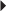G
Drug Class:
Indications and Dosages
 Postherpetic Neuralgia
Postherpetic Neuralgia
Serious Reactions
! Abrupt withdrawal may increase seizure frequency.
! Overdosage may result in diplopia, slurred speech, drowsiness, lethargy, and diarrhea.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Early-morning appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
• Place on frequent recall because of oral side effects.
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Determine type of epilepsy and quality of seizure control.
Drug Class:
Serious Reactions
! Overdose may cause cholinergic crisis, characterized by increased salivation, lacrimation, severe nausea and vomiting, bradycardia, respiratory depression, hypotension, and increased muscle weakness. Treatment usually consists of supportive measures and an anticholinergic such as atropine.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Drug is used early in the disease; ensure that patient or caregiver understands informed consent.
• Place on frequent recall because early attention to dental health is important for Alzheimer’s patients.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
Teach Patient/Family to:
• Encourage effective oral hygiene to prevent soft tissue inflammation.
• Have caregiver assist patient with oral home-care regimen as cognitive ability declines.
• Use powered tooth brush if patient has difficulty holding conventional devices.
• Update health and drug history if physician makes any changes in evaluation or drug regimens.
Drug Class:
Drug Class:
Antiviral, nucleoside analogue
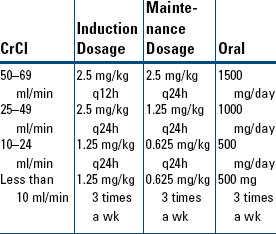
Indications and Dosages
Serious Reactions
! Hematologic toxicity occurs commonly: leukopenia in 29%–41% of patients and anemia in 19%–25%.
! Intraocular insertion occasionally results in visual acuity loss, vitreous hemorrhage, and retinal detachment.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Examine for oral manifestations of opportunistic infection.
• Examine for evidence of oral manifestations of blood dyscrasias (infection, bleeding, poor healing).
• Place on frequent recall to evaluate healing response.
• Consider local hemostasis measures to prevent excessive bleeding.
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular and respiratory side effects.
Drug Class:
Mechanism of Action
A fluoroquinolone that inhibits two enzymes, topoisomerase II and IV, in susceptible microorganisms.
Indications and Dosages
Side Effects/Adverse Reactions
Serious Reactions
! Pseudomembranous colitis as evidenced by severe abdominal pain and cramps, severe watery diarrhea, and fever may occur.
! Superinfection manifested as genital or anal pruritus, ulceration, or changes in oral mucosa and moderate to severe diarrhea may occur.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Determine why patient is taking the drug.
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Examine for oral manifestation of opportunistic infection.
• Advise patient if dental drugs prescribed have a potential for photosensitivity.
• Ruptures of the shoulder, hand, and Achilles tendons requiring surgical repair or resulting in prolonged disability have been reported with use of fluoroquinolones. Question patient about history of side effects associated with fluoroquinolone use.
Drug Class:
Antineoplastic-miscellaneous; epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor
Serious Reactions
! Pancreatitis and ocular hemorrhage occur rarely.
! Hypersensitivity reaction produces angioedema and urticaria.
Dental Considerations
General:
• If additional analgesia is required for dental pain, consider alternative analgesics (NSAIDs) in patients taking opioids for acute or chronic pain.
• This drug may be used in the hospital or on an outpatient basis. Confirm the patient’s disease and treatment status.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patients with respiratory disease.
• Examine for oral manifestation of opportunistic infection.
• Patients may have received other chemotherapy or radiation: confirm medical and drug history.
Drug Class:
Antineoplastic-miscellaneous; nucleoside analogue
Indications and Dosages
Serious Reactions
! Severe myelosuppression, as evidenced by anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia, is a common reaction.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patients with respiratory disease.
• If additional analgesia is required for dental pain, consider alternative analgesics in patients taking narcotics for acute or chronic pain.
• Examine for oral manifestation of opportunistic infection.
• Avoid products that affect platelet function, such as aspirin and NSAIDs.
• This drug may be used in the hospital or on an outpatient basis. Confirm the patient’s disease and treatment status.
• Chlorhexidine mouth rinse prior to and during chemotherapy may reduce severity of mucositis.
• Patient on chronic drug therapy may rarely present with symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing. If dyscrasia is present, caution patient to prevent oral tissue trauma when using oral hygiene aids.
• Palliative medication may be required for management of oral side effects.
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
• Patients may be at risk of bleeding; check for oral signs.
• Oral infections should be eliminated and/or treated aggressively.
Consultations:
• Medical consultation should include routine blood counts including platelet counts and bleeding time.
• Consult physician; prophylactic or therapeutic antiinfectives may be indicated if surgery or periodontal treatment is required.
• Medical consultation may be required to assess immunologic status during cancer chemotherapy and determine safety risk, if any, posed by the required dental treatment.
• Medical consultation may be required to assess disease control and patient’s ability to tolerate stress.
Teach Patient/Family to:
• Be aware of oral side effects.
• Use effective, atraumatic oral hygiene to prevent soft tissue inflammation.
• Report oral lesions, soreness, or bleeding to dentist.
• Prevent trauma when using oral hygiene aids.
• Update health and medication history if physician makes any changes in evaluation or drug regimens; include OTC, herbal, and nonherbal remedies in the update.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses