28 Swellings: Reactive lesions
Figure 28.1 Denture induced hyperplasia.
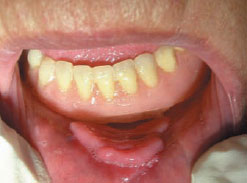
Figure 28.2 Inflammatory fibrous epulis.
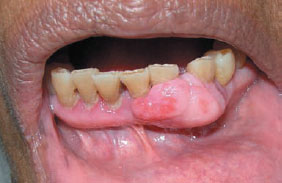
Figure 28.3 Fibrous lump.
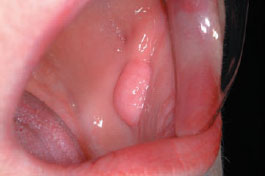
Figure 28.4 Fibrous hyperplasia.
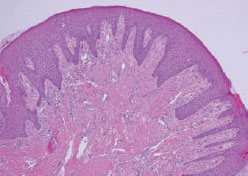
Figure 28.5 Pyogenic granuloma.
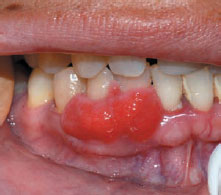
Figure 28.6 Pyogenic granuloma.
Denture-induced hyperplasia (epulis fissuratum)
Definition: Hyperplasia related to an overextended denture flange.
Prevalence (approximate): Common.
Age mainly affected: Middle-aged or older patients.
Gender mainly affected: F > M.
Etiopathogenesis: Where a denture flange irritates the vestibular mucosa, an ulcer and then a linear reparative process may be initiated. In time, an elongated fibroepithelial enlargement may develop. Such a lesion (once called a denture granuloma) is little different in structure from a fibroepithelial polyp.
Diagnostic features
History
Oral: Usually a symptomless lump.
Clinical features
Oral: Usually related to ill-fitting lower complete denture, especially anteriorly. Typically a lump with a smooth pink surface lying parallel with the alveolar ridge and sometimes grooved or ulcerated by the denture flange (Figure 28.1). Several leaflets with a fairly firm consistency may develop.
Differential diagnosis: fibrous lumps and neoplasms.
Management
Relieve the denture flange but, if this does not induce the lesion to regress within two to three weeks, the lump should be excised and examined histologically.
Prognosis
Good.
Fibroepithelial polyp (fibrous lump)
Fibrous lumps should not be/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


