41 Salivary conditions: Dry mouth
Figure 41.1 Dry mouth: cheilitis.
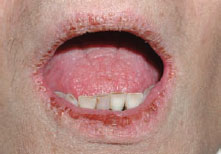
Figure 41.2 Dry mouth: candidosis.
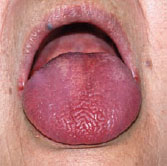
Figure 41.3 Dry mouth: angular stomatitis.
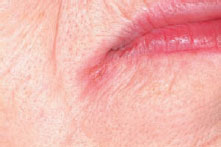
Figure 41.4 Dry mouth: caries.
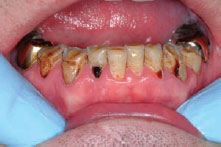
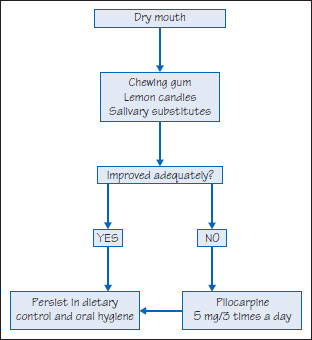
Figure 41.5 Dry mouth management.
Dry mouth (xerostomia; hyposalivation) is a common subjective complaint but objective evidence of hyposalivation is less common, and the complaint is sometimes perceived rather than real.
The main causes are iatrogenic (anticholinergic or sympathomimetic drugs, e.g. tricyclics, phenothiazines and antihistamines; irradiation of salivary glands including incidentally by 131 iodine therapy; cytotoxic agents; or graft-versus-host disease) and non-iatrogenic (dehydration, e.g. uncontrolled diabetes; Sjögren’s syndrome; sarcoidosis; HIV disease, rarely cystic fibrosis or salivary gland aplasia) (Table 41.1). Sialosis, calculi or removal of a single major gland rarely cause xerostomia.
Sequelae of hyposalivation include caries, candidosis and />
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


