47
Life-threatening surgical complications
Life-threatening complications are, fortunately, extremely rare. In any case, the surgeon must have the phone number of the closest emergency medical center. The operating room (OR) should be equipped with monitoring and emergency devices (Fig. 47.1). An automated external defibrillator (AED) and an oxygen unit should be located in the dental setting or in the operating room.
Figure 47.1 Monitoring and emergency devices.
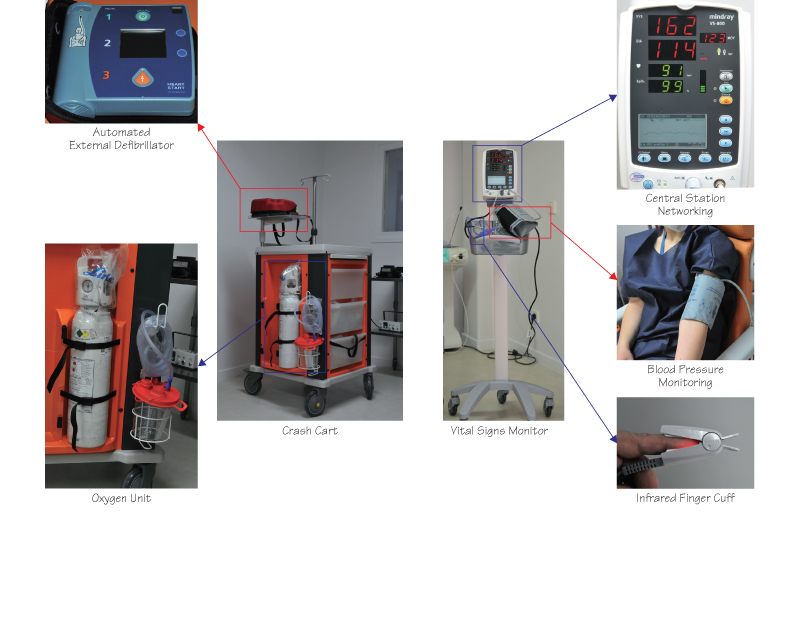
A vital signs monitor that can measure the blood pressure, pulse rate, and blood oxygen saturation is recommended in the OR. A crash cart containing the tools and drugs needed to treat a person in or near cardiac arrest should be located close to the OR. However, the emergency training of the operator may not be sufficient for adequate use of the drugs included in the crash cart.
The most serious complications occur during surgery and may be life-threatening (Box 47.1).
Box 47.1 Life-threatening complications
| Airway obstruction by hemorrhage | Airway obstruction by foreign body aspiration |
| Damage to the mandibular lingual cortical plate is usually described in association with hemorrhagic accidents during dental implant placement. There is much anatomical variation in this area, making identification of a bleeding artery difficult. Floor-of-the-mouth bleeding can lead to respiratory obstruction (a life-threatening complication). Massive internal hemorrhage of the floor of the mouth r/> |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


