R
Drug Class:
Antisecretory, proton pump inhibitor
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort because of GI side effects of disease.
• Patients with gastroesophageal reflux may have oral symptoms, including burning mouth, secondary candidiasis, and signs of tooth erosion.
• Question the patient about tolerance of NSAIDs or aspirin related to GI problems.
Drug Class:
Mechanism Of Action
A selective estrogen receptor modulator that affects some receptors like estrogen.
Therapeutic Effect: Like estrogen, prevents bone loss and improves lipid profiles.
Drug Class:
Drug Class:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor
Indications And Dosages
Serious Reactions
! Excessive hypotension (“first-dose syncope”) may occur in patients with CHF and in those who are severely salt or volume depleted.
! Angioedema and hyperkalemia occur rarely.
! Agranulocytosis and neutropenia may be noted in those with collagen vascular disease, including scleroderma and systemic lupus erythematosus, and impaired renal function.
! Nephrotic syndrome may be noted in those with history of renal disease.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular and respiratory side effects.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Limit use of sodium-containing products, such as saline IV fluids, for patients with a dietary salt restriction.
• Use vasoconstrictors with caution, in low doses, and with careful aspiration.
• Stress from dental procedures may compromise cardiovascular function; determine patient risk.
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
Consultations:
• Medical consultation may be required to assess patient’s ability to tolerate stress.
• In a patient with symptoms of blood dyscrasias, request a medical consultation for blood studies and postpone dental treatment until normal values are reestablished.
• Take precautions if dental surgery is anticipated and sedation or general anesthesia is required; risk of hypotensive episode.
ranitidine hydrochloride/ranitidine bismuth citrate
ra-ni′-ti-deen high-droh-klor′-ide/ra-ni′-ti-deen biss′-mooth sih′-trate
Drug Class:
H2 histamine receptor antagonist
Mechanism Of Action
An antiulcer agent that inhibits histamine action at H2 receptors of gastric parietal cells.
Indications And Dosages
Drug Class:
Drug Interactions Of Concern To Dentistry
• Opioids (particularly meperidine): potentially fatal interaction; serotonin syndrome
• St. John’s wort, cyclobenzaprine: contraindicated
• Dextromethorphan: concurrent use may cause psychosis or bizarre behavior; contraindicated
• MOA inhibitors: may increase the risk of hypertensive crisis
• Potent CYP1A2 inhibitors (cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, fluvoxamine): may increase levels of rasagiline
• CYP inducers: may reduce rasagiline levels
• Sympathomimetics, tyramine-containing foods: may increase the risk of hypertensive crisis
• Antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs): increased risk of serotonin syndrome
Serious Reactions
! Rasagiline may cause low blood pressure; increased risk of postural hypotension.
! May cause or exacerbate hallucinations and psychotic behavior.
! Symptoms of overdose may vary from CNS depression, characterized by sedation, apnea, cardiovascular collapse, and death, to severe paradoxical reactions, such as hallucinations, tremor, and seizures.
! Other serious effects may include involuntary movements, impaired motor coordination, loss of balance, blepharospasm, facial grimaces, feeling of heaviness in the lower extremities, depression, nightmares, delusions, overstimulation, sleep disturbance, and anger.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Assess for presence of extrapyramidal motor symptoms, such as tardive dyskinesia and akathisia. Extrapyramidal motor activity may complicate dental treatment.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
Drug Class:
Oral antidiabetic, meglitinide class
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• If dentist prescribes any of the drugs listed in the drug interactions section, monitor patient blood sugar levels.
• Be prepared to manage hypoglycemia.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort because of GI side effects of drug.
• Ensure that patient is following prescribed diet and regularly takes medication.
• Place on frequent recall to evaluate healing response.
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required.
• Diabetics may be more susceptible to infection and have delayed wound healing.
Drug Class:
Drug Class:
Precautions And Contraindications
Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to retapamulin or components of the formulation.
Drug Class:
Pharmacokinetics
Rapidly cleared from plasma. Eliminated primarily by the liver and kidney. Half-life: 13–16 min.
Serious Reactions
! Bleeding at internal sites may occur, including intracranial, retroperitoneal, GI, GU, and respiratory sites.
! Lysis or coronary thrombi may produce atrial or ventricular arrhythmias and stroke.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Acute-use drug for use in hospitals or emergency rooms.
• Patients are at risk for bleeding, check for oral signs.
• Monitor and record vital signs.
• Avoid products that affect platelet function, such as aspirin and NSAIDs.
• Patients who have been treated with this drug may present with cardiovascular disease or stroke, review medical and drug history.
Consultations:
• Medical consultation should include routine blood counts including platelet counts and bleeding time.
• In a patient with symptoms of blood dyscrasias, request a medical consultation for blood studies and postpone treatment until normal values are reestablished.
• Medical consultation may be required to assess disease control and patient’s ability to tolerate stress.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 GERD
GERD Duodenal Ulcer
Duodenal Ulcer NSAID-Induced Ulcer
NSAID-Induced Ulcer Pathologic Hypersecretory Conditions
Pathologic Hypersecretory Conditions Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori Infection
 Prevention or Treatment of Osteoporosis
Prevention or Treatment of Osteoporosis
 HIV Infection
HIV Infection Adult
Adult

 Hypertension (Monotherapy)
Hypertension (Monotherapy) Hypertension (in Combination with Other Antihypertensives)
Hypertension (in Combination with Other Antihypertensives) CHF
CHF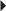 Risk Reduction for MI Stroke
Risk Reduction for MI Stroke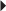 Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Renal Impairment
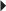 Duodenal Ulcers, Gastric Ulcers, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Duodenal Ulcers, Gastric Ulcers, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease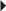 Duodenal Ulcers Associated with H. pylori Infection
Duodenal Ulcers Associated with H. pylori Infection Erosive Esophagitis
Erosive Esophagitis Hypersecretory Conditions
Hypersecretory Conditions OTC Use
OTC Use Usual Parenteral Dosage
Usual Parenteral Dosage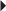 Usual Neonatal Dosage
Usual Neonatal Dosage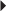 Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Renal Impairment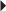 Parkinson’s Disease, Monotherapy
Parkinson’s Disease, Monotherapy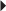 Parkinson’s Disease, Adjunct
Parkinson’s Disease, Adjunct Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic Impairment
 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension
Hypertension Psychiatric Disorders
Psychiatric Disorders
 Impetigo Caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes
Impetigo Caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes Adults
Adults Children
Children Acute MI, CHF
Acute MI, CHF