48 Neurological conditions: Bell palsy, and trigeminal sensory loss
Figure 48.1 Bell palsy of left side.
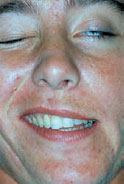
Table 48.1 Main causes of facial palsy.
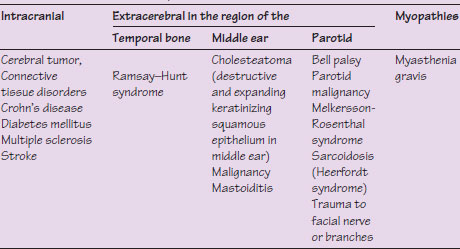
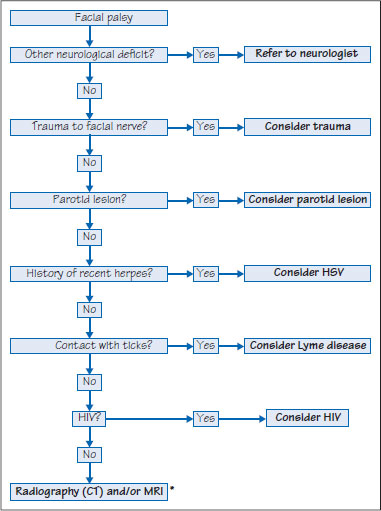
Figure 48.2 Diagnosis of facial palsy. *Brain/skull base.
Box 48.1 Causes of orofacial sensory loss.
Extracranial
Benign tumors
Malignant neoplasms
Osteomyelitis
Trauma (facial or dental)
Intracranial
Amyloidosis
Aneurysms
Cerebrovascular disease
Connective tissue diseases
Diabetes mellitus
HIV/AIDS
Malignant disease
Multiple sclerosis
Sarcoidosis
Sickle cell anemia
Syphilis
Trauma
Vasculitis
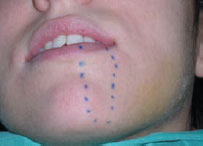
Figure 48.3 Mental nerve sensory loss.
Bell palsy
Definition: An acute lower motor neurone paralysis (palsy) of the face, representing about 50% of all facial palsies (Table 48.1).
Prevalence (approximate): 1 per 10,000.
Age mainly affected: Young adult.
Gender mainly affected: M = F.
Etiopathogenesis: No local or systemic cause can be identified in Bell palsy (it is idiopathic). There is pressure from inflammation and edema on the facial nerve, usually in the stylomastoid canal, with demyelination. Similar lesions are associated:
- Usually with herpes simplex virus (HSV).
- Rarely with another viral infection such as another herpesvirus/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


