40 Salivary conditions: Salivary swelling and salivary excess
Figure 40.1 Diagnosis of salivary swelling.
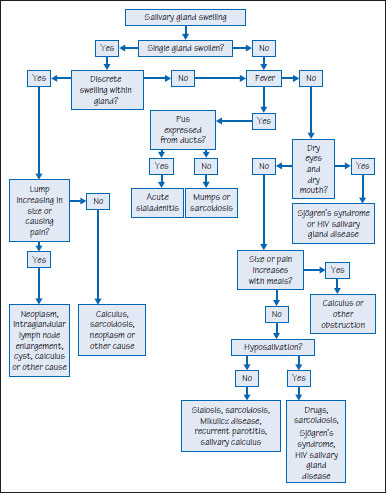
Figure 40.2 Causes of drooling.
Figure 40.3 Drooling in learning impairment.
Box 40.1 Causes of excess saliva.
Psychogenic (usually)
Painful lesions in the mouth
Drugs or poisoning
Foreign bodies in the mouth
Poor neuromuscular coordination
Others
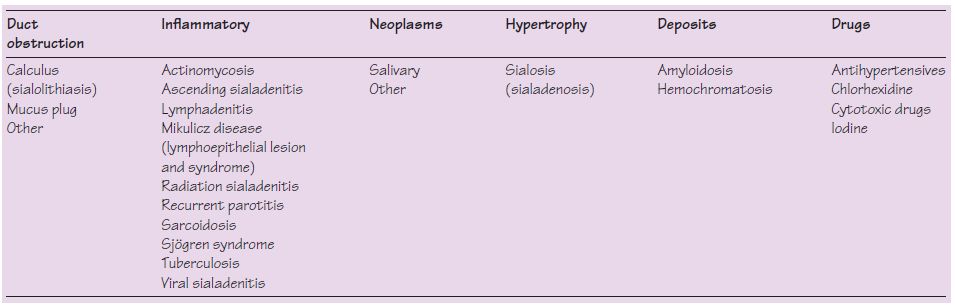
Table 40.1 Causes of salivary gland swelling.
Perhaps 700–1000 ml of saliva are produced each day, most by the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands (major salivary glands).
Parotid saliva makes the bulk of the stimulated saliva and the submandibular gland produces 70% of resting saliva. Mucus glands (minor salivary glands) in the lips, palate and elsewhere produce mainly mucin and immunoglobulin A (IgA). Functions of saliva include facilitating lubrication in the mouth, pharynx and esophagus, and assisting swallowing, speech, digestion (amylase), and defense against infections (mainly IgA, lysozyme and histatins).
Saliva is produced in response to taste, masticatory or psychogenic stimuli. Con/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


