase in neurologic side effects: fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole
Serious Reactions
! Extrapyramidal symptoms appear to be dose related and typically occur in the first few days of therapy. Marked drowsiness and lethargy, excessive salivation, and fixed stare occur frequently.
! Less common reactions include severe akathisia (motor restlessness) and acute dystonias (such as torticollis, opisthotonos, and oculogyric crisis).
! Tardive dyskinesia (tongue protrusion, puffing of the cheeks, chewing or puckering of the mouth) may occur during long-term therapy or after discontinuing the drug and may be irreversible. Elderly female patients have a greater risk of developing this reaction.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Avoid dental light in patient’s eyes; offer dark glasses for patient comfort.
• Assess for presence of extrapyramidal motor symptoms, such as tardive dyskinesia and akathisia. Extrapyramidal motor activity may complicate dental treatment.
• Geriatric patients are more susceptible to drug effects; use lower dose.
• Use vasoconstrictors with caution, in low doses and with careful aspiration. Avoid use of gingival retraction cord with epinephrine.
Consultations:
• Take precautions if dental surgery is anticipated and anesthesia is required.
• Confirm patient’s mental ability to give informed consent.
• Refer to physician if signs of tardive dyskinesia or akathisia are present.
• Physician should be informed if significant xerostomic side effects occur (e.g., increased caries, sore tongue, problems eating or swallowing, difficulty wearing prosthesis) so that a medication change can be considered.
Drug Class:
Gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist
Uses
Palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer and children with central precocious puberty (CPP).
Drug Class:
hydralazine hydrochloride
high-dral′-ah-zeen high-droh-klor′-ide
Drug Class:
Antihypertensive, direct-acting peripheral vasodilator
Indications and Dosages
Precautions and Contraindications
Coronary artery disease, lupus erythematosus, rheumatic heart disease
Serious Reactions
! High dosage may produce lupus erythematosus-like reaction, including fever, facial rash, muscle and joint aches and splenomegaly.
! Severe orthostatic hypotension, skin flushing, severe headache, myocardial ischemia, and cardiac arrhythmias may develop.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Limit dose or avoid vasoconstrictor.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
• Limit use of sodium-containing products, such as saline IV fluids, for patients with a dietary salt restriction.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 Dermatoses
Dermatoses Dermatoses, Corticosteroid-Unresponsive
Dermatoses, Corticosteroid-Unresponsive
 Treatment of Psychotic Disorders
Treatment of Psychotic Disorders Treatment of Nonpsychotic Disorders, Tourette’s Syndrome
Treatment of Nonpsychotic Disorders, Tourette’s Syndrome Mydriasis and Cycloplegia for Refraction
Mydriasis and Cycloplegia for Refraction Uveitis
Uveitis
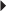 Moderate to Severe Hypertension
Moderate to Severe Hypertension Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Renal Impairment
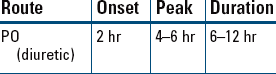
 Edema, Hypertension
Edema, Hypertension Usual Pediatric Dosage
Usual Pediatric Dosage