F
Drug Class:
Mechanism of Action
A synthetic nucleoside that inhibits viral DNA synthesis.
Therapeutic Effect: Suppresses replication of herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus.
Indications and Dosages
Drug Class:
Histamine H2-receptor antagonist
Indications and Dosages
Drug Class:
Precautions and Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to febuxostat or its components
Drugs metabolized by xanthine oxidase (e.g., azathioprine, mercaptopurine, theophylline)
Drug Class:
Anticonvulsant (carbamate derivative)
Indications and Dosages
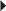 Monotherapy or Adjunctive Therapy in the Treatment of Partial Seizures, with and without Generalization
Monotherapy or Adjunctive Therapy in the Treatment of Partial Seizures, with and without Generalization
Dental Considerations
General:
• Examine for evidence of oral manifestations of blood dyscrasia (infection, bleeding, poor healing).
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
• Determine type of epilepsy, seizure frequency, and quality of seizure control. A stress reduction protocol may be required.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Advise patient if dental drugs prescribed have a potential for photosensitivity.
felodipine
(AGON SR[aus], Felodur ER[aus], Plendil, Plendil ER[aus], Renedil[can])
Do not confuse Plendil with Pletal, or Renedil with Prinivil.
Drug Class:
Precautions and Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, sick sinus syndrome, second- or third-degree heart block
Drug Interactions of Concern to Dentistry
• Decreased effect: NSAIDs, phenobarbital, carbamazepine
• Increased effect: parenteral and inhalational general anesthetics, other drugs with hypotensive actions
• Increased effects of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants, diazepam, midazolam
• Increased plasma levels: itraconazole, erythromycin, carbamazepine
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor cardiac status; take vital signs at each appointment because of cardiovascular side effects. Consider a stress reduction protocol to prevent stress-induced angina during the dental appointment.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension at dismissal.
• Place on frequent recall to monitor gingival condition.
• Limit use of sodium-containing products, such as saline IV fluids, for patients with a dietary salt restriction.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Use vasoconstrictors with caution, in low doses and with careful aspiration. Avoid use of gingival retraction cord with epinephrine.
• Use precaution if sedation or general anesthesia is required; risk of hypotensive episode.
Drug Class:
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Increases VLDL catabolism and reduces total plasma triglyceride levels.
Indications and Dosages
Side Effects/Adverse Reactions
Frequent
Pain, rash, headache, asthenia or fatigue, flu symptoms, dyspepsia, nausea or vomiting, rhinitis
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular and respiratory side effects.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort because of GI side effects of drug.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
• Avoid dental light in patient’s eyes; offer dark glasses for patient comfort.
Drug Class:
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory, propionic acid derivative
Mechanism of Action
An NSAID that produces analgesic and antiinflammatory effects by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis.
Therapeutic Effect: Reduces the inflammatory response and intensity of pain.
Drug Interactions of Concern to Dentistry
• GI bleeding, ulceration: salicylates, alcohol, corticosteroids, other NSAIDs, bisphosphonates
• May decrease effects of fenoprofen: phenobarbital
• Nephrotoxicity: acetaminophen (prolonged use)
• Possible risk of decreased renal function: cyclosporine
• Probable increased bleeding risk: warfarin
• Suspected increased risk for methotrexate toxicity
• First-time users of SSRIs also taking NSAIDs may have a higher risk of GI side effects; avoid use of NSAIDs in these patients
Serious Reactions
! Overdose may result in acute hypotension and tachycardia.
! Rare reactions with long-term use include peptic ulcer disease, GI bleeding, gastritis, severe hepatic reaction (jaundice), nephrotoxicity (hematuria, dysuria, proteinuria) and a severe hypersensitivity reaction (bronchospasm, angioedema).
Dental Considerations
General:
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Avoid prescribing in pregnancy.
• Possibility of cross-allergenicity when patient is allergic to aspirin.
• Severe stomach bleeding may occur in patients who regularly use NSAIDs in recommended doses, when the patient is also taking another NSAID, a blood thinning, or steroid drug, if the patient has GI or peptic ulcer disease, if they are 60 years or older, or when NSAIDs are taken longer than directed. Warn patients of the potential for severe stomach bleeding.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


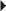 Herpes Zoster
Herpes Zoster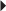 Recurrent Genital Herpes
Recurrent Genital Herpes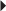 Suppression of Recurrent Genital Herpes
Suppression of Recurrent Genital Herpes Recurrent Herpes Simplex
Recurrent Herpes Simplex Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Renal Impairment Dosage in Hemodialysis Patients
Dosage in Hemodialysis Patients
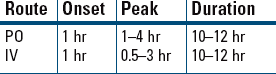
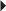 Acute Treatment of Duodenal and Gastric Ulcers
Acute Treatment of Duodenal and Gastric Ulcers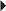 Duodenal Ulcer Maintenance
Duodenal Ulcer Maintenance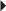 GERD
GERD
 Esophagitis
Esophagitis Hypersecretory Conditions
Hypersecretory Conditions Acid Indigestion, Heartburn (OTC)
Acid Indigestion, Heartburn (OTC) Usual Parenteral Dosage
Usual Parenteral Dosage Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Renal Impairment
 Hyperuricemia in Patients with Gout
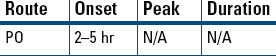
Hyperuricemia in Patients with Gout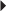 Adjunctive Therapy in the Treatment of Partial Seizures, with and without Generalization
Adjunctive Therapy in the Treatment of Partial Seizures, with and without Generalization

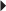 Hypertension
Hypertension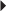 Reduction of Very High Serum Triglyceride Levels in Patients at Risk for Pancreatitis
Reduction of Very High Serum Triglyceride Levels in Patients at Risk for Pancreatitis Hypercholesterolemia
Hypercholesterolemia

 Mild-to-Moderate Pain
Mild-to-Moderate Pain Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis