C
Drug Class:
Dopamine agonist; antihyperprolactinemic
Mechanism of Action
Agonist at dopamine D2 receptors, suppressing prolactin secretion.
Therapeutic Effects: Shrinks prolactinomas, restores gonadal function.
Indications and Dosages
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Determine why patient is taking the drug.
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment for cardiovascular side effects.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Use precaution if sedation or general anesthesia is required; risk of hypotensive episode.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
Teach Patient/Family:
• When chronic dry mouth occurs, advise patient to:
• Avoid mouth rinses with high alcohol content because of drying effects.
• Use daily home fluoride products for anticaries effect.
• Use sugarless gum, frequent sips of water, or saliva substitutes.
• Update health and medication history if physician makes any changes in evaluation or drug regimens; include OTC, herbal, and nonherbal remedies in the update.
Drug Class:
Synthetic polypeptide calcitonins
Indications and Dosages
Drug Class:
Fat-soluble vitamin, vitamin D analogue
Indications and Dosages
Precautions and Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to calcitriol or other vitamin D products or analogues
Drug Interactions of Concern to Dentistry
• Aluminum-containing antacid (long-term use): May increase aluminum concentration and aluminum bone toxicity.
• Calcium-containing preparations, thiazide diuretics: May increase the risk of hypercalcemia.
• Didanosine: May alter intestinal phosphate absorption; increased risk of hypermagnesemia.
• Digoxin: May increase risk of arrhythmia.
• Magnesium-containing antacids: May increase magnesium concentration.
• Mineral oil: May cause fat-soluble vitamin malabsorption.
• Vitamin D analogues: Increased risk of hypervitaminosis D, hypercalcemia.
Serious Reactions
! Early signs of overdosage are manifested as weakness, headache, somnolence, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, constipation, muscle and bone pain, and metallic taste sensation.
! Later signs of overdosage are evidenced by polyuria, polydipsia, anorexia, weight loss, nocturia, photophobia, rhinorrhea, pruritus, disorientation, hallucinations, hyperthermia, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor the patient’s BUN, serum alkaline phosphatase, serum calcium, serum creatinine, serum magnesium, serum phosphate, and urinary calcium levels. Know that the therapeutic serum calcium level is 9 to 10 mg/dl.
• Estimate the patient’s daily dietary calcium intake.
• Encourage the patient to maintain adequate fluid intake.
• Avoid bright light in the patient’s eyes; offer dark glasses for patient comfort.
• Consider semisupine position if the patient experiences GI discomfort.
Teach Patient/Family to:
• Encourage the patient to consume foods rich in vitamin D including eggs, leafy vegetables, margarine, meats, milk, vegetable oils, and vegetable shortening.
• Warn the patient not to take mineral oil during calcitriol therapy.
• Advise the patient receiving chronic renal dialysis not to take magnesium-containing antacids during calcitriol therapy.
Drug Class:
Angiotensin II (AT1) receptor antagonist, antihypertensive
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Causes vasodilation, decreases peripheral resistance, and decreases B/P.
Serious Reactions
! Overdosage may manifest as hypotension and tachycardia. Bradycardia occurs less often.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment in patients with history of hypertension.
• Evaluate respiration characteristics and rate.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
• Observe appropriate limitations of vasoconstrictor doses.
• Limit use of sodium-containing products, such as saline IV fluids, for those patients with a dietary salt restriction.
• Stress from dental procedures may compromise cardiovascular function; determine patient risk.
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
• Use precaution if sedation or general anesthesia is required; risk of hypotensive episode.
Drug Class:
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Interferes with DNA synthesis, RNA processing, and protein synthesis.
Serious Reactions
! Serious reactions may include myelosuppression (evidenced by neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia), cardiovascular toxicity (marked by angina, cardiomyopathy, and deep vein thrombosis), respiratory toxicity (marked by dyspnea, epistaxis, and pneumonia), and lymphedema.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
• Patients taking opioids for acute or chronic pain should be given alternative analgesics for dental pain.
• Short appointments and a stress reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
• Question patient about tolerance of NSAIDs or aspirin related to GI side effects of drug.
• Consider local hemostasis measures to control and prevent excessive bleeding.
• Examine for oral manifestation of opportunistic infection.
• Be aware of oral side effects and potential sequelae.
• Palliative medication may be required for management of oral side effects.
• Avoid dental light in patient’s eyes; offer dark glasses for patient comfort.
• Prophylactic or therapeutic antibiotics may be indicated to prevent or treat infection if surgery or periodontal debridement is required.
Consultations:
• In a patient with symptoms of blood dyscrasias, request a medical consultation for blood studies and postpone treatment until normal values are reestablished.
• Medical consultation may be required to assess disease control and patient’s ability to receive dental treatment.
• Consultation with physician may be necessary if sedation or general anesthesia is required.
Teach Patient/Family to:
• Prevent trauma when using oral hygiene aids.
• See dentist immediately if secondary oral infection occurs.
• Encourage effective oral hygiene to prevent soft tissue inflammation.
• Report oral lesions, soreness, or bleeding to dentist.
• Update health and drug history if physician makes any changes in evaluation or drug regimens.
caprylidene
Drug Class:
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Dietary management for the treatment of symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Precautions and Contraindications
Allergy to milk or soy (contains caseinate, whey, and lecithin) and/or hypersensitivity to palm or coconut oil. Use with caution in patients at risk for ketoacidosis (alcoholics, poorly controlled diabetics) and in patients with a history of GI inflammatory conditions (IBS, diverticulitis, chronic gastritis, GERD). May increase serum triglycerides. May increase BUN, uric acid, or serum creatinine.
Drug Class:
Drug Class:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor
Indications and Dosages
Serious Reactions
! Excessive hypotension (“first-dose syncope”) may occur in patients with CHF and in those who are severely salt and volume depleted.
! Angioedema (swelling of face and lips) and hyperkalemia occur rarely.
! Agranulocytosis and neutropenia may be noted in those with collagen vascular disease, including scleroderma and systemic lupus erythematosus, and impaired renal function.
! Nephrotic syndrome may be noted in those with history of renal disease.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Observe appropriate limitations of vasoconstrictor doses.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Limit use of sodium-containing products, such as saline IV fluids, for patients with a dietary salt restriction.
• Stress from dental procedures may compromise cardiovascular function; determine patient risk.
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
Consultations:
• Medical consultation may be required to assess patient’s ability to tolerate stress.
• In a patient with symptoms of blood dyscrasias, request a medical consultation for blood studies and postpone dental treatment until normal values are reestablished.
• Take precautions if dental surgery is anticipated and sedation or general anesthesia is required; risk of hypotensive episode.
Drug Class:
Antiglaucoma agent, ophthalmic; Antihypertensive agent, ocular, postsurgical; Miotic
Precautions and Contraindications
Acute iritis, hypersensitivity to carbachol or any component of the formulation
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 Hyperprolactinemia (Idiopathic or Primary Pituitary Adenomas)
Hyperprolactinemia (Idiopathic or Primary Pituitary Adenomas) Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
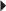 Skin Testing Before Treatment in Patients with Suspected Sensitivity to Calcitonin-Salmon
Skin Testing Before Treatment in Patients with Suspected Sensitivity to Calcitonin-Salmon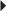 Paget’s Disease
Paget’s Disease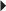 Osteoporosis Imperfecta
Osteoporosis Imperfecta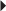 Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia Renal Failure
Renal Failure Hypoparathyroidism/Pseudohypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism/Pseudohypoparathyroidism Psoriasis, Mild-Moderate Plaque
Psoriasis, Mild-Moderate Plaque Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets
Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets
Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets
 Hypertension Alone or in Combination with Other Antihypertensives
Hypertension Alone or in Combination with Other Antihypertensives
 Metastatic Breast Cancer, Colon Cancer
Metastatic Breast Cancer, Colon Cancer
 Dietary Management of Metabolic Processes Associated with Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease
Dietary Management of Metabolic Processes Associated with Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment of Neuralgia, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis
Treatment of Neuralgia, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis Hypertension
Hypertension CHF
CHF Post-Myocardial Infarction, Impaired Liver Function
Post-Myocardial Infarction, Impaired Liver Function Diabetic Nephropathy Prevention of Kidney Failure
Diabetic Nephropathy Prevention of Kidney Failure
 Glaucoma
Glaucoma Miosis, Ophthalmic Surgery
Miosis, Ophthalmic Surgery