52 Jaw conditions: Temporomandibular pain-dysfunction
Figure 52.1a TMJ anatomy.
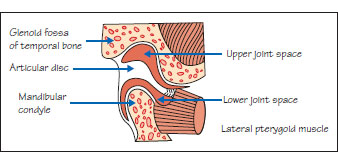
Figure 52.1b Temporomandibular joint.
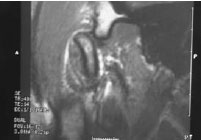
Figure 52.2 Causes of TMJ dysfunction.
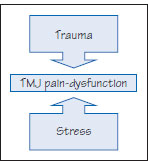
Table 52.1 Main causes of restricted jaw opening.
| Extra-articular | Intra-articular |
| Condylar neck fracture | Ankylosis |
| Coronoid hypertrophy | Condylar intracapsular fracture |
| Fibrosis (scar, scleroderma, submucous fibrosis) | Joint arthritis, dislocation or subluxation |
| Hysteria | |
| Masticatory muscle infection, hematoma or inflammation | |
| Neoplasm | |
| Temporomandibular joint dysfunction | |
| Tetanus | |
| Tetany |
Table 52.2 Investigations used in temporomandibular joint disease.
| Procedure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Arthrography (double contrast) | Provides excellent information | Danger of infection Painful |
| Arthroscopy | Good visualization Minimally invasive |
Requires anesthesia Technically demanding |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | Excellent information without exposure to ionising radiation Non-invasive | Expensive Not universally available |
| Radiography | Simple, can reveal much pathology DPT demonstrates both TMJs CT, especially cone beam, can provide excellent information |
— Ex/> |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


