39 White lesions: Hairy leukoplakia, lichen planus
Figure 39.1 Hairy leukoplakia.
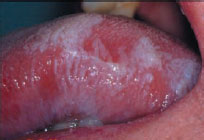
Figure 39.2 Lichen planus and lichenoid lesions etiology.
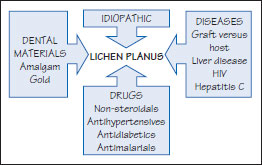
Figure 39.3 Lichen planus pathogenesis.
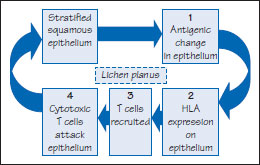
Figure 39.4 Lichen planus.
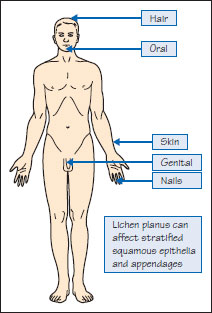
Figure 39.5a Lichen planus.
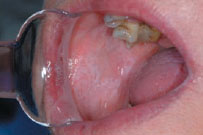
Figure 39.5b Lichen planus.
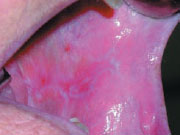
Figure 39.6 Lichen planus.
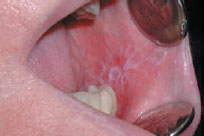
Figure 39.7 Lichen planus.
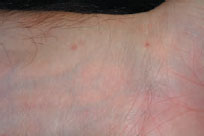
Figure 39.8 Histological features of LP.
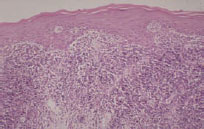
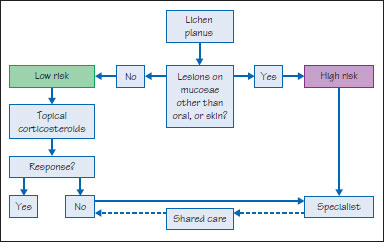
Figure 39.9 Lichen planus management.
Hairy leukoplakia
Definition: Bilateral white tongue lesions.
Prevalence (approximate): Uncommon.
Age mainly affected: Adult.
Gender mainly affected: M > F.
Etiopathogenesis: Epstein-Barr virus, usually in an immunocompromised patient, especially in HIV/AIDS. Cases have been reported in patients with hematological malignancies or organ transplants.
Diagnostic features
Clinical features
Oral: Vertically corrugated symptomless white lesions on the margins, dorsal or ventral surfaces of the tongue (Figure 39.1).
Extraoral: Maybe lesions of HIV/AIDS or immunodeficiency.
Differential diagnosis: Frictional keratosis, lichen planus, tobaccoassociated leukoplakia, geographic tongue.
Investigations
- HIV serotest.
- Biopsy/histopathology shows irregular parakeratosis and vacuolated cells with dark pyknotic nuclei (koilocytes-like) in the stratum spinosum.
Epithelial nuclei stain positively immunocytochemically and in situ hybridization for EBV capsid antigen.
Managem/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


