34 Ulcers and erosions: Blood diseases, gastrointestinal disorders
Figure 34.1 Leukemia.
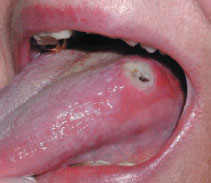
Figure 34.2 Aphthous-like ulcers in celiac disease.
Figure 34.3 Unilateral angular stomatitis.
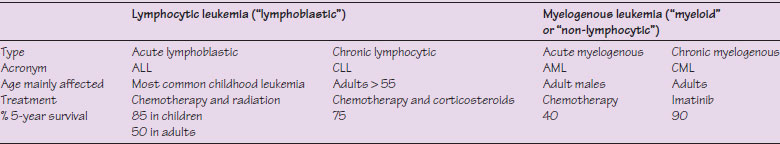
Table 34.1 Leukemias.
Aphthous-like and other mouth ulcers may be seen in disorders affecting the blood or gastrointestinal system.
Blood diseases
Ulcers may be seen in anemia and leukocyte defects (neutropenia, agranulocytopenia, leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes or chronic granulomatous disease). In leukocyte defects there may also be severe gingivitis, rapid periodontal breakdown, as well as infections – mainly viral and fungal – and lymphadenopathy. Chemotherapy treatment and hematopoietic stem cell (bone marrow) transplantation can also produce oral ulceration and infections.
Leukemias
Definition: Malignant leukocyte proliferation (Greek leukos, “white”; aima, “blood”); there are several types (Table 34.1).
Prevalence (approximate): Uncommon.
Age mainly affected: 50–60% of leukemias are acute, affect mainly children or young adults. CML is seen mainly in middle-aged adults; CLL is seen mainly in the elderly.
Gender mainly affected: M = F.
Etiopathogenesis: Ionizing radiation, immunosuppression, chemicals (e.g. hair dyes; benzene), chromosomal disorders (e.g. Down syndrome), retroviruses (rarely). Fanconi anemia predisposes to AML.
Diagnostic features
History
Oral: Ulcers, infections.
Extraoral: Pallor, fatigue, bruising, infections.
Clinical features
Oral: Oral purpura (petechiae and ecchymoses) and spontaneous gingival hemorrhage.
Mouth ulcers: Associated with cytotoxic therapy, with viral, bacterial or fungal infection, or non-specific (



