20
Patient evaluation: imaging techniques
With the development of implant therapy, many imaging devices have been suggested. The objective of the clinician is to select the most appropriate technique to obtain optimal information with the minimal radiation dose and the best financial cost.
ALARA principle: as low as reasonably achievable. The risk-benefit ratio must be evaluated to minimize the radiation dose, while obtaining the most reliable information.
Imaging Techniques (Table 20.1)
Radiography
Panoramic radiography is a good, quite systematic screening examination in implant therapy. It allows global visualization of many anatomical structures. Its drawbacks include major distortion and variable magnification, making it inappropriate for accurate measurements.
Table 20.1 Characteristics of different imaging techniques
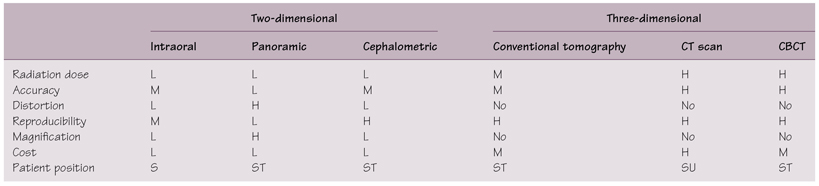
CBCT, cone beam computed tomography; CT, computed tomography; H, high; L, low; M, moderate; S, seated; ST, standing; SU, supine.
Intraoral (periapical) radiography, performed with the parallel technique, provides a good deal of information with a minimum radiation dose. It is the examination of choice for dental/periodontal preoperative evaluation and for implant monitoring. If intraoral positioning of the detector is not possible, panoramic radiography can be an alternative.
Cephalometric lateral radiography is indicated to evaluate the sagittal interjaw relationship, the soft tissue profile, and the anterior bone width.
Tomography
Tomography is the only way to precisely evaluate bone dimensions. Images perpendicular to the dental arch (cross-sectional images) allow measurement of bone width. The absence of deformation and a constant magnification allow direct measurements.
The presence of artifacts with metallic elements affects the quality of images and makes this technique unsuitable for the control of osseointegration.
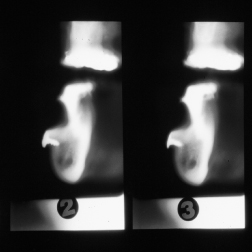
Conventional tomography (Fig. 20.1) can be used for examination of a limited zone, with relatively low radiation dose and cost. It provides thick cross-sectional images, which imply superposition of adjacent structures. Interpretation is not easy without proper training.
Figure 20.1 Conventional tomography image.
Co/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


