40
Bone augmentation: split osteotomy (split ridge technique)
Rationale
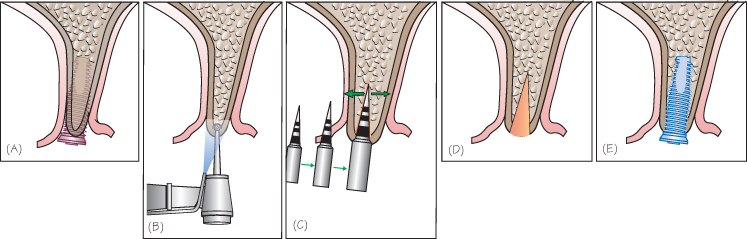
Split ridge and expansion techniques are effective for the correction of moderately resorbed edentulous ridges in selected cases. Transverse expansion is based on osseous plasticity obtained by corticotomy. It progressively allows for an adequate transversel intercortical diameter large enough to insert one or several dental implants. The gap created by sagittal osteotomy expansion undergoes spontaneous ossification, following a mechanism similar to that occurring in fractures (Fig. 40.1).
Figure 40.1 Ridge splitting technique for single dental implant placement at the maxilla. (A) The dental implant cannot be placed due to the knife-edge alveolar bone morphology. (B) Lamellar cortical splitting is initiated by using a bur. (C) A set of chisels of increasing width is used to split the alveolar ridge. (D) The gap created by splitting is left empty. (E) Transverse expansion allows for immediate dental implant installation.
Products and Devices
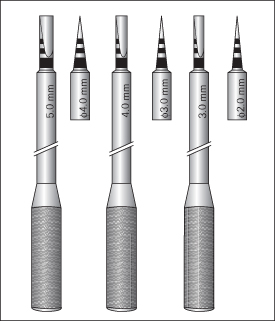
Various ridge splitting/expanding chisels (from 3 mm to 6 mm) are designed to define the appropriate shape and size of the osteotomy (Fig. 40.2). Ultrasonic units may facilitate and improve the safety of the procedure.
Figure 40.2 Set of chisels for split osteotomy.
Technical Procedure (Fig. 40.3)
- Full-thickness crestal incision with vertical releasing incisions one tooth further than the site being treated.
- Elevation of a mucoperiosteal flap palatally and buccally to expose the bone ridge.
- Lamellar cortical splitting is initiated by one horizontal crestal osteotomy using a diamond disk, a bur or, preferably, a piezosurgery tip. The longitudinal split can be limited by placing transverse cuts in the bone. Two additional vertical cuts, 2 mm distal to the site of implantation and 1 mm mesial to the adjacent teeth, can be performed to facilitate the expansion.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


