SECTION 10 Clients with Special Needs
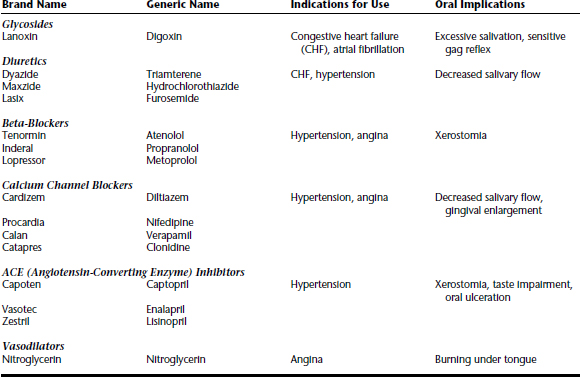
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
Quick Reference—Dental Hygiene Care Implications for Individuals with Cardiovascular Disease
| Disease | Implications for Dental Hygiene Care | Dental Hygiene Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatic heart disease | Special attention to oral self-care practices; self-inflicted bacteremias may occur when oral disease is present. | Careful manipulation of soft tissues during instrumentation; ADA-accepted antibacterial mouth rinse to reduce transient bacteremia. |
| Infective endocarditis |
DIABETES MELLITUS
Adapted from American Diabetes Association: Diabetes symptoms. Available at: http://www.diabetes.org/diabetes-symptoms.jsp. Accessed October 8, 2008.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is characterized by sudden appearance of the following:
| Signs and Symptoms | Hypoglycemia (40-50 mg/dL) | Hyperglycemia (400-600 mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Rapid (minutes) | Slow (days/weeks) |
| Thirst | Absent | Increased |
| Nausea and vomiting | Absent | Frequent |
| Vision | Double | Dim |
| Respirations | Normal | Difficult, hyperventilation |
| Skin | Moist, pale | Hot, dry, flushed |
| Tremors | Frequent | Absent |
| Blood pressure | Normal | Hypotension |
Features of Severe Diabetic Ketoacidosis
| Features | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Symptoms | |
| Thirst | Dehydration |
| Polyuria | Hyperglycemia, osmotic dieresis |
| Fatigue | Dehydration, protein loss |
| Weight loss | Dehydration, protein loss, catabolism∗ |
| Anorexia | ∗ |
| Nausea, vomiting | Ketones,∗ gastric stasis, ileus |
| Abdominal pain | Gastric stasis,∗ ileus, electrolyte deficiency∗ |
| Muscle cramps | Potassium deficiency∗ |
| Signs | |
| Hyperventilation | Acidemia |
| Dehydration | Osmotic diuresis, vomiting |
| Tachycardia | Dehydration |
| Hypotension | Dehydration, acidemia |
| Warm, dry skin | Acidemia (peripheral vasodilation) |
| Hypothermia | Acidemia-induced peripheral vasodilation (when infection is present) |
| Impaired consciousness or coma | Hyperosmolality |
| Ketotic breath | Hyperketonemia (acetone) |
∗ Indicates speculated or unknown cause.
Oral Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
| Clinical Signs and Symptoms | Pathophysiology |
|---|---|
| Salivary and Oral Changes | |
| Xerostomia | Increased fluid loss |
| Bilateral, asymptomatic parotid gland swelling with increased salivary viscosity | |
AGE, Advanced glycation end product.
∗ Although not a complication of diabetes per se, this pattern is seen when the person wants to maintain the weight-loss aspect of diabetes while ignoring or tolerating the hyperglycemic side effects. Client may not be taking proper insulin doses and may not be truthful when asked about this.
† Periodontal disease is seen in up to 40% of diabetic patients. Adequate periodontal therapy may result in decreased insulin requirements.
Adapted from Lalla RV, D’Ambrosio JA: Dental management considerations for the patient with diabetes mellitus, J Am Dent Assoc 132:1425, 2001.
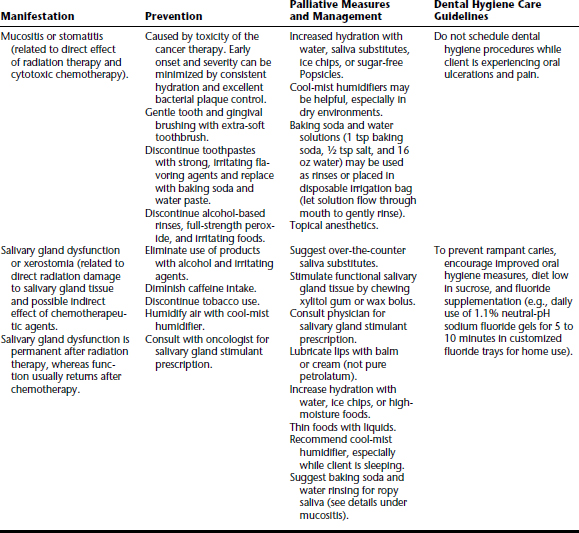
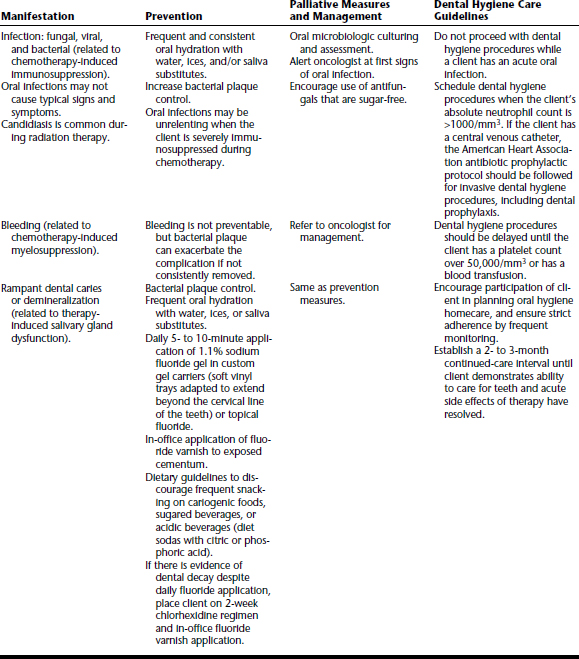
CANCER
HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS
| Condition | Signs and Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Candidiasis | Of the bronchi, trachea, lungs, or esophagus |
| Cervical cancer | Invasive |
| Coccidioidomycosis | Disseminated or extrapulmonary |
| Cryptococcosis | Extrapulmonary |
| Cryptosporidiosis | Chronic intestinal (>1 month duration) |
| Cytomegalovirus disease | Other than liver, spleen, or nodes |
| Cytomegalovirus retinitis | With loss of vision |
| Encephalopathy | HIV-related |
| Herpes simplex | Chronic ulcer(s) (>1 month duration), or bronchitis, pneumonitis, or esophagitis |
| Histoplasmosis | Disseminated or extrapulmonary |
| Isosporiasis | Chronic intestinal (>1 month duration) |
| Kaposi’s sarcoma | Intraoral or extraoral |
| Lymphoma |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses