35 Ulcers and erosions: Infections
Figure 35.1 Acute necrotizing gingivitis.
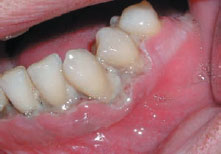
Figure 35.2 Secondary syphilis.
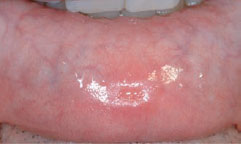
Figure 35.3 Rash of secondary syphilis.
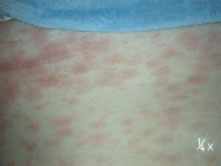
Figure 35.4 Syphilis 20 ×.
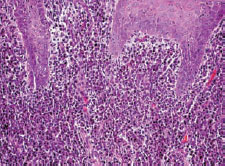
Herpesviruses and many other viruses can cause mouth ulceration (see Chapters 9 and 10) typically in children, and present with multiple ulcers and an acute febrile illness. EBV can also cause ulceration (see Chapter 60). Acute necrotizing gingivitis is a bacterial infection seen mainly where hygiene and/or nutrition are poor or in HIV/AIDS, especially in resource-poor areas. Chronic bacterial (e.g. syphilis, tuberculosis), fungal (e.g. histoplasmosis) and parasitic (e.g. leishmaniasis) infections may cause chronic ulceration, mainly in adults, again especially in resource-poor areas and in HIV/AIDS.
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFM; vesicular stomatitis with exanthem)
Definition: Oropharyngeal vesicles and ulcers, with vesicles on hands and/or feet.
Prevalence (approximate): Uncommonly reported.
Age mainly affected: Children; epidemics common in Asia and Australia. Sometimes seen in immunocompromised adults.
Gender mainly affected: M = F.
Etiopathogenesis: Picornaviridae (Coxsackie virus A16 usually, but A5, A7, A9 and A10 or B9, or other enteroviruses).
Diagnostic features
History
Oral: Infection may be subclinical. The incubation period is up to a week.
One or two days after fever onset, painful mouth sores develop.
Extraoral: Fever, headache, malaise, anorexia, diarrhea.
Clinical features
Oral: Shallow, painful, small ulcers mainly on tongue or buccal mucosa.
Extraoral: Non-itchy rash develops over 1–2 days on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, sometimes also on buttocks and/or genitalia. The rash is of flat or raised red spots, sometimes with small, painful vesicles.
Differential diagnosis: Herpetic stomatitis; herpangina.
Investigations
This is a clinical diagnosis. Serology is confirmatory but rarely required.
Management
No specific treatment is available. Mouth lesions can be treated symptomatically. Skin vesicles heal />
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


