42
Bone augmentation: alveolar distraction osteogenesis
Rationale
Distraction osteogenesis involves gradual, controlled displacement of surgically created fractures which results in simultaneous expansion of soft tissue and bone volume. The regeneration chamber created by the displacement of the bone segment is gradually filled with immature non-calcified bone that calcifies during a subsequent fixation period.
The principles of distraction osteogenesis have been adapted to implant surgery to increase alveolar bone volume (Chin, 1999).
Products and Devices
Various distraction devices are commercially available (Fig. 42.1). Basically, the device consists of three components (Fig. 42.2):
- a threaded rod, which activates the device by turning the hexagonal head
- a transport plate, which is attached to the transport segment
- a stabilizing plate, which is attached to the bone bordering the horizontal osteotomy.
Figure 42.1 The three components of a miniature intraoral distraction device.
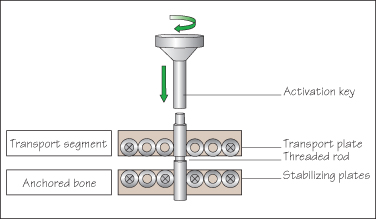
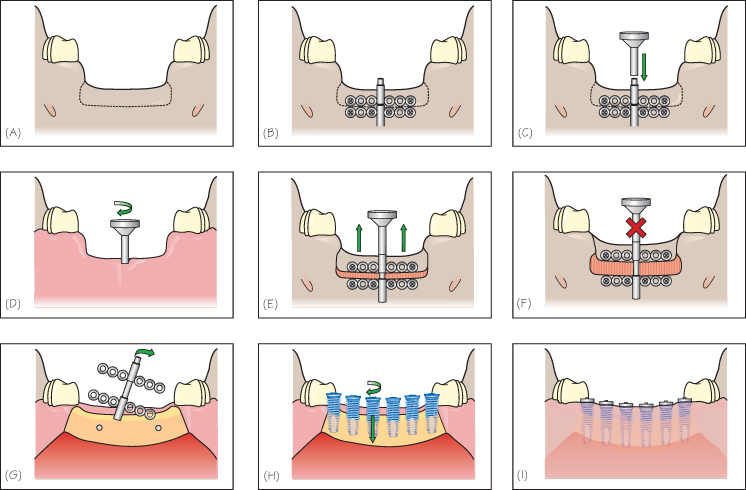
Figure 42.2 Alveolar distraction technique at the mandible. (A) Osteotomy is performed. (B) The stabilizing plate is fixed to the jaw bone and the transport plate is secured to the transport fragment. (C) The activation key is slightly turned to ensure the mobility of the transport fragment. (D) The distractor is activated with the key by the patient or a family member. (E) The transport segment is slowly mobilized in a coronal direction. (F) A consolidation period in static mode allows the calcification of the regeneration chamber. (G) The distractor is removed. (H) The implants are inserted at the same time. (I) The flap is secured around the implants neck. A two-stage procedure can be also performed.
Technical Procedures
The segment to be distracted has to be at least 3 mm in height.
- Buccal full-thickness flap reflections to allow proper visualization of the ridge during the osteotomy.
- Intimate adaptation of the fixation plates
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


